Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
-
Upload
ayshebayshe -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
0
Transcript of Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 1/30
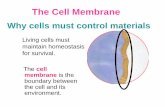
Transport Across The Membrane
Osmosis
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 2/30
Objectives of unit:
Explain passive transport mechanisms of diffusion and facilitated diffusion,including the role of channel and carrier proteins
Define the process of osmosis
Explain the process of active transport and the role of proteins and ATP
Explain the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis
Describe the properties of gas exchange surfaces in living organisms
Explain how the structure of the mammalian lung is adapted for rapidgaseous exchange
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 3/30
What can you remember about osmosis fro
IGCSE/GCSE? (convert pointer to pen tool by right clicking)
Osmosis
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 4/30
The diffusion of solvent molecules, such as water,
is known as osmosis
water
glucose Solvent
moleculese.g. water
Solute
molecules
e.g.glucose
Water is the solvent used in nature
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 5/30
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 6/30
Question 1: Complete the definition
Osmosis is the net movement of solvent
molecules from a region of their high
concentration to one of their low concentration
across a partially permeable membrane
answer
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 7/30
Osmotic concentration relates to the amount of
dissolved solutes in a solution
high osmotic concentration low osmotic concentration
Insoluble molecules do not affect the osmotic concentration
(concentrated) (dilute)
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 8/30
Water molecules will move down their
concentration gradient
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 9/30
Partially permeable membranes only let water
and very small molecules through
A partially permeable membrane results in an uneven distribution
across the membrane
Low osmotic
concentration:
A dilute solution
with a high water potential
High osmotic
concentration:
A concentrated
solution with alow water
potential
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 10/30
Which way will osmosis occur ?
water
glucoseNET osmosis
low osmotic concentrationhigh osmotic concentration
partially permeable membrane
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 11/30
Osmosis can be modelled using an osmometer
Pure water
Sucrose
solution
30 minutes later
Water molecules enter
the tubing by osmosis
Pure water
Sucrosesolution
30 minutes later
Water molecules leaves
the tubing by osmosis
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 12/30
Question 2: An osmometer was used to
investigate the affect of temperature on osmosis:
TemperatureoC
Rate of osmosis
mm/minute
Average rate
mm/minute
10 9 12 12
20 14 14 11
30 15 15 15
40 17 16 18
50 18 19 20
1. Calculate the averages and plot a graph to illustrate the
affect of temperature on the rate of osmosis.
2.Ex
plain the results. answer
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 13/30
Isotonic solutions have the same osmotic
concentration as the cytoplasm of the cell
external solution
blood cell
No NET osmosis
Cell just not change
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 14/30
Hypertonic solutions have a higher osmotic
concentration than the cytoplasm of the cell
external solution
blood cell
NET osmosis out of the cell
Causes animal cells to shrink
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 15/30
Hypotonic solutions have a lower osmotic
concentration than the cytoplasm of the cell
external solution
NET osmosis into the cell
blood cell
Can cause animal cells to burst
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 16/30
Question 3: Match the terms with the definitions
isotonic
hypotonic
hypertonic Same concentration as cell cytoplasm
higher concentration than cell cytoplasm
lower concentration than cell cytoplasm
answer
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 17/30
Question 4:
A scientist placed some red blood cells in a solution and
viewed the cells with a light microscope. After a few minutes
she noticed that many of the cells burst.
Explain why this may have occurred.
answer
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 18/30
Osmosis in red onion cells
Isotonic solution
Incipient plasmolysis
osmosisHypertonic solution
Full plasmolysis
osmosis
Causes a plant to wilt
Hypotonic solution
Turgor
Cell wall exerts an inward pressure
osmosis
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 19/30
Question 5: Match the label to the solution
A B C
1. Isotonic solution 2. hypertonic solution 3. hypotonic solution
answer
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 20/30
Question 6: Predict, with reasons, what will
happen to the flowers in the diagram below:
answer
very salty water
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 21/30
Summary:
Keywords you need to know the meaning of:
Osmosis
Partially permeable membrane
Isotonic
Hypertonic
HypotonicTurgor
Plasmolysis
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 22/30
Activity
Read pages 106 ± 107
Make brief notes
Answer questions 1 and 2 on page 107
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 23/30
End
www.clickbiology.com
Answers to questions
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 24/30
Question 1 answer
Osmosis is the net movement of solvent
molecules from a region of their high
concentration to one of their low concentration
across a partially permeable membrane
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 25/30
Question 2 answer
Temperature/oC
10 20 30 40 50
20
1816
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
Rate of
osmosis
mm/minxx
x
xx
xTemp Average
rate
10 11
20 13
30 15
40 1750 19
With increasing
temperature the
water molecules
gain kinetic
energy;
Increasing therate of osmosis
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 26/30
Question 3 answer
isotonic
hypotonic
hypertonic same concentration as cell cytoplasm
higher concentration than cell cytoplasm
lower concentration than cell cytoplasm
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 27/30
Question 4 answer
The solution was hypertonic;
So water entered the cells;
By osmosis;
Causing them to swell and burst
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 28/30
Question 5 answer
A B C
1. Isotonic solution 2. hypertonic solution 3. hypotonic solution
3 2 1
8/8/2019 Transport Across the Membrane Osmosis Teaching
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/transport-across-the-membrane-osmosis-teaching 29/30
Question 6 answer
The salty water is hypertonic;
As it has a higher osmotic
concentration than the cell cytoplasm;
So water leaves the cells of the stems;
By osmosis;
Causing the cells to plasmolyse;
And the flowers to wilt;