Transcription
description
Transcript of Transcription

Transcription

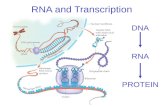
Central Dogma of Biology• Information flows from DNA RNA Proteins• Think of it as exchanging money in a different
country: proteins cannot be built directly from DNA
• Three main processes involved:– Replication (copies DNA)– Transcription: DNA RNA– Translation: RNA Protein

RNA vs. DNA
• 3 main differences:– Sugar is called
ribose (DNA has deoxyribose)–Uracil (U) instead
of thymine• pairs with
adenine (A)– Single-stranded

RNA Molecules
• 3 major types– Messenger RNA (mRNA): codes for proteins– Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): part of the ribosome– Transfer RNA (tRNA): helps read the mRNA code
to build proteins during the process of translation



What is Transcription?
• Transcription is a process that uses a portion of DNA to make a complementary RNA strand– Similar to replication
• Just one gene at a time is transcribed, not the whole DNA molecule

Transcription Process
• 3 basic steps, just as in replication:– Part of DNA double helix unwinds (initiation)– Complementary RNA bases are assembled
(elongation)– Completed RNA strand detaches from DNA
(termination)

Initiation
• RNA polymerase finds the beginning of a gene• A transcription complex made of RNA
polymerase and other enzymes begins to unwind part of the DNA strand

Elongation
• RNA polymerase uses the DNA strand as a pattern to build a complementary RNA strand– C pairs with G– A pairs with U
• RNA strand hangs off the DNA strand, and DNA helix zips back together

Termination
• After the whole gene has been transcribed, the RNA strand detaches completely from the DNA.
• The transcription complex made of RNA polymerase and other proteins falls apart.


Replication vs. TranscriptionWhere does the process take place?
Enzymes involved Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
Replication
Transcription

Replication vs. TranscriptionWhere does the process take place?
Enzymes involved Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
Replication Nucleus
Transcription Nucleus

Replication vs. TranscriptionWhere does the process take place?
Enzymes involved Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
Replication Nucleus
DNA helicase,DNA polymerase
Transcription Nucleus
RNA polymerase

Replication vs. TranscriptionWhere does the process take place?
Enzymes involved Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
Replication Nucleus
DNA helicase,DNA polymerase
DNA strand is unzipped
Transcription Nucleus
RNA polymerase
DNA strand is unzipped (initiation)

Replication vs. TranscriptionWhere does the process take place?
Enzymes involved Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
Replication Nucleus
DNA helicase,DNA polymerase
DNA strand is unzipped
Complementary bases attached; whole DNA strand
Transcription Nucleus
RNA polymerase
DNA strand is unzipped (initiation)
Complementary RNA bases attached; only one gene (elongation)

Replication vs. TranscriptionWhere does the process take place?
Enzymes involved Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
Replication Nucleus
DNA helicase,DNA polymerase
DNA strand is unzipped
Complementary bases attached; whole DNA strand
Two identical DNA molecules
Transcription Nucleus
RNA polymerase
DNA strand is unzipped (initiation)
Complementary RNA bases attached; only one gene (elongation)
mRNA strand floating free from DNA (termination)

Transcription Practice• List 3 differences between DNA and RNA.• Write the following DNA sequence: GTTCACTAG• Write the complementary DNA strand.• Circle one DNA strand. Simulate transcription by writing its
complementary RNA sequence.• Does the RNA strand more closely resemble the DNA strand from
which it was transcribed or the complementary strand that wasn’t used? Why?
• What is the main enzyme involved in transcription? What is its function?
• List 3 types of RNA and briefly describe each one.