Transcription
-
Upload
rudyard-wyatt -
Category
Documents
-
view
11 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Transcription
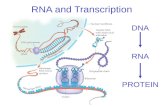
Genes in the DNA sequence encode Genes in the DNA sequence encode information about proteins and how information about proteins and how those proteins are assembledthose proteins are assembled– DNA is stored in the _______________DNA is stored in the _______________
– Proteins are made at the ____________Proteins are made at the ____________
nucleus
ribosome
Does anyone see a problem?
DNA DNA nevernever leaves leaves the nucleus and the ribosomes the nucleus and the ribosomes never never enterenter the nucleus. the nucleus.
NUCLEUS
DNARibosome
Key Point: Key Point: If the cell wants the information If the cell wants the information stored in DNA to be expressed as protein, we stored in DNA to be expressed as protein, we need to have a need to have a messengermessenger take the information take the information from the nucleus to the ribosome.from the nucleus to the ribosome.
The messenger that the cell uses is calledThe messenger that the cell uses is called
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid
SUGARSUGAR
Yes, there isYes, there isstill a phosphatestill a phosphate
# of strands = # of strands =
Ribose
1
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN DNA AND RNADIFFERENCES BETWEEN DNA AND RNA
Deoxyribose
DNA RNA
Strands
Sugar
Bases
Where in a cell?
Ribose
2 1
A, T, C, G A, U, C, GOnly in nucleus
Nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosome
What must be present during transcription?What must be present during transcription?
a. DNA gene gene – DNA sequence which codes for a protein
b. ribonucleotides
c. RNA Polymerase
What are the steps of transcription?What are the steps of transcription?
a. DNA separates at gene
b. RNA polymerasetranscribes gene strand to RNA
c. DNA strands reconnect; RNA leaves for ribosome
A – TA – T
T – AT – A
G – CG – C
A – TA – T
C - GC - G
A T
T A
G C
A T
C G
A –
T –
G –
A –
C –
U
A
C
U
G
- T
- A
- C
- T
- GDNA is
unzipped Gene strand is transcribed
Gene Copy
A – TA – T
T – AT – A
G – CG – C
A – TA – T
C - GC - G
DNA strands reform double helix
Where does transcription take Where does transcription take place?place?In the nucleusIn the nucleus
Starts at a DNA sequence called the “promoter”Starts at a DNA sequence called the “promoter”
Stops at a DNA sequence called the Stops at a DNA sequence called the “terminator”“terminator”
How does RNA Polymerase know How does RNA Polymerase know where to start and stop where to start and stop transcription?transcription?
Promoter Gene Terminator
Video Links – Video Links – originaloriginalnewnew
Heads to ribosome so the code can be used to Heads to ribosome so the code can be used to build proteinbuild protein
Where does RNA go after Where does RNA go after transcription?transcription?
mmessenger RNA; copy of DNA essenger RNA; copy of DNA gene sent to ribosomegene sent to ribosome
What types of RNA does a cell What types of RNA does a cell make?make?
1.1. mRNA – mRNA –
2.2. rRNA – rRNA –
3.3. tRNA – tRNA –
Let’s come back to the Let’s come back to the rest laterrest later
What happens to RNA What happens to RNA after it leaves the after it leaves the
nucleus?nucleus?
The rest of protein synthesisThe rest of protein synthesis
What happens to mRNA after it What happens to mRNA after it leaves the nucleus and how does leaves the nucleus and how does mRNA actually help a cell make mRNA actually help a cell make proteins?proteins?Translation –Translation – Let’s go to the Let’s go to the animation!animation!
What are the main steps in What are the main steps in translation?translation?
1. mRNA reaches 1. mRNA reaches ribosomeribosome
2. Ribosome scans 2. Ribosome scans for a place to start for a place to start – “start codon” – “start codon”
What is a codon?What is a codon?Codon – 3 Codon – 3 bases in bases in mRNA mRNA which code which code for 1 amino for 1 amino acidacidACG ACG = = CGA CGA = = UCG UCG = =
What is a codon?What is a codon?Codon – 3 Codon – 3 bases in bases in mRNA mRNA which code which code for 1 amino for 1 amino acidacidGAU GAU = = AUG AUG = = UAG, UAG, UGA, UGA, UAA UAA = =
What are the main steps in What are the main steps in translation?translation?3. tRNA with correct anti-3. tRNA with correct anti-codon brings amino acid codon brings amino acid to ribosometo ribosome
Anti-codonAnti-codon – 3 bases in – 3 bases in tRNA; complimentary to tRNA; complimentary to codoncodon
Ex. Anti-codon = AUG, Ex. Anti-codon = AUG, codon = codon =
tRNAtRNA – – ttransfer RNA; ransfer RNA; brings amino acids to brings amino acids to ribosomeribosome
UAC
What are the main steps in What are the main steps in translation?translation?
4. tRNA with 4. tRNA with correct anticodon correct anticodon for next codon for next codon brings its amino brings its amino acid into placeacid into place5. Peptide bond 5. Peptide bond forms between forms between amino acids amino acids
What are the main steps in What are the main steps in translation?translation?
6. Process 6. Process continues until continues until ribosome reaches ribosome reaches a stop codona stop codon
What happens to proteins after What happens to proteins after they are synthesized?they are synthesized?
Proteins for inside of cell:Proteins for inside of cell:- Folded into correct shape in Folded into correct shape in cytoplasmcytoplasmProteins for outside of cell:Proteins for outside of cell:- Folded into correct shape in ERFolded into correct shape in ER
- Further processed by Golgi BodyFurther processed by Golgi Body
- Exported from cell by exocytosisExported from cell by exocytosis