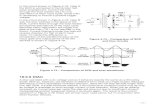
Triac and diac
-
Upload
taranjeet10 -
Category
Education
-
view
451 -
download
2
Transcript of Triac and diac

1
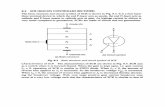
• Silicon-controlled rectifiers.– Best known of the thyristors.– Referred to as SCRs.– Three terminals:
• anode• cathode• gate
– Used primarily as switches.– Controls current in only one direction.

2
• A power transistor would require ten times the trigger signal of an SCR to control the same amount of current.
• Constructed of four alternately doped semiconductor layers.– Made from silicon by the diffusion or diffusion-
alloy method.– Three junctions are formed.

3
– Leads are attached to only three layers to form the anode, cathode, and the gate.

4
• This figure shows that the anode is positive with respect to the cathode and the gate is open.

5
• SCRs are used: – primarily to control the application of DC and
AC power to various types of loads.– As switches to open or close circuits.
• A small gate current can control a large load current.

6
• TRIACs– An acronym for triode AC semiconductor.– Conduct both directions of AC current flow.– Have the same switching characteristics as
SCRs.– Equivalent to two SCRs connected in parallel,
back to back.

7
• TRIACs are widely used to control application of power to various types of loads.

8
• TRIAC construction– A four-layer NPNP device in parallel with a
PNPN device.– Designed to respond to a gating current through
a single gate.– Not equally sensitive to the gate current
flowing in opposite directions.

9
• Advantages and disadvantages of SCRs and TRIACs:– Current ratings:
• TRIACs up to 25 amperes.• SCRs up to 1400 amperes.
– Voltage ratings:• TRIACs maximum rating is 500 volts.
• SCRs maximum rating is 2600 volts.

10
– Frequency:• TRIACs from 50 to 500 hertz.• SCRs up to 30,000 hertz.
– TRIACs have difficulty switching power to inductive loads.

11
• Bi-directional (two-directional) trigger diodes– Used in TRIAC circuits because they have
nonsymmetrical triggering characteristics.
– Most frequently used triggering device is the DIAC (diode AC).

12
• DIAC construction:– Three alternately doped layers.– The doping concentration around both
junctions is equal.– Leads are only attached to the outer layers.– Packaged like a PN junction diode.

13
• A DIAC has the same effect on current regardless of the direction of flow.– One junction is forward biased.– The other is reverse biased.– Performs as if it contained two PN junction
diodes connected in series back-to-back.

14
• DIACs are most commonly used in conjunction with TRIACs to provide full-wave control of AC signals.
• Useful for controlling– lamps– heaters– speeds of small motors

15
• Thyristors can be tested with commercial test equipment or an ohmmeter.– Refer to the operator manual for proper settings
and readings when using commercial test equipment.
– An ohmmeter can detect the majority of defective thyristors.
– It cannot detect marginal or voltage-sensitive devices.

16
• In Summary– Thyristors include SCRs, TRIACs, and DIACs.– SCRs:
• Control current in one direction by a positive signal gate.
• Turned off by reducing the anode-to-cathode voltage to zero.
• Used to control current in both AC and DC circuits.

17
• Can handle up to 1400 amperes.
• Have voltage ratings up to 2600 volts.
• Can handle frequencies up to 30,000 hertz.
– TRIACs:• Bi-directional triode thyristors.
• Control current in either direction by either a positive or negative gate signal.
• Can handle up to 25 amperes.

18
• Have voltage ratings up to 500 volts.• Can handle frequencies up to 400 hertz.• Require the use of a DIAC because they have
nonsymmetrical triggering characteristics.
– DIACs:• Bi-directional trigger diodes.
• Mostly used as triggering devices for TRIACs.
– Testing is done using commercial transistor testers or ohmmeters.