© Folens 2009 FOR EDEXCEL1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system Blood 1...
-
Upload
melinda-hodges -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
2
Transcript of © Folens 2009 FOR EDEXCEL1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system Blood 1...
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Blood 1
Blood
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
What you will learn about in this topic:
1.Red blood cells
2.White blood cells
3.Platelets
4.Plasma
5.The effects of exercise on blood flow
6.Factors affecting blood pressure
Blood 2
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Blood 3
Learning objectives
By the end of this presentation you should be able to:
•Understand the effects of exercise on heart rate and blood flow
•Describe the effects of exercise on blood pressure
•Explain the different types of blood cell
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Red blood cells
Red blood cells (erythrocytes) are small but the body contains millions of them.
The main job of the red blood cell is to carry oxygen around the body and to transport carbon dioxide, a waste product, to the lungs.
Blood 4
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Blood 5
In adults, red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow of long bones.
During exercise the blood increases in thickness as water is removed as waste.
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
In these cells is haemoglobin. Oxygen chemically attaches itself to it to make oxyhaemoglobin.
This is how oxygen is transported to the working muscles and carbon dioxide is taken to the lungs transported in solution of plasma.
Blood 6
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
White blood cells
White blood cells (leukocytes) protect the body by fighting infection at its source, repairing damaged tissue after an injury and destroying bacteria.
Blood 7
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
When a cut or graze occurs, the white blood cells gather to stop bacteria entering the body. When a scab forms it is made up dead of leukocytes.
There are three major classes of white blood cells which are further divided into other groups.
Blood 9
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
There are fewer white than red blood cells in the body.
60 to 70 per cent of white blood cells are produced in the bone marrow of long bones while the other 20 to 30 per cent is made in the lymph tissue of the body.
Blood 10
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Platelets
Platelets are small parts of larger cells.
Platelets clump together and clot at the skin surface after a graze or cut.
They also do the same job internally on small, damaged blood vessels.
Blood 11
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Clotting is important to stop blood loss from the body and to stop internal bleeding.
Blood 12
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Plasma
Plasma is mostly made up of water. It makes up 55 per cent of the volume of blood and helps the blood flow easier by the use of plasma proteins.
Blood 13
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
The ten per cent of plasma that is not water contains a mixture of: salts, chlorine, amino acids, glucose, antibodies, fibrinogens (which help clotting), hormones and waste products, such as urea and carbon dioxide.
Blood 14
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
During exercise, hormones such as endorphins, cortisol, adrenalin and testosterone are produced and transported in the plasma.
Adrenalin can help a performer heighten their performance levels during competition.
Blood 15
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Effects of exercise on heart rate and blood flow
The resting heart rate is about 72 beats per minute, although this varies with gender and age.
This is sufficient to supply the muscles with the necessary blood and nutrients.
Blood 16
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Every heartbeat pumps blood out of the heart; this is called the stroke volume.
At rest the heart pumps about 85ml of blood, during exercise this is nearer 130ml (nearly a quarter of a pint) depending on fitness levels.
Blood 17
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
The total volume of blood pumped out of the heart, calculated over a minute, is called the cardiac output.
To work out the cardiac output, multiply the stroke volume by the heart rate:
cardiac output =stroke volume x heart rate
Blood 18
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
The heart rate increases when extra demands are made on the body such as during exercise.
The rate will depend on the type of exercise being performed.
Blood 19
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
The heart rate usually needs to be raised to at least 60 per cent of the maximum to improve cardiovascular fitness levels.
To work out the maximum heart (or pulse rate) the following formula is used:
220 – age =maximum heart rate
Blood 20
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
After exercise, the heart returns to its resting rate. The time it takes to do this is referred to as the recovery rate.
A cool-down can help the body gradually return to the resting heart rate.
Blood 21
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
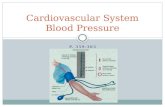
Blood pressure
Blood pressure is the amount of force the blood applies on the sides of the blood vessels.
It is used as an indicator of how fit the circulatory system is.
Blood 22
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
A sphygmomanometer is the instrument that measures blood pressure.
Blood 23
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Blood pressure is like a garden hose.
Blood 24
When a hose is on full, the water pressure is very high and the water flows quickly.
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
When the hose is half on, the pressure is less and the water does not flow as quickly.
Blood 25
The pressure depends on how much water is flowing through the hose and how easily it can flow out.
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Blood pressure works in the same way: it depends on how much blood flows into a blood vessel and how easily it can flow out of it again.
There are different blood pressures in different blood vessels.
Blood 26
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Blood pressure is highest in the arteries.
Blood 27
The blood is pumped quickly but it cannot easily flow out through arterioles because they are narrow.
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Blood pressure is lower in the capillaries because the blood flows into them more slowly and flows out to wider vessels.
Blood 28
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Blood pressure is at its lowest in the veins because the blood slowly drains into them (the widest veins).
Blood 29
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
As you get older the blood vessel walls become less elastic and the small vessels do not expand as much to let through the blood pumped from the heart.
Blood 30
This means that resistance to the flow of blood is increased so blood pressure rises.
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Blood pressure varies with:
•Age
•Gender
•Altitude
•Muscular development
•Stress
•Tiredness
Blood 31
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Reducing the risk of high blood pressure
The following are things you can do to reduce the risk of having high blood pressure:
Blood 32
• Check your weight
• Limit your alcohol consumption
• Avoid smoking
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
•Eat a balanced diet to decrease the amount of fatty foods consumed (the more fat in a person’s body, the greater the risk there is of high blood pressure).
•Avoid too much salt as it can unbalance the body chemistry and affect blood pressure
Blood 33
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
•Avoid situations that cause stress, anxiety or worry.
•Exercise regularly (this will help to control stress, keep your blood pressure normal and keep your whole system in good shape.)
Blood 34
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Task 1
Produce a fact sheet to display in a doctor’s surgery to inform people about high blood pressure.
Blood 35
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Exam questions
1. What is the main job of the red blood cells?
2. What do white blood cells do?
Blood 36
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Blood 37
What you have learntin this topic:
1.Red blood cells
2.White blood cells
3.Platelets
4.Plasma
5.The effects of exercise on blood flow
6.Factors affecting blood pressure
© Folens 2009FOR EDEXCEL 1.2.2 A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system
Blood 38
Learning objectives
You should now be able to:
•Understand the effects of exercise on heart rate and blood flow
•Describe the effects of exercise on blood pressure
•Explain the different types of blood cell