Von Neumann Machine - .: FTSMweek3).pdf · Von Neumann Machine John Von Neumann – research of...
Transcript of Von Neumann Machine - .: FTSMweek3).pdf · Von Neumann Machine John Von Neumann – research of...

Von Neumann Machine

Babbage Analytical MachineThe basis of modern computers is proposed by a professor of mathematics at Cambridge University named Charles Babbage (1972-1871).He has invented a mechanical machine known as differential machine.This mechanical device can only add and subtract, designed to calculate the number of charts that are useful in piloting.This engine is the first ever computer that has four components:
Store (memory)Contains 1000 words of 50 decimal digits which is used to hold variables and results
Memory unitReceive operand from store, add, subtract, multiply or divide and will return the result to store
Input – punch cardsOutput – output punch cards

Konrad Zuse
German Engineering StudentCreate an automatic calculation machine which uses electromagnetic currents

John Atanasoff
From College of Iowa StatesCreate Atanasoff MachineUse binary arithmetic and capacitors to store memoryBut.. This machine is not working because of technology constraints

Howard Aiken
Create computer for general useThe extended of Babbage Machine
Mark 1 Completed in Havard (1944)Use 72 words Input/Output punched on tape

ENIAC ENIAC is stand for Electronic Numerical Integrated And ComputerThe first ever electronic computerUsed to understand the secret codes used by the German army … but it was never completedOrganization
18000 vacuum tube1500 relayWeight 30 tanPower 140 KW20 register – each one capable of handling up to 10 digits decimal number6000 multi position switchMany cables and sockets

Motivation from ENIACEDSAC
The first electronic computer operating properly (1945)Build at University of Cambridge, UK by Maurice Wilkes
JOHNIAC – Rand CompanyILLIAC – University of IllinoisMANIAC – Built at Alanos LabWEIZAC – Built at Institute of Weizmann, IsraelEDVAC – unsuccessful

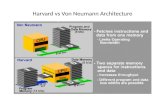
Von Neumann MachineJohn Von Neumann – research of ENIAC machine ENIACBuilt IAS – another version of EDVACImprovement made:
Use the binary number system in parallel.Use the concept of stored programs
Von Neumann bottleneck referred to:The separation between CPU and memoryThe limited throughput between CPU and memory compared to the amount of memory.In modern computers, throughput is much smaller that the rate at which CPU can work.This seriously limits the effective processing speed when CPU is required to perform minimal processing on large amount of data. The CPU is forced to wait for needed data to be transferred to or from memory.The bottleneck has become more of a problem whose severity increases with every newer generation of CPU.

Von Neumann Machine
Memory
Control Unit Arithmetic and Logic
Unit
Input
Output
•5 important parts

Bus System
Direct connection of each component in a computer
Began to be used on the PDP-8 machineConsist of 50 – 100 parallel wires are covered with copper

Bus System
Type of buses:System Bus
Connect all the chips that form a computer system
Local busSpecial bus that connecting 2 components directlyExample: connection between the microprocessor and co-processor
Internal BusConnecting components in one chip

Bus System
Co-processor
Memory I/O
Register
ALU
Local bus
System bus
Internal Bus

Bus Structure
Although there are many different bus designs, on any bus the lines can be classified into three functional groups: data, address and control lines.
Data lines: Provide a path for moving data among system modules. These lines, collectively are call data bus. The data bus may consist of 32. 64, 128 or even more separate lines. The number of lines referred to as the width of the data bus.

Bus Structure
Address Line:Used to designate the source or destination of the data on the data bus. Example: if the processor wishes to read a word of data from memory, it put the address of the desired word on the address lines.Clearly, the width of the address bus determines the maximum possible memory capacity of the system.Furthermore, the address lines are generally also used to address I/O ports.

