Unit%J%Review%#1%KEY% 1. %Arteries,%Arterioles,Capillaries...
Transcript of Unit%J%Review%#1%KEY% 1. %Arteries,%Arterioles,Capillaries...

Unit J Review #1 KEY
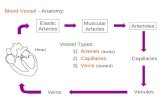
1. Arteries, Arterioles, Capillaries, Venules, Veins.
2.
3. Arteries carry blood AWAY from the heart, usually this blood is already oxygenated, unless it is an artery that is carrying blood away from the heart toward the lungs. -‐ Veins carry blood back to the heart, usually deoxygenated blood, unless it is carrying blood back to the heart from the lungs.

-‐ Capillaries allow blood to exchange materials with tissue fluid.
4. Arterial structure has a much thicker wall with a thicker layer of smooth muscle. They are more rigid to handle higher blood pressure. -‐ Veins are not as rigid, they have thinner walls that are not as rigid. They also possess valves to prevent backflow.
-‐ Capillaries have a wall that is only one cell thick. This wall of squamous epithelium is the perfect design for allowing diffusion between blood and tissue fluids.
5. Arteries and arterioles have the ability to contract and relax their smooth muscle to dilate and constrict the vessel. During constriction blood pressure goes up, when arteries dilate blood pressure falls.

6. Sphincter muscles open or close pathways to certain capillary beds. This allows the circulatory system to direct blood to where the body needs it the most at that time. Ex digestion vs. exercising.
7. Blood pressure goes up in areas where more blood volume has been sent. When more capillary beds are opened up at the same time overall blood pressure will go down.

8. Blood Vessel Type Blood Pressure Arteries Highest Capillaries Moderate Veins Lowest
9. Blood Vessel Type Blood Velocity Arteries Very Fast Capillaries Slow Veins Fast LO J-‐2 1. Pulmonary Artery 2. Renal Artery
3. Femoral Vein and Great Saphenous à Iliac Vein

4. The AORTA
5. Most veins carry Deoxygenated blood, the exception to this rule are the PULMONARY Veins which carry Oxygenated blood back to the heart from the lungs.

6. Most arteries carry Oxygenated blood, the exception to this rule are the PULMONARY Arteries which carry Deoxygenate blood away from the heart toward the lungs.
7. The Superior (Anterior) Vena Cava receives blood from the upper extremities (arms) and head via the Subclavian veins and Jugular veins.
8. The Superior (anterior) Vena Cava and the Inferior (Posterior) Vena Cava enter into the Right Atrium.
9. Three main Coronary arteries branch off of the Aorta and branch off to supply the Myocardium (Heart Muscle) to keep the cardiac muscle tissue nourished with oxygen and nutrients so that it remains healthy and alive. (see pic below)

10. The Hepatic Portal Vein has a large network of capillaries at one end (associated with the small intestine) and another large network of capillaries at the other end (associated with the liver) so it transports blood from small intestine to the liver where the nutrients are processed.
11. A portal system is any vessel that has a network of capillary beds at both ends.
12. The Systemic circuit circulates oxygenated blood from the left ventricle out to all the tissues and systems of the body and then it brings deoxygenated blood back from the capillaries and drops it off in the Right Atrium.

The Pulmonary circuit circulates deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle out to the Pulmonary capillaries around the lungs and then it brings this oxygenated blood back from these capillaries and drops it off in the Left Atrium so it can head out into the System Circuit.
Practice Quiz:
1. B
2. B – This is a vein as it has a valve in it!
3. C
4. C – The smaller the type of vessel is the more cross-‐sectional area they add up to have. Capillaries have the most, while venules and arterioles have the second most cross-‐sectional area.

5. D – Blood moves most slowly through capillaries to allow for exchange with tissue fluid.
6. A -‐ Blood vessel "X" must be an artery or a decent sized arteriole to have that much pressure.
7. A – Veins have the lowest blood pressure and they also have a very small total cross-‐sectional area.
8. D – This vessel is returning blood from lower body and transporting it to the right atrium
9. D
10. D
11. D

Unit J Rev #2 KEY
LO – J-‐4
1. Pulmonary Circuit
2. Systemic Circuit
3. Both the Pulmonary Arteries and the Umbilical Arteries carry deoxygenated blood.
4. The Left side of the heart drives the Systemic Circuit.
5. The right atrium is the collecting chamber for the systemic circuit.

