Triangles of the neck
-
Upload
arya-v-devi -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
1.677 -
download
1
Transcript of Triangles of the neck

Triangles Of The Neck
Divisions Created By Muscles
Presented By,Arya V Devi

Introduction
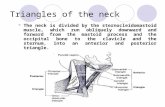
It is limited

•This quadrilateral space is divided by the Sternocleidomastoid muscle into two main triangles
•The Sternocleidomastoid muscle passes obliquely upwards and backwards from its site of origin at the clavicle and sternum to its point of insertion on the mastoid process and the occipital bone
•The triangle in front of this muscle is the anterior triangle and the one behind it is the posterior triangle

Anterior TriangleBoundari
esAnterior border of the
SCM muscle
Midline of the neck
Inferior border of the mandible
RoofSkin
Superfacial fascia
Platysma muscle
Investing layer of deep cervical fascia

Posterior triangle
Boundaries
Anteriorly: The Sternocleidomastoid
musc
posteriorly:The Trapezius muscle.
Inferiorly:The Clavicle
The apex: occipital bone
Roof
Skin
Superficial fascia
Platysma muscle
Investing layer of the deep cervical fascia
Floor
Splenius Capitis
Levator scapulae
Posterior scalene
Middle scalene
Anterior scalene

Subdivisions
Anterior Triangle•Digastric/submandibular
•Submental •Muscular •Carotid triangles
Posterior Triangle• Occipital triangle• Subclavian triangle

Anterior Triangle

Contents Of The Anterior Triangle
Vessels• Carotid system• Internal jugular
vein
Nerves• Cranial nerves
7,9,10,11,12• Cervical plexus
Muscles• Suprahyoid
muscles: (digastric , mylohyoid,stylohyoid,geniohyoid )
• Infrahyoid muscles: (sternohyoid,sternothyroid,thyrohyoid, omohyoid )

Submandibular Triangle

Submandibular Triangle
Superiorly•Mastoid & mandiblePosteriorly •Stylohyoid•Posterior belly of digastric
Anteriorly•Anterior belly of digastric

Submandibular Triangle
Roof•Platysma •Facial vein (fv) •Cervical branch of facial nerve (cbf)
Removal of the superficial structures displays the submandibular salivary gland itself.

Contents Of The Submandibular Triangle
Facial
artery
Lingual
nerve
and submandibul
ar ganglion
•The lingual nerve and submandibular duct pass through a gap between the hypoglossal (hg) and mylohyoid (mh) muscles
Submandibul
ar duct Ling
ual arter
y
• The lingual artery passes deep to the hyoglossus muscle
Hypogloss
al nerv
e

Submental TriangleUnpaired triangle

Submental Triangle
Formed by the :Anterior midline of
neckHyoid bone
Anterior belly of digastric muscle
Located between the two anterior
digastric muscles
Structures Submental lymph node-
drain the floor of the mouth.
Mylohyoid muscle (mh) arise from the body of
the hyoid bone and insert into the
mylohyoid line of the inside of the mandible.

Carotid Triangle

Carotid Triangle
Boundaries of the carotid triangle are:
posterior belly of digastric muscle (pbd) superior belly of the omohyoid muscle (so)
anterior border of sternomastoid muscle (st)
Roof: skin
superficial fascia platysma

Carotid TriangleDeepest aspect of the carotid triangle
The muscles, at this level, are the middle and lower pharyngeal constrictors
Floor
Superior laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus its 2 terminal branches
Internal laryngeal (ilb--sensory to upper part of the larynx)
External laryngeal (elb--motor to the cricoid muscle)
Structures seen passing through

Contents Of Carotid Triangle
Veins• Common facial
vein • Near by:
• Retromandibular vein
• Posterior auricular vein (pav)
• Facial vein (fv)
• External jugular vein
• Anterior jugular vein
Arteries• Facial• Lingual• Occipital• Common carotid• External carotid• Internal carotid• Superior thyroid
Nerves• Hypoglossal (XII) • C1 root of ansa
cervicalis (C1) • C1 fibers running
with hypoglossal nerve (nerve to thyrohyoid muscle (nth)
• C2-C3 root of ansa cervicalis
• Ansa cervicalis (ac)

