Totalitarianism 1920-1940 Chapter 29-1. Totalitarianism vs. Conservative Authoritarianism...
-
Upload
pearl-morgan -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of Totalitarianism 1920-1940 Chapter 29-1. Totalitarianism vs. Conservative Authoritarianism...

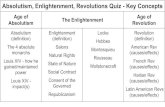
TotalitarianismTotalitarianism1920-19401920-1940
Chapter 29-1Chapter 29-1

Totalitarianism vs. Totalitarianism vs. Conservative Conservative
Authoritarianism Authoritarianism (Absolutism)(Absolutism) Conservative AuthoritarianismConservative Authoritarianism
(absolutism) was the traditional (absolutism) was the traditional European form of anti-democratic European form of anti-democratic governmentgovernment
Examples: Louis XIV, Peter the Examples: Louis XIV, Peter the Great, Frederick the Great, Great, Frederick the Great, Catherine the Great, MetternichCatherine the Great, Metternich

Conservative Conservative AuthoritarianismAuthoritarianism
Tried to prevent changes that Tried to prevent changes that threatened the existing social orderthreatened the existing social order
Most people tended to be more Most people tended to be more concerned with local affairs that had a concerned with local affairs that had a real impact on their livesreal impact on their lives
Popular participation in government Popular participation in government was discouragedwas discouraged
This is a contrast with Totalitarianism: This is a contrast with Totalitarianism: Hitler Youth, Stalin’s 5-Year PlansHitler Youth, Stalin’s 5-Year Plans

Conservative Conservative AuthoritarianismAuthoritarianism
In a Totalitarianism regime people were In a Totalitarianism regime people were expected to participate enthusiasticallyexpected to participate enthusiastically
Conservative Authoritarianism was Conservative Authoritarianism was limited in its power and objectives so limited in its power and objectives so usually sought the status quo: lacked the usually sought the status quo: lacked the technology necessary to control all technology necessary to control all aspects of people’s livesaspects of people’s lives
Usually limited their demands to taxes, Usually limited their demands to taxes, army recruits and passive acceptance of army recruits and passive acceptance of the regimethe regime

After WWIAfter WWI
Conservative Authoritarianism was revivedConservative Authoritarianism was revived Especially in Less-developed Eastern Especially in Less-developed Eastern
Europe, Spain, PortugalEurope, Spain, Portugal
The New Czech Republic remained The New Czech Republic remained democraticdemocratic
The Depression saw the end of various The Depression saw the end of various levels of democracy in Austria, Bulgaria, levels of democracy in Austria, Bulgaria, Romania. Greece, Estonia, LatviaRomania. Greece, Estonia, Latvia

TotalitarianismTotalitarianism
Was made possible by new technology: Was made possible by new technology: radio, automobile, telephoneradio, automobile, telephone
Government could wiretap phone lines and Government could wiretap phone lines and spy on citizensspy on citizens
Improved transport and communication Improved transport and communication allowed regimes to coordinate with local allowed regimes to coordinate with local officialsofficials
Autos and trucks gave regimes new Autos and trucks gave regimes new mobilitymobility
Radio was used as tool for propagandaRadio was used as tool for propaganda

Tools of Totalitarianism: Tools of Totalitarianism:
Censorship: No freedom of the press. Censorship: No freedom of the press. It became an organ of the governmentIt became an organ of the government
Indoctrination: education was geared Indoctrination: education was geared to create loyalty to the state while to create loyalty to the state while demonizing the nation’s enemiesdemonizing the nation’s enemies
Terror: Failure to comply = serious Terror: Failure to comply = serious consequences: imprisonment, deathconsequences: imprisonment, death

Totalitarian RegimesTotalitarian Regimeseithereither
FascistFascist or or CommunistCommunistGlorified the stateGlorified the state Dictatorship of Dictatorship of
the the proletariat; a proletariat; a classless classless societysociety
Condemns democracyCondemns democracy Condemns Capitalism Condemns Capitalism
Supports capitalism if No private Supports capitalism if No private propertyproperty
it serves the needs of it serves the needs of the statethe state

Fascism vs. Fascism vs. CommunismCommunism
Corporate State: Corporate State: Economy is Economy is centralizedcentralized
Captains of Industry Captains of Industry under the communist under the communist become statebecome state party partyeconomic deputieseconomic deputies
Aggressive nationalism Spread of Aggressive nationalism Spread of communismcommunism
for the benefit of the for the benefit of the world’s working classworld’s working class (Comintern)(Comintern)

Fascism vs. Fascism vs. CommunismCommunism
Advocates Social Darwinism Condemns Advocates Social Darwinism Condemns (stronger states should (stronger states should
imperialism: imperialism: Control weaker states)Control weaker states) Workers Workers
united in united in world withoutworld without nationalismnationalism
Believes that peace showsBelieves that peace showsWeakness of the governmentWeakness of the government Peace is Peace is
the the GoalGoal

