Vinnitsa National Pirogov Memorial Medical University / Department of microbiology
description
Transcript of Vinnitsa National Pirogov Memorial Medical University / Department of microbiology
-
Herpes viruses. Adenoviruses. Biological properties, pathogenecity for humans. Laboratory diagnostics, prophylaxis and therapy of diseases. Vinnitsa National Pirogov Memorial Medical University / Department of microbiology
-
Herpes viruses. ClassificationAlphaherpesvirinae includes next speciesHerpes simplex viruses 1 and 2 (HSV1 and HSV2)Varicella-zoster virus (VZV or HHV 3)Betaherpesvirinae contains species Cytomegalovirus (CMV or HHV 5)HHV6 and HHV7Gammaherpesvirinae includes speciesEpstein-Barr virus (EBV or HHV4)Kaposi`s sarcoma associated virus (HHV8)
-
Herpes viruses
-
Herpes simplex virusThere are two types of the herpes simplex virus (HSV):HSV type 1 causes herpes labialis HSV type 2 causes herpes genitalis
-
Cultivation of the HSVChick embryo Cell cultures Experimental keratoconjunctivitis
-
Epidemiology and pathogenesisThe source of infection is ill person with typical lesionsInfection is transmitted by close direct contact (labial herpes) or sexual intercourse (genital herpes)
-
Laboratory diagnosticsMicroscopy:CytoscopyImmune electron microscopyImmunofluorescence
Virus isolation
Serology
-
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV)causes chickenpox after primary infection and herpes zoster
The source of infection is person with chickenpox or more rarely with herpes zosterInfection is transmitted with air droplets (chickenpox) or with direct contact with lesions
-
Varicella (chickenpox)Herpes zoster
-
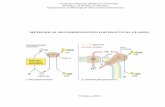
Pathogenesis of varicella/zoster infection
-
Laboratory diagnosticsMicroscopy:Tzanck smear Immune electron microscopyImmunofluorescenceVirus isolation Serology
-
Prevention is possible by active immunization with live, attenuated VZV (OKA strain)For contact person varicella-zoster immunoglobulin (VZIG) is used to prevent disease
-
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)In persons with adequate immunity CMV causes subclinical or unapparent infection.In persons with waned immunity CMV can provoke generalized infection.Congenital CMV-infection often is very severe, associated with hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice, hemolytic anemia, and microcephaly, chorioretinitis
-
Cells infected by CMV
-
Laboratory diagnosticsRapid diagnostics
Virus isolation
Serological method
-
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)It belongs to gamma-herpes viruses (HHV-4) and has oncogenic properties.It can cause different diseases from latent infection in children, infectious mononucleosis in adulthood to EBV-associated malignancies such as Burkitt`s lymphoma and nasopharingeal carcinoma
-
Laboratory diagnosticsBlood assay Serological tests are used to reveal:Heterophile antibodies with Paul-Bunnell test Specific anti-EBV antibodies with ELISA and immunofluorescence
-
AdenovirusesThey belong to family Adenoviridae, genus Mastadenovirus divided into 7 serogroups (A-F) and 47 serotypes
-
Adenovirus structure
-
Pathogenecity Respiratory disease in children (pharyngitis, pneumonia)Common cold in adultsConjunctivitis (swimming pool follicular conjunctivitis and keratoconjunctivitis -shipyard disease)Diarrhea in childrenAcute hemorrhagic cystitis in young males
-
Epidemiology and pathogenesisAdenoviruses are transmitted with different mechanisms:Via aerosol dropletsWith fecal-oral routeBy direct contact
-
Laboratory diagnosticsDiagnosis is based onto:Rapid diagnostics with electron microscopy, immune electron microscopy, immunofluorescence
Virus isolation
Serological tests demonstrate rising in titer of antibody, demonstrated in paired patient sera