1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
-
Upload
liyana-rais -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
1/27
Sludge Treatment and Disposal - 1
Mohamed Hasnain Isa
Civil Engineering Department
Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS31750 Tronoh, Perak, Malaysia
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
2/27
22
Able to manage biosolids resulting fromtreatment of water and wastewater.
Able to apply engineering principles to design
water and wastewater treatment processes.
Able to identify/solve water and wastewater
problems (domestic and industrial)..
Learning Outcomes 2, 3, 5, 6
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
3/27
33
Objectives
To identify the sources and characteristics of
water and wastewater sludges.
To explain methods for sludge thickening.
To analyse and design gravity sludge thickener.
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
4/27
44
Sources and Characteristics of Solids and Sludgesdepend on the type of plant and method of operation
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
5/27
55
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
6/27
66
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
7/27
77
Sludge Thickeningphysical process
increases the concentration of solids of sludge
reduces sludge volume to facilitate ease in handling,
treatment and disposal
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
8/27
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
9/27
99
Table Recommended hydraulic overflow rates for
gravity thickeners
Type of sludge Max. overflow rate, m3/m2.d
Primary 15.5-31
Waste activated sludge 4-8
Combined primary and
waste activated sludge
6-12
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
10/27
1010
Sludge discharge
Scraper blades
Sludge influentSlats/pickets
Inlet baffle
Supernatant
overflow
Sludge discharge
Scraper blades
Sludge influentSlats/pickets
Inlet baffle
Supernatant
overflow
Figure Gravity sludge thickener
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
11/27
1111
Figure Gravity sludgethickener (partially filled)
Figure Gravity sludgethickener (empty)
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
12/27
1212
Table Typical sludge concentrations and solid loading for
gravity thickeners
Type of sludge Solids concentration, % Solids loading
Unthickened Thickened kg/m2.d
Separate:
Primary sludge 2-6 5-10 100-150
Trickling filter 1-4 3-6 40-50RBC 1-3.5 2-5 35-50
Air-ASP 0.5-1.5 2-3 20-40
High purity oxygen-ASP 0.5-1.5 2-3 20-40
Extended aeration-ASP 0.2
-1.02
-32
5-4
0Anaerobically digested primary
sludge from primary digester
8 12 120
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
13/27
1313
Type of sludge Solids concentration, % Solids loading
Unthickened Thickened kg/m2.d
Combined:
Primary and trickling filter 2-6 5-9 60-100
Primary and RBC 2-6 5-8 50-90
Primary and waste activatedsludge
0.5-1.5 4-6 25-70
2.5-4.0 4-7 40-80
Trickling filter and waste
activated sludge
0.5-2.5 2-4 20-40
Chemical (tertiary):
High lime 3-4.5 12-15 120-300
Low lime 3-4.5 10-12 50-150
Iron 0.5-1.5 3-4 10-50
contd.
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
14/27
1414
Figure Suspended solids and BOD removal as a function
of surface overflow rate
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
15/27
1515Figure Excessive sludge production v. F/M ratio
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
16/27
1616
Dissolved Air Floatation
air is forced into solution under pressure and then mixed
with sludge in the influent
the mixture enters a floatation tank and the rising air
bubbles carry the sludge flocs to the liquid surface
the layer of thickened sludge formed on the liquid surfaceis skimmed off
the skimmed effluent exits as underflow
sludge can be thickened to about 6 % solids by floatation
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
17/27
1717
thickening of solids by floatation is primarily influenced by
air-to-solids ratio, sludge characteristics (in particular the
SVI), solids loading rate and polymer application
the air-to-solid ratio at which the float solids are maximised
ranges from 2 to 4 %
good thickening has been observed with SVI less than
200
higher loadings can be used with dissolved air floatation
than gravity thickeners due to the rapid separation of solids
from the wastewater
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
18/27
1818
Influent
Sludge
Pressurized
air
Effluent
Sludge skimming
Rising air bubbles
with sludge
Influent
Sludge
Pressurized
air
Effluent
Sludge skimming
Rising air bubbles
with sludge
Figure Sludge thickening by dissolved air floatation
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
19/27
1919
Table Typical solids loadings for sludge thickeners using
dissolved air floatation
Type of sludge Solids loading, kg/m2.h
Without chemical
addition
With chemicals
addition
Air-ASP:
Mixed liquor 1.2-3.0 Up to 10Settled 2.4-4.0 Up to 10
High purity oxygen-ASP 3.0-4.0 Up to 10
Trickling filter 3.0-4.0 Up to 10
Primary and air ASP 3.0-6.0 Up to 10
Primary and trickling filter 4.0-6.0 Up to 10
Primary sludge only 4.0-6.0 Up to 12.5
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
20/27
2020
a
a
SfPs
SA )1(3.1
!
