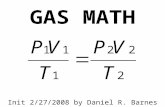Versus By Daniel R. Barnes, init 11/14/2006. But before we get started... Do you remember when you...
-
Upload
brianna-loren-lang -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Versus By Daniel R. Barnes, init 11/14/2006. But before we get started... Do you remember when you...

versus
By Daniel R. Barnes, init 11/14/2006

But before we get started . . .
Do you remember when you read about “resonance structures” and learned they didn’t really resonate?
Well, galloping gertie did.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j-zczJXSxnw&desktop_uri=%2Fwatch%3Fv%3Dj-zczJXSxnw&app=desktop(Thank you, Kristian Alarcon)
CLICK ME


Page 238, Prentice Hall Chemistry:
Electronegativity difference range
Most probable type of bond
Example
0.0 – 0.4Nonpolar covalent H—H (0.0)
0.4 – 1.0Moderately
polar covalentH—Cl (0.9)
1.0 – 2.0 Very polar covalent
H—F (1.9)
>= 2.0 Ionic Na+ Cl- (2.1)


Formula =
H2O

electronegativity
2.1
3.5
3.5-2.11.4
+
-
+

NOTE: Click in the grey to avoid jumping to the web page where this picture came from.


+
-
+
-
This attraction is an example of an “intermolecular force.”
It is a specific kind of attraction called a “hydrogen bond”.

-
++
-
++
-
++
-+
+
-+
+
-+
+
-
+
+
-+
+
-+
+
-
+
+
-
+
+
-
+
+
-
+
+
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES
EXAMPLE: HYDROGEN BONDING

Attraction between water molecules causes
“surface tension”

Hydrogen bonding between water molecules causes
“surface tension”

Gravity round planets/moons/stars
Surface tension round water droplets


Surface tension Insect’s foot can’t get in between
water molecules Insect walks on water



See how her foot makes a dimple in the surface?
Springs help provide tension. They pull the skin of the trampoline tight.


Hydrogen bonding solidity and form of ice crystals

Unusual “open lattice” of ice crystal Ice is less dense than water




+
-
+
-
s
H2O H2S
waterhydrogen sulfide

+
-
+
-
s
oxygen = 3.5hydrogen = 2.1--------------------- = 1.4
Electronegativitycomparison:
sulfur = 2.5hydrogen = 2.1--------------------- = 0.4
Electronegativitycomparison:
Bonding in a water molecule is . . .
. . . “very polar covalent.”
Bonding in a hydrogen sulfide molecule is . . .
. . . on the borderline of “nonpolar” and “moderately polar”.

+
-
+
-
s
+
-
+
-
s
More polarity Stronger attraction
Less polarity Weaker attraction

+
-+
-
s
+
-+
-
s
Stronger attraction Molecules huddle together
but free to wander
Weaker attraction Molecules fly away
from each other
+
-+-+
-
+
-
+
-+-+
-
+
-
s
+
-
s
+
-
s
+
-
s
+
-
s
WATER is a LIQUIDHYDROGEN SULFIDE
is a GAS

-
S
This would be a good time to read that little passage from Fast Food Nation about hydrogen sulfide on page 178

. . . and now for the other one . . .

2.1 2.5electronegativity 2.5-2.1
0.4
Formula =
C8H18

No +’s No -’s
DISCLAIMER: C may be slightly negative & H slightly positive, but not enough to matter
2.1
2.5
+ -

No +’s No -’s

+
-
How do gasoline and water interact?
No attraction, no repulsion.
No minuses or plusses on the octane molecule, so . . .
. . . whatever . . .
Huh?
. . . but . . .

+
-
+
-
. . . but . . . . . . so . . .







Oily layer
Waterylayer
Italian Salad Dressing

Oily layer
Waterylayer
What kind of bonds are there in each layer?
Example: C--H
Example: O--H

Oily layer
Waterylayer
As a result of polarity differences, how are atoms charged differently?
+ - + - + - + -
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0

Q: Why is the bond between H & O polar, whereas the bond between H & C is nonpolar?
A: H & C have electronegativities that are almost the same (2.1 & 2.5), whereas H & O have very different electronegativities (2.1 & 3.5).

Q: Why does Italian salad dressing separate into two layers?
A: It contains polar materials and nonpolar materials.

Q: Why is the oily layer on the top rather than on the bottom?
A: Oil is less dense than water.

Water is polar, so when you need to wash, you often need to add soap to the water to dissolve the nonpolar substances like fat, grease, and oil.

The sodium salt of a fatty acid
“carbon backbone”
H
H
H H
H
H
H H
H
H
H H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H H
H
HH
hydrocarbon nonpolar covalent bonds
Hydrogen and carbon atoms are neutral
Mixes with oily or watery materials?
?

The sodium salt of a fatty acid
“carbon backbone”
H
H
H H
H
H
H H
H
H
H H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H H
H
HH
hydrocarbon nonpolar covalent bonds
Hydrogen and carbon atoms are neutral
Mixes with oily or watery materials?
?
?O
O
?Na+

nonpolar oily “hydrophobic”
polar or charged like water“hydrophilic”
Soap acts as a “bridge” between water and nonpolar materials.
Soap sticks to both water AND oily materials, so the oil and water don’t have to separate

H
H
H H
H
H
H H
H
H
H H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H H
H
HH
Soap: part metal, part fat.Weird combo, huh?