What type of food? Carbohydrates, protein, lipids?1 2 3 4 5 6 7.
-
Upload
jeremy-brendan-armstrong -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of What type of food? Carbohydrates, protein, lipids?1 2 3 4 5 6 7.
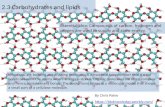
BIOMOLECULESMACROMOLECULESmade by polymerization-large
compounds built by joining smaller ones together.
Smaller units (subunits) are called monomers.
4 major molecules important to life. Carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic
acids and proteins.
CARBOHYDRATES 1:2:1 RATIO
1 Carbon: 2 Hydrogen: 1 Oxygen Example: the sugar glucose - C6H12O6
Monomer (1 sugar) – Monosaccharide Polymer (2+) - Polysaccharide
2 sugars - disaccharide Main source of energy for living things Also has structural purpose for living things.
1. Plant cells have cell walls made of cellulose
2. Animal cells store excess sugars as glycogen
LIPIDS Made of Carbon and Hydrogen NOT soluble in water (hydrophobic)
doesn’t mix with water Used to store energy, and as chemical
messengers (hormones, steroids), and structure of cells
Three Types of Lipids Steroids – ex: hormones, cholesterol Part of the cell membrane (phospholipids). Fats: made up of fatty acids
Saturated-Solid at room temperature. No double bonds
Unsaturated-liquid at room temperature. Double bonds between Carbons.
NUCLEIC ACIDSComposed of Hydrogen, Oxygen,
Nitrogen, Carbon and Phosphorus.Subunits (monomers) are called
nucleotides. Store and transmit hereditary
information.Ex. DNA , RNA
PROTEINS
Composed of Nitrogen, Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen.
Polymers are known as Polypeptides.Monomers are called amino acidsControl rate of reactionsFunction in transport and formation of
bone and muscle cells. Ex: Hemoglobin, Insulin, Enzymes
Folded shape is important in enzyme recognition process.