LO – J-‐5 1. The key differences between the circulation systems of fetus and developed human are: a) Arterial Duct – Connects pulmonary trunk right onto Aorta – to help bypass lungs.
b) Oval Opening – Opening between right atrium and left atrium to help shunt blood straight from right atrium into left atrium.
c) Venous Duct – Connection between Umbilical vein carrying oxygenated blood from placenta and Fetus’s Inferior Vena Cava.
d) Umbilical arteries and vein. Blood vessels that connect fetal circulatory system to placenta. Umbilical arteries carry blood AWAY from fetal heart, umbilical vein brings back to fetal heart.

2. See diagram
3. Both the oval opening and the arterial duct are both structures that help with by-‐passing the fetus’ lungs.
4. As soon as the baby starts breathing the pressure in the thorax helps close off the oval opening. This allows blood to start moving to babies lungs for oxygenation.

5. Umbilical Vein 6. PLACENTA 7. Primarily through DIFFUSION. Baby's blood cells do not exchange with mother’s blood cells.
LO – J-‐6
1. Right Atrium à R. Ventricle à Pulmonary Trunk à Pulmonary Arteries à Pulmonary Capillaries of Lungs à Pulmonary Veins à Left Atrium à Left Ventricle à Aorta à Abdominal Aorta à Common Iliac Artery à Femoral Artery à Capillary Beds of Toe à Femoral Vein or Great Saphenous Vein à Common Iliac Vein à Inferior Vena Cava à Right Atrium.

2. Left Atrium à Left Ventricle à Aorta à Carotid Artery à Brain.
3. Intestines à Hepatic Portal Vein à Liver à Hepatic Vein à Inferior Vena Cava à Right Atrium à Right Ventricle à Pulmonary Trunk à Pulmonary Arteries à Pulmonary Capillaries of Lungs à Pulmonary Veins à Left Atrium à Left Ventricle à Aorta à Abdominal Aorta à MESENTERIC artery à Intestines.
4. Superior Vena Cava à Right Atrium à R. Ventricle à Pulmonary Trunk à Pulmonary Arteries à Pulmonary Capillaries of Lungs à Pulmonary Veins à Left Atrium à Left Ventricle à Aorta à Subclavian Artery à Brachial Artery à Capillary Beds of finger

PRACTICE QUIZ: 1. C – Hepatic Vein à Inferior VC à R.A. à R.V. à Pulm Trunk à Pulm Art à Pulm Caps
2. B -‐ W = a major artery, X = A Vein, Y = An arteriole, Z = A Capillary.
3. C 4. D – Hepatic Vein drains blood from small int. 5. C 6. B 7. B 8. C -‐ W = Arteries X= Arterioles or Venules, Y= Capillaries, Z = Veins
9. A

Unit J Review #3 Key
1. Approximately 55%.
2. Approximately 90-‐92%
3. The source for this water is absorbed mostly through the Intestines. So diarrhea could cause the blood to become thicker and the volume would go down (4 L à 3.4 L).
4. With less blood volume, blood pressure would definitely be lower.
5. Plasma proteins have a variety of roles, But collectively they create a hypertonic environment that helps draw tissue fluid back into capillaries. So they help maintain correct blood volume levels.

6. If the blood was lacking these proteins, fluid would build up in the tissues around organs.
7. Nutrients (AA’s, sugars, fats) pass into the blood stream from the small intestine. These nutrients are then dropped off at cells, cells use them for energy and for building materials.
8. Plasma carries key metabolic wastes like CO2, Urea and Uric Acid.
LO – J-‐8
1. A) To pick up excess tissue fluid B) To absorb the products of Fat Digestion. C) To filter Lymph and fight infections using lymphocytes.

2. The Subclavian Veins merge with rt subclavian duct and with thoracic duct.

3. Lacteals are found in Villi and they absorb the final products of fat digestion.
4. Lymph nodes house lymphocytes and filter lymph to fight pathogens.
5. 6 lymphoid structures are :
-‐ Spleen -‐ Thymus gland -‐ Lymph Nodes -‐ Red bone Marrow -‐ Lymphatic vessels -‐ Adenoids/Tonsils

6. The Spleen – It filters blood and recycles old red blood cells. It also store blood as a reservoir. Spleen also plays a role in cleaning the blood by fighting pathogens.

7. T-‐Lymphocytes differentiate from some stem cells and reach maturation in the Thymus gland.
8. Tonsils (Palatine Tonsils) and Adenoids (Pharyngeal Tonsils).
9. EDEMA – Swelling and poor circulation.

