Transcription & Translation
description
Transcript of Transcription & Translation

Transcription &
Translation
Objective 3.01Analyze the molecular basis of heredity as it
relates to Protein Synthesis

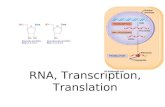
Transcription• Occurs in the nucleus• The process begins with the DNA unzipping.• Single-stranded messenger RNA (mRNA) is
made by base pairing. The mRNA is a copy of the DNA (replacing T with U).

• The mRNA then separates from the DNA and the DNA zips back up.
• The mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytoplasm.

So Let’s Practice TranscriptionG -- ___C -- ___T -- ___A -- ___T -- ___G -- ___A -- ___T -- ___C -- ___
OriginalDNA
Strand
New mRNAStrand

Translation• Occurs at the ribosome• mRNA is read by the ribosome 3 bases at a time.– These 3 bases are called a codon.– Each codon on the mRNA CODES for an amino acid.
• Translation begins when the ribosome finds the codon AUG (Start Codon)


• Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino acids to the ribosome.
• Translation stops when the ribosome reads a STOP codon (there are 3 stop codons).
• Amino acids at the ribosome link together by a peptide bond to form a protein!
“Hey, tRNA! I gotta code for an amino
acid, here! Why don’t you go fetch it for me!”
GGCGlycine
“Terrell” tRNA
AminoAcid
“Ref”Ribosome

Nucleus
mRNAtRNAAminoAcid
Ribosome
mRNA Start codon

Growing polypeptide chain A.K.A. PROTEIN!!!!
Ribosome
tRNA
mRNA
tRNAAmino Acid
mRNA Ribosome Translation direction

Protein Synthesis Animation
• Protein Synthesis Animation

• There is also Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), component that makes up about 50% of a ribosome.
• It keeps the ribosome functioning and protects the RNA during the translation process.
rRNA Ribosome

Check Point!• Why do cells have to replicate their DNA?Because before they do mitosis and divide into
daughter cells, they need to copy all the DNA to give to the new cell!
• When in the cell cycle does DNA replication occur?Remember 2 phases in the Cell Cycle: Interphase &
Mitosis! Replication must occur BEFORE the cell divides, so it happens during interphase!
• What kind of bond holds the nitrogen bases together? Why is this important?
Hydrogen; because it’s a weak bond…remember, an enzyme is going to come along and “unzip” it anyway!