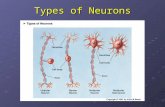
What is a neuron?. The Neuron b A neuron is a nerve cell like any other cell in the bodylike any...
-
Upload
rosaline-francis -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
description
Transcript of What is a neuron?. The Neuron b A neuron is a nerve cell like any other cell in the bodylike any...

What is a neuron?What is a neuron?

The NeuronThe NeuronA neuron is a nerve cellA neuron is a nerve cell
•like any other cell in the bodylike any other cell in the body
Neurons are similar to other cells in Neurons are similar to other cells in the body in some waysthe body in some ways
However, neurons differ from other However, neurons differ from other cells in the body in some wayscells in the body in some ways

3 major classes of neurons3 major classes of neuronsSensory (afferent)Sensory (afferent)Motor (Efferent)Motor (Efferent)InterneuronsInterneurons
Glia cellsGlia cells•developmentdevelopment•housekeepinghousekeeping
•insulationinsulation•protectionprotection

Simple Reflex PathwaySimple Reflex Pathway

The process of neural The process of neural communicationcommunicationWithin cells - action potentialWithin cells - action potentialBetween cells - synaptic Between cells - synaptic transmissiontransmissionComponents: dendrites, soma (cell Components: dendrites, soma (cell body), axon, and terminal buttons body), axon, and terminal buttons of axonof axon


The Neuron at RestThe Neuron at RestResting potential - Cell is PolarizedResting potential - Cell is Polarizedneuron membrane separates neuron membrane separates charged ions, producing a voltage charged ions, producing a voltage potentialpotentialsodium (NA+), potassium (K+), sodium (NA+), potassium (K+), chloride chloride (Cl-), and protein molecules (A-)(Cl-), and protein molecules (A-)selectively permeable (semi-selectively permeable (semi-permeable)permeable)sodium-potassium pump maintains sodium-potassium pump maintains ionic imbalanceionic imbalanceinside of neuron is negative inside of neuron is negative relative to outside (about -70mV)relative to outside (about -70mV)

Reception of InputReception of InputGraded potentials:Graded potentials:
•Excitatory potentials -depolarizing Excitatory potentials -depolarizing currentcurrent
•Inhibitory potentials - hyperpolarizing Inhibitory potentials - hyperpolarizing currentcurrent
determines which ion channels determines which ion channels openopen
•Excitatory input causes the ion Excitatory input causes the ion channels to allow sodium ions into channels to allow sodium ions into
neuronneuron–allows neuron to fireallows neuron to fire
•Inhibitory input causes ion channels Inhibitory input causes ion channels to keep neuron negatively chargedto keep neuron negatively charged
–prevents neuron from firingprevents neuron from firing

Synaptic TransmissionSynaptic TransmissionPresynaptic and postsynaptic Presynaptic and postsynaptic neuronsneuronsTransmission involves movement Transmission involves movement of neurotransmitters across of neurotransmitters across synaptic cleftsynaptic cleft
•about 200 angstroms (one ten-about 200 angstroms (one ten-millionth of a millimeter) in width b/t millionth of a millimeter) in width b/t
neuronsneuronsOnce AP reaches terminal button, Once AP reaches terminal button, vesicles spill contents into gapvesicles spill contents into gapTraverse cleft, attach to receptor Traverse cleft, attach to receptor moleculesmoleculesEither increase (E) or decrease (I) Either increase (E) or decrease (I) neural firingneural firing

NeurotransmittersNeurotransmittersAcetylcholine, ACHAcetylcholine, ACH
•learning and memorylearning and memory•motor neurons and musclesmotor neurons and muscles•major excitatory neurotransmittermajor excitatory neurotransmitter
Gamma-Amino Butyric Acid Gamma-Amino Butyric Acid (GABA)(GABA)
•major inhibitory neurotransmittermajor inhibitory neurotransmitter•anxietyanxiety

NeurotransmittersNeurotransmittersCatecholamines:Catecholamines:
•NorepinephrineNorepinephrine–undersupply - depressionundersupply - depression
•DopamineDopamine–oversupply - schizophreniaoversupply - schizophrenia–undersupply - Parkinson’sundersupply - Parkinson’s
SerotoninSerotonin•mood, sleep, and eatingmood, sleep, and eating
EndorphinsEndorphins•natural pain killersnatural pain killers

NeurotransmittersNeurotransmitters