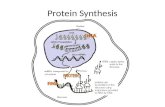
Transcription and Translation. Transcription Process by which genetic instructions in a specific...
-
date post
20-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
1
Transcript of Transcription and Translation. Transcription Process by which genetic instructions in a specific...

Transcription and
Translation

Transcription
• Process by which genetic instructions in a specific gene are transcribed (“rewritten”) into an RNA molecule
• Location? Where the DNA is– Nucleus (eukaryote)– DNA-containing region of cytoplasm (prokaryote)

Steps of Transcription: Step #1• 1) RNA polymerase
binds to a promoter (a specific nucleotide sequence of DNA)– After RNA polymerase
binds to the promoter, the DNA strands unwind and separate

Transcription – Step #2• 2) RNA polymerase adds
free nucleotides (that are complementary to the nucleotides on one of the the DNA strands) results in an RNA molecule– These nucleotides follow
RNA base pairing rules (e.x. if the DNA strand reads A-G-T-A-T-C-C, the corresponding RNA would read U-C-A-U-A-G-G
– As RNA polymerase moves past, the separated DNA strands rewind

Transcription – Step #3
• 3) RNA polymerase reaches a termination signal (a specific sequence of nucleotides that marks the end of a gene) = “stop”– RNA releases the DNA
and the newly formed RNA
– The new RNA could be mRNA, rRNA or tRNA

Transcription Animations:
• http://www.fed.cuhk.edu.hk/%7Ejohnson/teaching/genetics/animations/transcription.htm
• http://www-class.unl.edu/biochem/gp2/m_biology/animation/gene/gene_a2.html
• http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/molgenetics/transcription.swf

Moving along in Gene Expression: The Genetic Code
• Amino acids will now be assembled based on instructions encoded in the sequence of nucleotides in mRNA
• The genetic code is the term used to describe the rules that relate how a sequence of nitrogenous bases corresponds to a particular amino acids– Three adjacent nucleotides (“letters”) in mRNA
specify an amino acid (“word”) in a polypeptide– Each three-nucleotide sequence of this sort (encodes
an amino acid or gives a start or stop signal) is called a codon

The Genetic Code Cont’d• Below are the 64 mRNA codon and the amino acids they encode
in most organisms• Codons to memorize: AUG = the start codon (the sequence of
nucelotides in mRNA that indicates where translation should begin); UAA, UAG, or UGA = stop codons that do not code foramino acids but signal for translation to end

Practice
• If the following is an mRNA strand, figure out which amino acids this protein would contain:
AACGAUUAUGCUAGUAAAAUAAGCGAUG
Step 1: look for the start codonStep 2: from the start codon’s location, split up the
codons and read them until you are told to “stop”

Translating:
AACGAUU AUG CUA GUA AAA UAA GCGAUG
AUG = “Start” (methionine)CUA = LeucineGUA = Valine AAA = Lysine UAA = “stop”
Amino acid chain = (Methionine)-Leucine-Valine- Lysine

Protein Structure• Every protein is made up of one or more
polypeptides, or chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
• There are about 20 different amino acids found in the proteins of living things (could be 100s or 1000s within a protein but how they’re arranged is key)
• The amino acid sequence determines how the polypeptides will twist and fold into the 3-D structure of protein (shape = critical to function)

Steps of Translation• INITIATION1) tRNA and mRNA join
together (subunits of ribosomes) carrying methionine
2) The amino acid that corresponds to the start codon (AUG) at one end and the “code” for the match-up of UAC at the other end (anticodon = 3 nucleotides complementary to the codon sequence in mRNA)

Translation Steps Cont’d
ELONGATION• 1) a polypeptide chain is put together
(condon/anticodon pair by pair)– A tRNA carrying the appropriate amino acid pairs
its anticodon with the codon– Ribosome detaches tRNA in previous
codon/anticodon pair and that amino acid forms a peptide bond with the newly added peptide
– Ribosome keeps moving along codon by codon

Elongation Cont’d
• Polypeptide chain grows; new tRNA moves in carrying correct amino acid for next mRNA codon, etc.

Termination & Disassembly
• Termination: “Stop” codon is reached; newly made polypeptide falls off (is released)
• Disassembly: the components of trnaslation come apart (ribosome complex)– Last tRNA, ribosome,
mRNA..can be used to translate another

Translation Animation• http://www-class.unl.edu/biochem/gp2/m_biology/animatio
n/gene/gene_a3.html
• http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/molgenetics/translation.swf
• http://www.fed.cuhk.edu.hk/~johnson/teaching/genetics/animations/translation.htm
• http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter15/animations.html#

THE END OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS• Yay, we’ve made a protein!• DNA (a specific gene) RNA protein

Ending blurb in Chapter 10: The Human Genome
• The entire gene sequence (complete genetic content of human beings)
• Biologists determined the order of the 3.2 billion base pairs in the 23 human chromosomes!
• If, now, we can learn which gene sequences control which functions, we may be able to diagnose, treat & prevent genetic disorders, cancers, infections, diseases, etc.

Gene Practice
• http://nature.ca/genome/04/041/041_e.cfm• http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/
index_tj.asp?objID=AP1302• http://www.biostudio.com/
demo_freeman_protein_synthesis.htm• http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/
dna/transcribe/• http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/
dna/firefly/