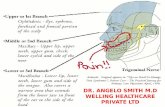
Trigeminal Neuralgia
-
Upload
imelda-junaedi -
Category
Documents
-
view
55 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Trigeminal Neuralgia


“Tic Doloureau”
4.3 per 100,000
Slight female predominance : 1.74 t0 1
Peak incidence 60-70 y.o. Unusual before age 40 No racial prediliction

“Tic Doloureau”
Higher incidence with M.S. & HTN
Spontaneous remission possible, BUT unusual
Most patients will have episodic attacks over many years

Now 2 Types Are Identified
Classical
Symptomatic

Classical Criteria
A. Paroxysmal attacks of pain lasting from a fraction of a second to 2 minutes, affecting 1 or more divisions of the trigeminal nerve, & fulfilling criteria B & C.
B. Pain has at least 1 of the following characteristics: 1. Intense, sharp, superficial, or stabbing Precipitated from trigger zones or by
trigger factors

Classical Criteria
C. Attacks are stereotyped in the individual patient
D. No clinically evident neuro deficit
E. Not attributed to another disorder.

Symptomatic Criteria
A. Paroxysmal attacks of pain lasting from a fraction of a second to 2 minutes, with or w/o persistence of pain between paroxysms, affecting 1 or more divisions of the trigeminal nerve, & fulfilling criteria B & C.
B. . Pain has at least 1 of the following characteristics: 1. Intense, sharp, superficial, or stabbing Precipitated from trigger zones or by
trigger factors

Symptomatic Criteria
C. Attacks are stereotyped in the individual patient
D. A causative lesion, other than vascular compression, has been demonstrated by special investigations &/or posterior fossa exploration.

Pathophysiology

? Pathophysiology ?
Demyelination of the trigeminal nerve, causing ectopic impulses and then ephaptic conduction
Vascular compression of the nerve root by aberrant or tortuous vessels
Compression by tumor Amyloid A-V malformation Pons Infarct Bony compression

Diagnosis
Clinical Consider in all patients with
unilateral facial pain Prompt Dx important as pain can be
severe Distinguish classical from
symptomatic for RX purposes Look for “red flags” of other diseases

Red Flags
Abnormal Neuro exam
Abnormal oral, dental, or ear exam
Age < 40 yrs
Bilateral SXs
Dizziness or vertigo

Red Flags
Hearing loss
Numbness
Pain lasting > 2 minutes
Pain outside of trigeminal distribution
Visual changes

Diagnostic History
Very important Recurrent, unilateral facial pain Lasts seconds May recur 100’s of times per day Pain :
Severe Stereotypical Sharp Stabbing Superficial Shock-like

Diagnostic History
1 or more of the nerve’s divisions Trigger factors:
Talking Shaving Smiling Applying make-up Chewing Wind Teeth brushing
Age > 40 yrs. Ask about other neuro Sx Asymptomatic time or not ?

Physical Exam
Usually a normal exam Useful for identifying abnormals that
point to other DXs HEENT, including TMJ & Masseter Oral exam, including teeth & gums Neuro exam Check for trigger zones

Diagnostic Testing Generally Not helpful MRI is the Test of Choice : ‘C’ Rec ? Trigeminal reflex testing? Unclear
usefulness & I would NOT do it

Differential List
Cluster HA Dental Pain Giant Cell Arteritis Migraine Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia Otitis Media Intracranial Tumor Sinusitis Multiple Sclerosis TMJ Syndrome Postherpetic Neuralgia Paroxysmal
Hemicrania

Treatment
Medical
Surgical
No Behavioral, unless it becomes a cause of Chronic Pain

Medical Treatment
Carbamazepine : ‘A’ Rec NNT = 2.5 (For trigeminal Neuralgia) NNH = 3.7 (For all diseases) Some suggest it as a diagnostic trial Doses range from 100 to 2,400 mg per
day Most respond to 200 to 800 mg per day Immediate release (lasts about 6 hrs.) Extended release (lasts about 12 hrs.)

Medical Treatment
Carbamazepine Should be the initial Rx of choice for classical Trigeminal Neuralgia
If get no or only partial response to carbamazepine, add or substitute another pharmacologic agent:

Medical Treatment
Other agents to try : ( Not listed in any order)
Baclofen : 10 m- 80 mg daily Dilantin Lamictal Neurontin Topamax Klonopin Orap Depakene

Medical Treatment
A recent Cochrane review said there was insufficient evidence to show benefit from non-epileptic agents in trigeminal neuralgia

Follow-up
Achieve balance between pain and med side effects
Most want complete remission, which is possible and warranted
Can try a trial sans meds after “several” months symptom free (Think 4-6)

Surgical Treatment
After failure of Pharm agents Unusual Recurrences occur for many Both percutaneous & open techniques
Glycerol injection Ballon Compression
Radio Rhizotomy Gamma knife Partial Rhizotomy Microvascular
decompression

Summary
2 Types of trigeminal neuralgia A clinical DX Everyone gets a head & face
MRI Carbamazepine is the
treatment of choice.

References
Kraft, RM. Trigeminal Neuralgia. AFP. 2008;77:1291-1296.
Cochrane Collaboration Haanpaa M, et al. Neuropathic
Facial Pain. Suppl Clin Neurophysiol. 2006;58:153-170.