Water Underground
description
Transcript of Water Underground

Water Underground
Drought: A long period of scarce precipitation•Droughts can affect surface water and
underground water sources.

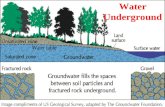
Fresh Water Locations--Groundwater
• What is groundwater?– The water found in cracks and pores in sand,
gravel and rocks below the earth’s surface
• What is an aquifer?– A porous rock layer underground that is a
reservoir for water

• How does water move Underground?
–Through cracks and spaces in layers of rock
• Effects of different underground Materials–Permeable: gravel, rock, soil– Impermeable: clay & granite

WATER ZONES• Begins when water reaches an impermeable layer.
• Unsaturated zone: The layer of rocks and soil above the water table.
• Water table: the area on top of the saturated zone. Can rise and lower depending on precipitation.
• Saturated zone: is the area of permeable rock or soil that is totally filled, or saturated, with water.


Bringing up Groundwater• Aquifers: any underground layer of rock or
sediment that holds water.– Can range in sizes – Can rise and lower depending on precipitation.– Ogallala aquifer runs from South Dakota to Texas
• Wells:– Used to obtain underground water from an aquifer–Wells are a channel dug into the aquifer.–Wells can go dry when the level of the aquifer drops.

Bringing up Groundwater (cont.)
• Artesian well: uses the pressure within an aquifer to raise the water to the surface.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KMtEQqbi4CI

Springs and Geysers
• Springs – is where water blows out of openings in rocks or ground.– They can be normal temperature– They can be “hot” springs – meaning the water is warm.
• Geysers – are formed when boiling hot water and white steam burst out of the earth.– Geyser is an Icelandic word meaning “gusher”– Water is boiling– http://www.yellowstone.co/oldfaithfulstreamingcam.ht
m

http://www.nps.gov/yell/photosmultimedia/yellowstone-indepth-episode-1.htm

Remote Sensing

•Remote sensing involves the collection of data.
•Earth scientists use the technique of remote sensing to monitor or measure phenomena or processes found in the Earth's lithosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere.

•Electromagnetic radiation is energy transmitted through space as particles or electromagnetic waves or the process of their emission. Electromagnetic radiation is emitted in discrete units known as photons that travel at the speed of light as electromagnetic waves.

•Data is then stored or filed as layers of information in a GIS (Geographic Information Systems)
http://egsc.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/gis_poster/#special

•Today, the GOES (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite) system of satellites provides most of the remotely sensed weather information for North America.
•In the 1960s, a revolution in remote sensing technology began with the deployment of space {C}satellites. - TIROS-1, which was launched by the United States using an Atlas rocket on April 1, 1960.
•Early satellite remote sensors did not use conventional film to produce their images. Instead, the sensors digitally capture the images using a device similar to a television camera.
•Once captured, the data is then transmitted electronically to receiving stations found on the Earth's surface.
•Aerial Photographs from planes
What is used to obtain Data

SUMMARY
• SUMMARIZE UNDERGROUND WATER