where
A/S = air to solids ratio, mL (air)/mg (solids)sa = air solubility, mL/L
f = fraction of air dissolved at pressure P, usually 0.5
P = pressure, atm =
Sa = influent suspended solids, mg/L
35.101
35.101p
If entire flow is pressurised,
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
21/27
2121
QSRfPs
SA
a
a )1(3.1
!
where
R = pressurised recycle, m3
/dQ = mixed liquor flow, m3/d
If only recycle is pressurised,
Temp., C 0 10 20 30
sa, mL/L 29.2 22.8 18.7 15.7
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
22/27
2222
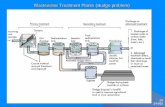
Q.1 The flow diagram for a wastewater treatment plant is as
shown below. The following information is also given:
Treatment plant:Diameter of PST = 20 m
Volume of aeration tank = 2 500 m3
MLSS in aeration tank = 3 000 mg/l
Wastewater:
Influent suspended solids = 220 mg/l
Influent BOD = 250 mg/l
Effluent BOD = 20 mg/l
Flow = 20 000 m3
/d
Sludge solids:
Primary sedimentation tank = 3.5 %
Secondary sedimentation tank = 0.8 %
Gravity thickener = 5 %
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
23/27
2323
Determine:
(i) the mass and volumetric loading rates to the thickener.
(ii) the percent volume reduction by the gravity thickener.
Primary
Sedimentation
Tank
Secondary
Sedimentation
TankAeration Tank
EffluentInfluent
Gravity
Thickener
Return liquid
Thickened sludge
disposal
Return sludge
Primary
Sedimentation
Tank
Primary
Sedimentation
Tank
Secondary
Sedimentation
Tank
Secondary
Sedimentation
TankAeration TankAeration Tank
EffluentInfluent
Gravity
Thickener
Gravity
Thickener
Return liquid
Thickened sludge
disposal
Return sludge
Primary
Sedimentation
Tank
Secondary
Sedimentation
TankAeration Tank
EffluentInfluent
Gravity
Thickener
Return liquid
Thickened sludge
disposal
Return sludge
Primary
Sedimentation
Tank
Primary
Sedimentation
Tank
Secondary
Sedimentation
Tank
Secondary
Sedimentation
TankAeration TankAeration Tank
EffluentInfluent
Gravity
Thickener
Gravity
Thickener
Return liquid
Thickened sludge
disposal
Return sludge
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
24/27
2424
Q.2 Design a gravity thickener for a wastewater treatment
plant with the following sludge characteristics:
Type of sludge Specific gravity Solids
%
Flow rate
m3/d
Average design conditions:
Primary sludge 1.03 3.3 400
Waste activated 1.005 0.2 2250
Peak design conditions:
Primary sludge 1.03 3.4 420
Waste activated 1.005 0.23 2500
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
25/27
2525
Q.3 Design a floatation thickener without and with pressurised
recycle to thicken the solids in an activated sludge mixed
liquor from 0.2
to4%. The following conditions apply:
Optimum A/S ratio = 0.012 mL/mg
Temperature =2
0 CAir solubility = 18.7 mL/L
Recycle system pressure = 280 kPa
Fraction of saturation = 0.5
Surface loading rate = 9 L/m2.min
Sludge flow rate = 500 m3/d
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
26/27
2626
Q4.
-
8/3/2019 1 Sludge Treatment and Disposal-1
27/27
2727
Thank you