VON RECKLINGHAUSEN DISEASE Neurofibromatosis (nf) Tiffany Calderon.
-
Upload
martha-dennis -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
2
Transcript of VON RECKLINGHAUSEN DISEASE Neurofibromatosis (nf) Tiffany Calderon.

VON RECKLINGHAUSEN DISEASE
Neurofibromatosis (nf)
Tiffany Calderon

What causes NF?
Neurofibromatosis is a genetic defect that causes neural crest cells to develop abnormally. This results in numerous tumors and malformations of the nerves, bones, and skin.

Target population
Both forms of neurofibromatosis are caused by a defective gene. NF-1 is caused by a defect on chromosome 17; NF-2 results from a defect on chromosome 22. Both are inherited as a dominant trait. This means that anybody who receives just one defective gene will have the disease. However, a family pattern of NF is only evident for about half of all cases of NF. The other cases of NF occur due to a spontaneous mutation. The chance of a person with NF passing on the NF gene to their child is 50%. Neurofibromatosis-I is one of the most common genetic disorders that is dominantly inherited

Affects on the CNS/PNS
Neurofibromatosis affects both the CNS and the PNS, symptoms of neurofibromatosis (such as tumors) can appear on the spinal cord and extend to all other areas of the body. The tumors can cause body parts to lose their function

Symptoms
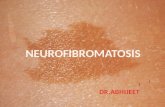
The presence of café-au-lait (French for coffee-with-milk) spots. These are patches of tan or light brown skin, usually about five to 15 mm in diameter. Nearly all patients with NF-1 will display these spots.
Multiple freckles in the armpit or groin area.
Ninty percent of patients have tiny tumors called Lisch nodules in the iris.
Skeletal deformities, such as a twisted spine (scoliosis), curved spine (humpback), or bowed legs

Prognosis
Prognosis varies depending on the tumor type which develops. As tumors grow, they begin to destroy surrounding nerves and structures. Ultimately, this destruction can result in blindness, deafness, increasingly poor balance, and increasing difficulty with the coordination necessary for walking. Deformities of the bones and spine can also interfere with walking and movement. When cancers develop, prognosis worsens according to the specific type of cancer.

Cure?
There are no cure for the neurofibromatosis. The symptoms of NF-1 and NF-2 can be treated individually. Skin tumors can be surgically removed. Some brain tumors, and tumors along the nerves, can be surgically removed, or treated with drugs or x-ray treatments. Twisting or curving of the spine and bowed legs may require surgical treatment, or the wearing of a special brace

Notable case
The elephant man (Joseph Carey Merrick) His skin appeared thick and lumpy, he developed an enlargement of his lips, and a bony lump grew on his forehead. One of his arms and both feet became enlarged. He was thought NF-I was the accepted diagnosis through most of the 20th century, although other suggestions included Maffucci syndrome or Albright's disease

Organizations/ medical faculties

Citations
2002). S. L. Blachford (Ed.), The Gale Encyclopedia of Genetic Disorders. Detroit: Gale. Retrieved from http://go.galegroup.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE|0OLG&v=2.1&u=cary81451&it=aboutJournal&p=GPS&sw=w&id=GALE|0OLG
Gulli, L. F. (2005). Neurofibromatosis. In B. Narins (Ed.), The Gale Encyclopedia of Genetic Disorders (2nd ed., Vol. 2, pp. 909-911). Detroit: Gale. Retrieved from http://go.galegroup.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE%7CCX3451500303&v=2.1&u=cary81451&it=r&p=GPS&sw=w
http://kidshealth.org/parent/general/aches/nf.html