Water - lifeeverywhere.kellijaebaeli.com · 1 Water Water.....1
Water
-
Upload
malik-hardin -
Category
Documents
-
view
1.028 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Water
Evaporation: Evaporation is when the sun heats up water in rivers or lakes or the ocean and turns it into vapor or steam. The water vapor or steam leaves the river, lake or ocean and goes into the air.
Do plants sweat?Well, sort of.... people perspire (sweat) and plants transpire. Transpiration is the process by which plants lose water out of their leaves. Transpiration gives evaporation a bit of a hand in getting the water vapor back up into the air.
Transpiration
Condensation:
Water vapor in the air gets cold and changes back into liquid, forming clouds. This is called condensation.
Precipitation:Precipitation occurs when so much water has condensed that the air cannot hold it anymore. The clouds get heavy and water falls back to the earth in the form of rain, hail, sleet or snow.
Collection:When water falls back to earth as precipitation, it may fall back in the oceans, lakes or rivers or it may end up on land. When it ends up on land, it will either soak into the earth and become part of the “ground water” that plants and animals use to drink or it may run over the soil and collect in the oceans, lakes or rivers where the cycle startsall over again.
Collection
The flow of water from the ground surface into the ground. Once infiltrated, the water becomes soil moisture or groundwater
Infiltration
Groundwater is water located beneath the Earth’s surface in soil pores and rock fractures.
Groundwater
When rain falls to the ground, the water does not stop moving.
Some of it flows along the land surface to streams, lakes, or oceans.
Some is used by plants. Some evaporates and returns to the atmosphere.
Groundwater
Water seeps underground, into pores between sand, clay and rock formations called aquifers.
Water moves through aquifers much like a glass of water poured onto a pile of sand.
Aquifers
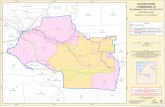
Catawba Aquifer
Charlotte
Drainage Area, square miles (NC): 3,343
River miles (including tributaries): 3,004
Population (2000): 1,170,512
A drainage basin is where surface water from rain, melting snow or ice converges to a single point.
The drainage basin acts as a funnel by collecting all the water within the area covered by the basin and channeling it to a single point. Each drainage basin is separated topographically from adjacent basins by a geographical barrier such as a ridge, hill or mountain.
Drainage Basin