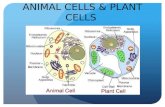
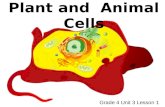
Water and Plant Cells - Western Oregon Universitywou.edu/~guralnl/gural/330Water and Plant...
Transcript of Water and Plant Cells - Western Oregon Universitywou.edu/~guralnl/gural/330Water and Plant...
Water and Plant Cells• Properties of Water• Water Potential• Components of Water
Potential• Water relations
Water in plant life
• Corn yield as a function of water availability.• Productivity of ecosystems as a function of
annual precipitation.• Most water lost through transpiration.
Properties of Water
• Polar molecule • Thermal Properties• Specific Heat • Melting Point • Heat of fusion • Boiling point • Heat of vaporization
Water movement
• Fick’s law of diffusion• Js = - Ds (∆Cs / ∆x)• Js is rate of transport (mol/m2s1)• Ds = diffusion coefficient through a medium• (∆Cs / ∆x) = concentration gradient of a substance
separated by distance x.
Components of water potential: Solutes (osmotic potential)
• Ψs = 0 for pure water Or always negative
• Ψs = - R T Cs
• R = 8.32 J/mol K• T = absolute
temperature• Cs = solute
concentration (mol/L)
Pressure potential
• Hydrostatic pressure (Ψp )• Positive (turgor pressure)• Negative (tension)• Ψp = 0 for water at ambient pressure (0 MPa)
Gravity
• Ψg = pwgh
• Pw = density of water• g = acceleration due to gravity• pwg = 0.01 MPa m-1
• At cell level we can ignore gravity or for small plants.
Plant cell volume• Small changes in
volume cause large changes in turgor
• 10-15% change in volume, turgor goes to zero
• Modulus of elasticity (ε) or rigidity of cell wall.
• High ε wall is stiff, low εwall is soft