Muscular Triangle

Muscular TriangleBoundaries•Mid line of neck •Superior belly of omohyoid •Sternomastoid
The muscles forming and within the triangle•Superficial layer •Sternohyoid (sh) •Superior belly of omohyoid (oh) •Deep layer •Thyroid (th) •Sternothyroid (st)
Strap Muscles

Muscular Triangle
When the strap muscles are reflected, you can see the
thyroid gland with its arteries (superior and inferior thyroid artery)
If the thyroid gland is reflected laterally, the
structures making up the larynx and trachea are seen: thyrohyoid membrane (thm)
thyroid cartilage (Adam's apple)(tc)
cricothyroid membrane and ligament (ctm)
cricoid cartilage (cc) tracheal rings (tr)

Table of MusclesMuscle Origin Insertion Nerve supply
Sternohyoid Sternum Hyoid Ansa
Omohyoid Suprascapular notch Hyoid Ansa
Sternothyroid Below sternohyoid on manubrium
Thyroid cartilage oblique line Ansa
Thyrohyoid Thyroid cartilage oblique line Hyoid C1-C2 (ansa)
Anterior belly digastric Intermediate tendon Inner surface of mandile Trigeminal nerve
Posterior bellyDigastric
Medial aspect of the mastoid process -Intermediate tendon- Facial nerve
Mylohyoid Mylohyoid line of mandible Hyoid bone Trigeminal nerve
Hyoglossus Hyoid bone Lateral side of tongue Hypoglossal
Stylohyoid Styloid process Hyoid Facial nerve

Clinical Considerations
The cricothyroid ligament and membrane are frequently pierced in emergency situations to open the airway.
It has been known that an empty ball-point pen or a hollow stem has been used in the field to save lives, where an air passage has been closed above this region.

Posterior Triangle

Boundaries of Posterior Triangle

Boundaries of Posterior Triangle
Anteriorly •Sternocleidomastoid
Posteriorly •Anterior edge of trapezius
Inferiorly •Middle third of the clavicle
Apex •Between the attachments of sternocleidomastoid and trapezius to the occiput and is often blunted, so that the 'triangle' becomes quadrilateral
Roof •Investing layer of the deep cervical fascia
Floor •Prevertebral fascia overlying splenius capitis, levator scapulae and the scalene muscles

Nerves And Plexuses• Spinal
acessory nerve.
• Branches of Cervical plexus
• Roots and trunks of brachial plexus
Vessels• Subclavian
artery• Transverse
Cervical artery
• Suprascapular artery
• External jugular vein (terminal part)
Lymph Nodes• Occipital• Supraclavi
cular
Muscles• Inferior
belly of Omohyoid muscle
Contents of the posterior triangle

Clinical Significance Of The Posterior Triangle
The Accessory Nerve may be damaged, while taking lymph node biopsy.
The External Jugular Vein is present in a superficial location here and this makes it vulnerable to injury.

Lower and smaller division of the posterior triangle
It corresponds in the living neck with the lower part of a deep, prominent hollow, namely, the greater supraclavicular fossa
Its size varies with the extent of the clavicular attachments of sternocleidomastoid and trapezius and also the level of the inferior belly of omohyoid
Subclavian Triangle

BoundariesBorders•It shares the same boundaries• Except that superiorly it is limited by omohyoid
Floor•The first rib, •Scalenus medius•The first slip of serratus anterior
Roof•Supraclavicular nerves•Platysma•Superficial and deep fasciae•Skin

Contents
The suprascapular
vesselsBrachial plexus Third part of the
subclavian artery
Subclavian veins
The external jugular vein
The nerve to subclavius
The triangle contains some lymph nodes.

Occipital triangleUpper and larger part of the posterior
triangle

BoundariesShares the same borders
Except that inferiorly by the inferior belly of omohyoid
Borders
Semispinalis capitis
Occasionally appears at the apex
Posteriorly

Boundaries Platysma
Superficial and deep fasciae
Skin
Roof
Spleniuscapitis
Levator scapulae
Scaleni medius
Floor

Contents Cutaneous and muscular branches of the
cervical plexusUppermost part of the brachial plexus
Transverse cervical vessels
Spinal accessory nerveSupraclavicular nerves
Lymph nodes

That’s it!!!