Bus structure
Control line:Used to control the access to and the used of the data and address line.Because the data and address line are shared by all components, there must be a means of controlling their use.Control signal transmit both command and timing information among system modules.Typical control line include: memory write, memory read, I/O write, I/O read, Transfer ACK, Bus request, bus grant, clock, reset, etc

Bus System – Omnibus
Connect all components use only one bus
CPU Ingatan Konsol I/O

Bus OperationMaster – the device that gives instructionsSlave – the device that receive instructionsExample:
CPU directs disk controller to read dataMaster – CPUSlave – disk controller
Disk controller directs the memory to receive a word from disk drive
Master – disk controllerSlave – memory

Bus Operations
Bus Driver Used to strengthen the signal to be sent
Bus ReceiverUsed to strengthen the received signal
TransceiverChip consisting bus driver and bus receiver

Bus System
3 important types of busData Bus
Transfer data from one place to anotherAddressing Bus
State memory address such as memory address, address of I/O peripherals
Control BusCarrying control signals such as signal for read or write

Bus System
CPU MEMORY I/O
Bus System
Control Bus
Address Bus
Data Bus

Bus Synchronization
Bus Synchronization:Bus driven by a crystal oscillatorThe crystal oscillator will produce a signal wave 5 to 50 MHz

Bus ArbitrationMechanism for determining which device to use the bus at the time2 mechanism:
Centralized – requires hardware that will grant the bus to one of the requesting devices. This hardware can be part of the CPU or it can be a separate device on the motherboard.Distributed – there isn’t an arbiter, so the devices have to decide who goes next. This makes the devices more complicated, but saves the expense of having an arbiter.
Arbitration:Device arbitration mechanismIn CPU ChipAlso in separated chip

Operation of Bus Arbitration
The arbitration received a bus request
Arbitration was a recognition in the bus
line recognition
Nearest device will check whether there is
a bus request
Take over the bus and end the recognition
Send acknowledgment to the device next to his
yes
no

Operation of Bus Arbitration
Arbitration
Device 1
Device 2
Device 3
This arbitration mechanism is called daisy chain

Bus Arbitration
Disadvantage of daisy chainThe remote device – low priority
Other techniqueEach device is given priority repectivelyHigh priority device will make revisions before the other deviceFor devices that have the same priority
Used daisy chain

Distributed Bus Arbitration
Does not need arbitrationUse different bus requests – 1 device 1 busEach line has its own prioritiesHigh priority was given first review

Multi-programming and Input/Output Processor
Execution of several programs in memory is done at the same timeI/O Processor (IOP)
Handle I/O deviceModify the received data to a format adapted to the CPU data
After IOP processing is complete, it will interrupt the CPUCPU stop doing his duties and perform operations duties for the IOP

Input Output Processor
IOP for the IBM Machine known as channel3 types of channel
Multiplexor Connected to several devices that slow or medium speed.
Selector Handle only one device with high-speed data transfer is done byte by byte
Blocked-MultiplexorProvide facilities to handle multiple high-speed device – transfer I/O performed by block.

Microcomputer
Use a single bus
Processor
Main memory
DMA controller
IO Controller
IO deviceDMA-Direct Memory Access

DMA – Direct Memory Access
• Fully controlled by the CPU
• DMA request from the CPU to control bus
• If the CPU allows:
• It will take over the bus
• Do data transfer between the I/O and memory without the CPU
• DMA Controller – Intel 8237A
• Interfaces to the 80x86 family of processors and to DRAM memory to provide a DMA capability.

DMA – Direct Memory AccessThe DMA mechanism can be configured in a variety of ways. Some possible ways are;
Single bus, detached DMAThe DMA module, acting as surrogate processor, uses programmed I/O to exchange data between memory and an I/O module through DMAThis configuration may inexpensive, is clearly inefficient.
Single bus, integrated DMA-I/OThe DMA may actually a part of an I/O module using an I/O bus. This reduces the number of I/O interfaces in the DMA module to one and provides for an easily expandable configuration.
I/O Bus.The DMA module shares with the processor and memory is used by the DMA module only to exchange data with memory.The exchange of data between DMA and I/O modules takes place of the system bus.
Turn to page 256 (Stalling, Eight Edition)

Other Bus
• EISA – Extended Industry Standard Architecture
• To handle data size 32 bit
• VESA – Video Electronics Standard Association
• Disk and monitor connected directly to the microprocessor
• SCSI – Small Computer System Interface
• Connect the I/O device to a PC
• PCI – Peripheral Control Interface

PCI – Peripheral Control Interface
Very popular with high bandwidth processor-independent bus.Deliver better system performance for high speed I/O subsystems.Designed to meet economically the I/O requirements of modern system.It requires very few chips to implement and supports other busesattached to the PCI Bus.Provides 2 type of busses
32 bit bus64 bit bus
Can support 1 processor or multiprocessor.The structure of PCI can be divided into the following functional groups:
System pins.Address and data pinsInterface control pins.Arbitration pinsError reporting pins.