10. Lymph fluid is moved in lymphatic vessels when skeletal muscles contract and relax. This muscle movement force the Lymph to move in one direction because lymph vessels contain valves.
11. Lymph veins and Cardiovascular Veins both contain valves, they both move fluid back toward the chest/heart. They both rely on skeletal muscle to drive their fluids.
SEE FIGURE – 13.10 for Table Corrections

Unit J Review #4 KEY
L.O. -‐J-‐9
1. Approximately 45%
2.a) Erythrocytes = Red Blood Cells
b) Leukocytes = White Blood Cells
c) Thrombocytes = Platelets
3. Blood plays a role in the following :
-‐Transportation : Respiratory gases, nutrients and wastes as well as hormones (controlling the body).
-‐ Regulating things (homeostasis) : pH, Body Temp, salts, blood pressure etc.
-‐ Protection : Fighting infection, preventing invasion.

4. Erythrocytes have a biconcave shape, this allows them to have more surface area to carry greater numbers of Hemoglobin (Therefore O2). This shape also allows them to be more flexible to move more easily.
5. A Nucleus.
6. All types of blood cells form from Bone Marrow.
7. A typical RBC lives about 4 months (120 days).
8. Kidneys are stimulated to put out more ERYTHROPOIETIN, this hormone triggers the bone marrow to speed up the development and maturation of RBCs.

9. Both the Liver and the Spleen play a role in the break down and recycling of old RBCs.
10. Hemoglobin can combine with Oxygen, Hydrogen ions and with Carbon Dioxide.

11. Both temperature and Oxygen concentration levels as well as pH are all factors that influence the combining capacity of Hb. It binds best to oxygen when the temp is cool, the O2 level is high, and the pH is higher. Such is the environment near the lungs.
12. Platelets play an important role in initiating and forming blood clots.
13. Leukocytes work with each other to help fight and infections.
14. White blood cells are much larger, they possess a nucleus, they have no colour, less numerous, and function to fight infection rather than for transportation.

15. Leukocytes are either GRUNULAR Leukocytes or they are AGRANULAR Leukocytes. The granular ones contain visible spheres (vesicles) that contain enzymes and proteins. These chemicals play a specific role in fighting infections.
16. Monocytes often go on to develop into Macrophages. These macrophages squeeze out through triggered permeable capillaries into damaged tissues. These macrophages then perform phagocytosis on pathogens like bacteria.

17. The Epstein Barr Virus causes Mononucleosis. Results in an excessive amount of irregular B-‐Lymphocytes
-‐ B Lymphocytes convert to plasma cells, which then go into rapid reproduction. These abnormal B-‐Cells proliferate while killer T-‐cells try to attack them.

18. Two key clotting plasma proteins are required Prothrombin and Fibrinogen along with Thrombocytes (platelets).
19. The liver is responsible for the production of the majority of plasma proteins including these specific clotting factors.
20. Adequate levels of Vitamin K must be present in order for the liver to manufacture Prothrombin.
21. Prothrombin Activator AKA (Thromboplastin) acts as an enzyme to initiate the clotting process. Prothrombin Activator chemically changes Prothrobin into Thrombin.
22. This newly formed Thrombin will then act as an enzyme to chemically transform Fibrinogen into Fibrin.

23. Calcium ions (Ca ++) must be present in the blood to convert Prothrombin into Thrombin.
24. Threads of FIBRIN form the mesh of a clot.
25. Eventually when the body is trying to properly heal the wound, the clot needs to be broken down. Plasmin is the enzyme that helps break down this clot.

26.
34. 34
PRACTICE QUIZ :

1. A
2. C
3. B
4. D
5. C
6. A
7. C
8. B
9. B
10. B
11. B

Unit J Rev #5 KEY
1. In the systemic circuit, arteriole blood is rich in Oxyhemoglobin (O2) and nutrient molecules.
2. Hemoglobin + Oxygen à Oxyhemoglobin (HbO2)
3. When blood first enters a capillary bed coming in from the arteriole, blood pressure is usually around 30-‐40 mm Hg.
4. At this same location, osmotic pressure of the tissue fluid trying to come back into the hypertonic blood is about 15-‐20 mm Hg.
5. On the venule side blood pressure has significantly dropped while, osmotic pressure has increased a bit.

6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 6. On the arteriole side more fluid is pushed out than enters because BP is greater (30 mm Hg) than the osmotic pressure of (20 mm Hg). On the venule side the blood pressure is lower than the osmotic pressure.
7. The high concentration of salts, plasma proteins and formed elements that stay behind in the blood creates the osmotic pressure.

8. Formed elements and plasma proteins are too large to leave the blood stream.
9. The LIVER
10. B