1 The Rendering Pipeline. CS788 Topic of HCI 2 Outline Introduction The Graphics Rendering...
-
Upload
marcia-sharp -
Category
Documents
-
view
228 -
download
6
Transcript of 1 The Rendering Pipeline. CS788 Topic of HCI 2 Outline Introduction The Graphics Rendering...
CS788 Topic of HCI 2
Outline
Introduction
The Graphics Rendering Pipeline
Three functional stages
Example
Bottleneck
Optimization
The Haptics Rendering Pipeline
3
Introduction
For smooth simulations Need to display at least 24, or, better 30 frame/secs Total latency is not over 100msec
Low latency and fast graphics require a VR engine that has a powerful computer architecture These architectures are designed around a rendering pipeline
Rendering The process of converting the 3D geometrical models
populating a virtual world into a 2D scene presented to the user
5
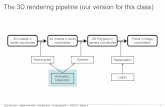
Three functional stages
Graphics rendering has three functional stages.
FIF
O b
uff
er
Applicationstage
Applicationstage
Geometrystage
Geometrystage
Rasterizerstage
Rasterizerstage
FIF
O b
uff
er
Ou
tpu
t bu
ffer
Userinput
Videocontroller
6
Application stage
Implemented in software Run on several CPUs
Read the world geometry database & the user’s input
Basic operations take care of user’s input acceleration algorithm
Output: 3D geometric primitives (polygons, meshes)
Geometrystage
Geometrystage Rasterizer
stage
Rasterizerstage
Applicationstage
CPU1
CPU2
Userinput
Videocontroller
7
Geometry stage
Implemented in software or hardware Run on the geometry engines
Basic operations
Output: 2D geometric primitives (2D polygons)
Applicationstage
Applicationstage Rasterizer
stage
Rasterizerstage
Geometrystage
GE1
GE2
Userinput
Videocontroller
Model transformation
Lightcomputation
Sceneprojection
ClippingScreen
mapping
8
Rasterizer stage
Implemented in hardware
Convert the vertex information output into pixel information needed by the video display
Basic operations: Scan conversion (rasterization) Z-buffering Anti-aliasing Texture mapping
Output: pixel values
Applicationstage
Applicationstage Geometry
stage
Geometrystage
Rasterizerstage
RU1
RU2
Userinput
Videocontroller
9
Bottleneck
One of the three stages will be the slowest => bottleneck stage
CPU-limited In the application stage
Transform-limited In the geometry stage
Fill-limited In the rasterizer stage
10
Optimization (1/2)
Application stage : CPU-limited Replace the CPU with a faster one or add another CPU Reduce CPU’s load
Reduce the scene complexity by using 3D models with a lower polygonal count
Optimize the simulation software
Geometry stage : Transform-limited Need to look at the computation load assigned to the GEs
Reduce the number of virtual light sources Use the Simple shading mode Use the type of polygon for which its rendering hardware was
optimized
11
Optimization (2/2)
Rasterizer stage : fill-limited Reduce the number of pixel in the displayed image
Reduce the size of the display window Reduce the window resolution
13
The Haptics Rendering Pipeline
Userinput
Hapticinterface
Collisiondetection stage
Force computationstage
Tactile computationstage
CPU1
CPU2
Com
pu
te fo
rce
Forc
e s
mooth
ing
Forc
e m
ap
pin
gHaptic
texturing
14
The stages of the Haptics Rendering Pipeline (1/2)
Collision detection stage
Load the physical characteristics of the 3D objects from the database
Perform collision detection to determine which virtual objects collide
Force computation stage
Compute the collision forces Force smoothing Force mapping
15
The stages of the Haptics Rendering Pipeline (2/2)
Tactile computation stage
Render the touch feedback component of the simulation
The computed effects are added to the force vector send to the haptics output display
The haptics rendering pipeline has a much less standardized architecture compared to its graphics counterpart.
CS788 Topic of HCI 17
Conceptual Model of VR
H-sensor
perception
cognition
motion control
H-effector
P-effector
P-sensor
L-effector
L-sensor
sensing
action
Human
avata
r
virtu
al
agen
t
Logical devicesfordisplacements,angles,events.
virtualobject
V-effector
V-sensor