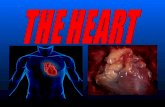
- Consists of mostly cardiac muscle - 2 atria – thin-walled - Act as collection chambers for...
-
Upload
job-sutton -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
description
Transcript of - Consists of mostly cardiac muscle - 2 atria – thin-walled - Act as collection chambers for...


- Consists of mostly cardiac muscle- 2 atria – thin-walled
- Act as collection chambers for returning blood
- 2 ventricles – thick-walled - stronger contraction than atria (esp. left)

Heart Cyclesystole – contraction – blood pumped out
cardiac output – volume of blood/min. that L ventricle pumps into systemic circuit
diastole – relaxation – chambers fill w/ blood
cardiac cycle – one complete pump and fill
pulse – rhythmic stretching of arteries by pressure of blood powered by contractions of ventricles
- measure heart rate (rate of heart contraction)

Heart Beat Controlself-excitable cells – contract w/o any signal from nervous system (even if removed from heart)
Coordination of Contractions – begin in atriasinoatrial (SA) node – (pacemaker)
- specialized muscle tissue in wall of R atrium- sets rate & timing of contraction of all cells- electrical impulses spread rapidly through
atria walls making them contract in unison

Coordination of Contractions - spread to ventriclesatrioventricular (AV) node – (relay point)- located in wall between R atrium & R ventricle- delays impulse by 0.1 sec before spreading - allows atria to empty completely
Specialized fibers for conduction of impulse to apex & back to atria:1. Bundle of His (bundle branches) - intraventricular septum2. Purkinje fibers- interventricular septum Pg. 877

electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)- measures electrical impulse as conducted through body fluids skin (detected by electrodes)

Factors that affect SA node (heart rate)1. Two sets of nerves
- one set speeds up- one set slows down
2. Hormonesex: epinephrine “fight or flight”
3. Body temp.- 1˚C can inc h.r. by 10
beats/min

Hydrostatic Pressure – force exerted by fluids against surfaces they contact
- drives fluids through pipes
Blood Pressure – hydrostatic force blood exerts against wall of vessel that propels
- highest in arteries when ventricles contract (systolic pressure)

Diastolic pressure – blood pressure that remains between heart contractions
Measuring Blood Pressure- sphygmomanometer/stethoscope- inflate cuff: *closes artery by exceeding pressure of it- slowly deflate cuff:*sounds from blood pulsing into artery (systolic pressure)*blood flows freely, no sounds (diastolic pressure)
- regular: 120/70 mm Hg (systolic/diastolic)Pg. 880

Factors that affect blood pressure:1. Inc./dec. of cardiac output - exercise, sleep2. Inc./dec. of arteriole resistance-vasoconstriction: smooth muscles contract*physical/emotional stress (trigger nervous/hormonal responses)*cold weather – decreased s.a. for heat loss-vasodilation: smooth muscles relax*inc cardiac output*warm weather- inc. plaque
During exercise, blood vessels dilate to allow more blood flow to muscles. What keeps blood pressure from going to low?

Functions:1. Returns fluid & proteins to circ. system after lost during capillary exchange
2. Aids in body defense
3. Transports fats from sm. intestine to circ. system

Returning fluid & proteins
- leakage occurs during exchange between capillaries & tissues
- lost materials diffuse into tiny, intermingled lymph capillaries*fluid/proteins now called lymph*valves prevent backflow*movement of skeletal muscles to squeeze fluid to
heart*fluid drains near junction of superior vena cava

Lymph nodes – organs along lymph vessels-filter lymph-attack viruses & bacteria
*lymphocytes – cells that fight infectionmultiply rapidly & cause swelling of
nodes

Consists of:1. plasma2. cells & cell fragments

Plasma Composition- 90% water
- electrolytes - inorganic salts in ion form-maintain osmotic balance of blood-buffer blood (neutral pH)-maintain normal functioning of muscles & nerves
*function depends on [ ] of key ions in ISF, which reflects [ ] in plasma

Plasma Composition- proteins (various)
- some escort lipids- immunoglobulins/antibodies – fight foreign
particles- fibrinogens – clotting
- nutrients, metabolic wastes, resp. gases, & hormones

Cells & Cell Fragments
1. Red blood cells (RBCs)2. White blood cells (WBCs)3. Platelets

Cells
RBCs (erythrocytes)- most numerous – 25 trillion in 5 L (concave
shape)- transport oxygen- contain Hb
*no nucleus to leave room*single RBC 250 mil Hb carry
billion O2

Cells
WBCs (leukocytes)5 major types:1. monocytes2. neutrophils3. eosinophils4. basophils5. lymphocytes (lymph nodes)

Cells
WBCs – fight infection*monocytes/neutrophils – phagocytes- engulf bacteria & debri*eosinophils/basophils – combat parasitic infections*lymphocytes- develop into B cells & T cells to produce immune response

Cells
WBCs – spend most time patrolling:1. ISF2. lymphatic system

Cell Fragments
Platelets – blood clotting- release clotting factors
*convert fibrinogen fibrin *fibrin threads – framework of clot
Hemophilia – inherited defect of clotting process that results in excessive bleeding

Blood Groups – A, B, AB, O- based on type of antigen on RBC- transfusion w/ wrong blood can be fatal
ex: A type blood (RBC has A antigen)- if given B blood antibodies attack foreign particles (B antigen) & clump, inhibiting blood flow

Blood Groups
universal donor – O blood (no antigens)universal recipient – AB (A & B anitgens) – 4% of pop.
Rh Factor – antigens- Rh+ (have them), Rh- (do not)- Rh- expectant mothers – Rh+ baby will need
exchange transfusion

- Leading cause of death in US
- Heart attack – blockage of one or more coronary arteries death of cardiac muscle
- Stroke – blockage or rupture of arteries in head death of nervous tissue in brain

Causes:atherosclerosis – arteries gradually become impaired by growths called plaques, which develop on inner walls of vessel & narrow - encourages adhesion of platelets triggers clotting process (thrombus) - more likely for embolus (mobile clot) to become trapped
arteriosclerosis – plaques become hardened by Cadeposits (hardening of arteries) reduced elasticity

Causes:
Hypertension – high blood pressure- promotes atherosclerosis- causes chronic damage to endothelium
lining the arteries plaque formation- diastolic pressure above 90 cause for
concern

Causes:Cholesterol – steroid, lipid made up of 4 carbon rings- travels plasma in particles- 1000s cholesterol molecules + other lipids bound to a protein- LDLs (low-density lipoproteins) – “bad cholesterol”- deposit cholesterol in arterial plaques- smoking inc. - HDLs (high-density lipoproteins) – “good cholesterol”- carry less cholesterol than LDLs- reduce cholesterol deposition- exercising inc.