Translation: From RNA to Protein
description
Transcript of Translation: From RNA to Protein
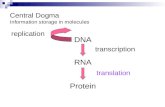
tRNA• To translate the mRNA transcript into
a protein the codons must be read one at a time to assemble amino acids in the right sequence
• This occurs in the ribosomewith the help of transfer RNA (tRNA)
Structure of tRNA• Folded RNA molecule with an
anticodon loop– anticodon contains nucleotide triplet which
is complementary to mRNA codon; each codon codes for a specific amino acid
• each tRNA carries a particular amino acid corresponding to its anticodon
Structure of tRNA
3’
5’
amino acid
anticodon
Ileu
A tRNA molecule bound to an amino acid is called an amino - acyl tRNA ( aa-tRNA)
Wobble• The cell only makes 30 - 45 tRNA
molecules of the possible 64 because of the redundancy in the genetic code
• “wobble” phenomenon The 3rd nucleotide in the anticodon is less important(binds weakly ; not specific)
The Ribosome• A ribosome is a cluster of protein
combined with ribosomal RNA (rRNA)• 2 subunits : small (40s) and large (60s)3 binding sites for tRNA• P site
holds one aa - tRNA and the growing chain of amino acids
• A site receives the tRNA with the next aa to beadded to the chain
• E site releases the tRNA back into the cytoplasm
E P A
Small ribosomal subunit
Large ribosomal subunit
Initiation
1. In the cytoplasm the ribosome attaches onto the mRNA at the 5’ cap.
2. A tRNA molecule with the start anticodon UAC (to complement the start codon AUG) binds to the mRNA - rRNA complex. The start tRNA carries the amino acid methionine
3. This complex then binds to the large ribosomal subunit
Initiation
E P A
5´ 3´S
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
U
P S
A
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
PS
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
A
P S
U
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
P
3’
5’
tRNA
ElongationThe cycle of elongation has 3 steps:
1. aa-tRNA binds to the A site (aminoacyl site).
2. The large ribosomal subunit catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond with the previous amino acid. At the same time the polypeptide chain is passed from the tRNA in the P site (peptide site) to the tRNA in the A site. The ribosome moves along mRNA in 5’ 3’
*ie. Translates in 5’ 3’ direction
3. Translocation: The ribosome moves 3 nucleotides (one codon) along the mRNA. This releases the used tRNA at the E site (exit site) and frees the A site for a new aa-tRNA to bind
Elongation
E P A
5´ 3´S
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
U
P S
A
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
PS
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
A
P S
U
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
P
Elongation
E P A
5´ 3´S
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
U
P S
A
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
PS
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
A
P S
U
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
P
Elongation
E P A
5´ 3´S
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
U
P S
A
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
PS
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
A
P S
U
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
P
Elongation
E P A
5´ 3´S
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
U
P S
A
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
PS
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
A
P S
U
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
P
Elongation
E P A
5´ 3´S
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
U
P S
A
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
PS
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
A
P S
U
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
P
Growing polypeptide
chain
Termination
• There is no tRNA with the complementary anticodon for the stop codon (UGA, UAG, UAA)
• A protein release factor binds to the A site• This cleaves the polypeptide from the tRNA
and breaks apart the ribosomal sub-units
I love protein
Termination
E P A
3´S
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
U
P S
A
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
PS
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
PS
U
P S
U
P S
C
P S
C
P S
A
P S
A
P S
C
P
I’ll be back!
protein
mRNA
Release factor (protein)
3D Shape• During translation polypeptides fold into
a 3D shape
• NOT DONE YET! Most newly synthesized proteins need modification in the ER and/or Golgi:
After translation: - some amino acids may be removed- polypeptide can be divided into pieces- sugar and phosphate may be added- several polypeptides can join to form
quaternary structure
Polysome• One mRNA can be bound
simultaneously to more than one ribosome. This is a polysome!(called a polyribosome in your textbook)
E P A
5´ 3´S
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
C
P S
C
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
PS
G
P S
G
P S
U
P S
C
P S
C
P S
G
P S
A
P S
U
P S
C
P