UNIT IV - DNA & CELL DIVISION. I. INTRODUCTION TO DNA ________________ – All of an organism’s...
-
Upload
christal-webb -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of UNIT IV - DNA & CELL DIVISION. I. INTRODUCTION TO DNA ________________ – All of an organism’s...

UNIT IV - DNA & CELL DIVISION

I. INTRODUCTION TO DNA• ________________ – All of an
organism’s DNA; must be copied prior to cell division
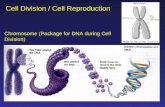
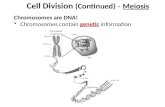
• __________________ – Single molecule of DNA wrapped in protein. Proteins maintain chromosome structure & control DNA activity Somatic cells - ___________
_________________________
Gametes - ___________
_________________________
• ________________ – Term used to describe fine strands of uncoiled DNA

II. A CLOSER LOOK AT DNA
• Discovery of DNA o Early 1900s – Scientists determined genes determined inherited
characteristics. Also realized chromosomes were composed of DNA & protein.
o Griffith (1928) – Studied 2 strains of bacteria. Determined that pathogenicity could be transferred when living non-pathogens were exposed to remains of dead pathogens.
o Avery (1944) – Identified “transforming substance” as DNA
o Hershey & Chase (1952) – Used radioactively-viruses that infect bacteria - known as bacteriophages. Virus is made up of DNA & protein – Hershey & Chase proved it was the DNA component that was injected into host cell and used to make new virus particles.
o Rosalind Franklin (late 1950s) – Produced x-ray crystallography image of DNA; “borrowed” by Watson & Crick

II. A CLOSER LOOK AT DNA, cont• _______________ & _______________
o Realized DNA was a __________ composed of _____ nucleotide strands
o Franklin suggested backbone of DNA was composed of alternating ______________________________ molecules
o Watson & Crick determined interior of DNA was made up of paired ___________________
o Eventually deduced bases always paired a specific way
• Chargaff– Chemically proved the same base-pairing rules that Watson &
Crick proved structurally

II. A CLOSER LOOK AT DNA, cont
• Monomers of DNAo Nucleotideso Composed of _____________,
_____________, & _________
o _______________ o Single-ring N-baseo Ex: Cytosine & Thymine
_______________ Double-ring structures Ex: Adenine & Guanine

II. A CLOSER LOOK AT DNA, cont
• Structure of DNA Double helix Strand of nucleotides held together
by ________________ bonds Nitrogen bases held together with
________________ bonds Pairs
__________________________________________
2 nucleotide strands are ____________________
Each strand has a ______ end (terminus) and a _______ end; named for carbon on deoxyribose

II. A CLOSER LOOK AT DNA, cont

III. DNA REPLICATION• DNA Replication
o Prior to cell division, DNA must be replicatedo Known as _______________________ model of replication
Meselson-Stahl Experiment

III. DNA REPLICATION, cont.
• ________________ - Two identical DNA molecules; copied prior to cell division________________ –
Site where sister chromatids are most closely attached

III. DNA REPLICATION, cont.
• Steps Involved in Replication ___________________________ unwinds the DNA double helix Replication begins at specific points on the DNA molecule
known as ____________________________________________. The Y-shaped region where new strands of DNA are elongating are called ________________________________

III. DNA REPLICATION, cont.
As DNA is “unzipped”, _______________________ binding proteins hold the DNA open
A ______________________________ untwists the nucleotide strand. DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to an already-existing strand
so an ___________________ is synthesized to get replication going

III. DNA REPLICATION, cont.______________________________ add complementary
nucleotides to each side of the DNA molecule. Can only add nucleotides to the _______ end of the growing strand,
so the daughter DNA is synthesized _________________So…..only one side of the DNA (3’ – 5’) molecule can be replicated
as a continuous strand which is known as the _______________________________.

III. DNA REPLICATION, cont.• Synthesis of ____________________
To synthesize the other new strand of DNA, DNA polymerase must work away from the replication fork. Leads to synthesis of short pieces of DNA known as ________________ fragments.
____________________ binds fragments together to form a continuous strand of nucleotides.
• Proofreading & Repair DNA Polymerase proofread nucleotides as they are added

III. DNA REPLICATION, cont.

III. DNA REPLICATION, cont.
An Overview of Replication

III. DNA REPLICATION, cont.• ___________________
5’ ends of daughter strands cannot be completed because DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3’ end
Results in shorter and shorter DNA molecules with jagged ends To protect genetic integrity, ends of chromosomes do not contain
genes – instead there are nucleotide sequences known as telomeres
Contain nucleotide repeat sequences Telomeres shorten each time cell divides - limits the number of
times a cell can divide; thought to protect organism from cancer Telomerase – Enzyme produced by stem cells, cancer cells that
restores telomere length