MCAS Guide Pages 7-8 DNA Structure RNA DNA & RNA activities.
12.3 dna, rna, and protein
-
Upload
kathylambert -
Category
Documents
-
view
500 -
download
2
Transcript of 12.3 dna, rna, and protein

Learning Objectives1. Explain how the code of DNA
transcribed into messenger RNA.
2. Explain how messenger RNA is translated into a protein.
3. Describe how to make a protein beginning with a gene.

Bodies are made up of cells
All cells run on a set of instructions spelled out in DNA
Bodies → Cells → DNA

How does DNA code for cells & bodies? how are cells and bodies made from the
instructions in DNA?
DNA → Cells → Bodies

DNA has the information to build proteins genes
DNA → Proteins → Cells → Bodies
proteinscells
bodiesDNA gets all the glory,Proteins do all the work

How do proteins do all the work?
– Proteins run living organisms
– Enzymes control all chemical reactions in living organisms
– Structure
• all living organisms are built out of proteins

cytoplasm
nucleus
Cell organization– DNA is in the nucleus
• genes = instructions for making proteins
– want to keep it there = protected• “locked in the vault”

Cell organization
• Proteins– chains of amino acids– made by a “protein factory” in
cytoplasm = ribosome
nucleus
cytoplasm
ribosome
buildproteins

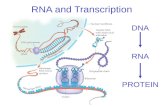
Passing on DNA information
• Need to get DNA gene information from nucleus to cytoplasm– need a copy of DNA– messenger RNA (mRNA) does this
nucleus
cytoplasm
ribosomemRNA
buildproteins

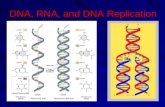
DNA vs. RNA
DNA• deoxyribose sugar • nitrogen bases
– G, C, A, T– T : A– C : G
• double stranded
RNA• ribose sugar • nitrogen bases
– G, C, A, U– U : A– C : G
• single stranded

mRNA
From nucleus to cytoplasm
DNA
transcription
nucleus
cytoplasm
translation
trait
protein

Transcription
• Making mRNA from DNA
• DNA strand is the template (pattern)– match bases
• U : A
• G : C
• Enzyme– RNA polymerase

Matching bases of DNA & RNA
• Double stranded DNA unzips
A G GGGGGT T A C A C T T T T TC C C CA A

Matching bases of DNA & RNA
• Double stranded DNA unzips
A G GGGGGT T A C A C T T T T TC C C CA A

Matching bases of DNA & RNA
• Match RNA bases to DNA bases on one of the DNA strands
U
A G GGGGGT T A C A C T T T T TC C C CA A
U
UU
U
U
G
G
A
A
A C CRNA
polymerase
C
C
C
C
C
G
G
G
G
A
A
A
AA

Matching bases of DNA & RNA
• U instead of T is matched to A
TACGCACATTTACGTACGCGGDNA
AUGCGUGUAAAUGCAUGCGCCmRNA

How does mRNA code for proteins?
• mRNA leaves nucleus
• mRNA goes to ribosomes in cytoplasm
• Proteins built from instructions on mRNA
aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa
How?
mRNA
U C CCCCCA A U G U G A A A A AG G G GU U

How does mRNA code for proteins?
How can you code for 20 amino acids withonly 4 DNA bases (A,U,G,C)?
TACGCACATTTACGTACGCGGDNA
AUGCGUGUAAAUGCAUGCGCCmRNA
Met Arg Val Asn Ala Cys Alaprotein
?
ribosome
aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa

AUGCGUGUAAAUGCAUGCGCCmRNA
mRNA codes for proteins in triplets
TACGCACATTTACGTACGCGGDNA
AUGCGUGUAAAUGCAUGCGCCmRNA
Met Arg Val Asn Ala Cys Alaprotein
?
Codon = block of 3 mRNA bases
codon
ribosome

The mRNA code• For ALL life!
– strongest support for a common origin for all life
• Code has duplicates– several codons for each
amino acid– mutation insurance!
Start codon AUG methionine
Stop codons UGA, UAA, UAG

How are the codons matched to amino acids?
TACGCACATTTACGTACGCGGDNA
AUGCGUGUAAAUGCAUGCGCCmRNA
anti-codon
codon
tRNAUAC
MetGCA
ArgCAU
Val Anti-codon = block of 3 tRNA bases
aminoacid

mRNA to protein = Translation
• The working instructions → mRNA• The reader → ribosome• The transporter → transfer RNA (tRNA)
mRNAU C CCCCCA A U G U G A A A A AG G G GU U
aaaa
aa
tRNA
GGU
aa
tRNA
U A C
aa
tRNA
GA C
tRNA
aa
A GU
ribosome

aa
aa
aaaa
aa
aa
aa
mRNA
From gene to protein
DNA
transcription
nucleus
cytoplasm
protein
translation
trait
U C CCCCCA A U G U G A A A A AG G G GU Uribosome
tRNA
aa

transcription
cytoplasm
nucleus
translation
trait
protein

From gene to protein
transcriptiontranscription
translationtranslation
proteinprotein

Whoops!See what happens when
your genes don’t work right!
Any Questions??