Fascism vs. Fascism vs. CommunismCommunism
Military service isMilitary service is Violent revolution is Violent revolution is glorified the means to glorified the means to
the endthe end
Emphasizes inequalities Emphasizes Emphasizes inequalities Emphasizes the the
among humans perfectibility of among humans perfectibility of society: Mankind issociety: Mankind isbasically goodbasically good

The USSR under LeninThe USSR under Lenin
Marxist-Leninist Philosophy: Marxist-Leninist Philosophy: Theory of Imperialism: Imperialism is Theory of Imperialism: Imperialism is
the highest form of capitalism as the the highest form of capitalism as the search for new markets and raw search for new markets and raw materials feeds the bourgeoisie’s materials feeds the bourgeoisie’s hunger for more profitshunger for more profits
Conquered people are ruthlessly Conquered people are ruthlessly exploitedexploited

Leninist PhilosophyLeninist Philosophy
Marx did not envision a totalitarian Marx did not envision a totalitarian dictatorship ruled from abovedictatorship ruled from above
Lenin envisioned a new type of Lenin envisioned a new type of party: a cadre of educated party: a cadre of educated professional revolutionaries to professional revolutionaries to develop a political class develop a political class consciousness and guide the consciousness and guide the Dictatorship of the ProletariatDictatorship of the Proletariat

Lenin and MarxLenin and Marx
Both sought a world-wide communist Both sought a world-wide communist movementmovement
1919 a 1919 a CominternComintern was created (aka was created (aka The Third International) to serve as The Third International) to serve as the first step of the International the first step of the International movement: Workers of the world movement: Workers of the world Unite!Unite!

War CommunismWar Communism
The purpose was to win the Russian Civil The purpose was to win the Russian Civil WarWar
Nationalized (socialized) the means of Nationalized (socialized) the means of production and central planning of the production and central planning of the economyeconomy
In the end the Bolsheviks destroyed the In the end the Bolsheviks destroyed the economy: mass starvation, decrease in economy: mass starvation, decrease in industrial outputindustrial output

War Communism War Communism ContinuedContinued
The The ChekaCheka (secret police) liquidated (secret police) liquidated about 250,000 opponentsabout 250,000 opponents
1921 1921 Kronstadt RebellionKronstadt Rebellion: Mutiny by : Mutiny by previously pro-Bolshevik sailors at the previously pro-Bolshevik sailors at the Kronstadt naval baseKronstadt naval base
Was crushed but caused by the Was crushed but caused by the economic disaster and social upheaval economic disaster and social upheaval of the civil warof the civil war

1921-1928 The NEP1921-1928 The NEP
The New Economic Policy attempted to The New Economic Policy attempted to eliminate the harsher aspects of war eliminate the harsher aspects of war communismcommunism
It was a response to economic ruin, peasant It was a response to economic ruin, peasant revolts, and military mutinyrevolts, and military mutiny
It allowed for some capitalist measuresIt allowed for some capitalist measures Called Called a necessary step backwarda necessary step backward by Lenin by Lenin

NEPNEP
Government would no longer seize Government would no longer seize surplus grainsurplus grain
Peasants could sell it on the open marketPeasants could sell it on the open market Small manufacturers could run their own Small manufacturers could run their own
businessesbusinesses Government still controlled heavy Government still controlled heavy
industry, banks, and railroadsindustry, banks, and railroads Results of the NEP: Some economic Results of the NEP: Some economic
improvementimprovement

Results of the NEPResults of the NEP
Economy back to pre-war levelsEconomy back to pre-war levels Workers enjoyed shorter hours and Workers enjoyed shorter hours and
better working conditionsbetter working conditions Temporary relaxation of censorship Temporary relaxation of censorship
and terrorand terror
1923 Russia was renamed the Soviet 1923 Russia was renamed the Soviet Union…..The Union of Soviet Socialist Union…..The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics….USSRRepublics….USSR

Lenin died in 1924Lenin died in 1924
He had not chosen a successorHe had not chosen a successor StalinStalin: a realist: a realist Believed in “Socialism in one country”Believed in “Socialism in one country” Wait until Russia was strong…THEN Wait until Russia was strong…THEN
an international communist movementan international communist movement Wanted to establish a socialist Wanted to establish a socialist
economy without the aid of the Westeconomy without the aid of the West

TrotskyTrotsky
Also wanted controlAlso wanted control Was more of a MarxistWas more of a Marxist Believed in the continuation of a world Believed in the continuation of a world
communist revolutioncommunist revolution Party leaders believed Trotsky was too Party leaders believed Trotsky was too
much of an idealist and supported much of an idealist and supported StalinStalin
Stalin gained control by 1927Stalin gained control by 1927 Trotsky was exiled and assassinated Trotsky was exiled and assassinated
(1940 Mexico) by Stalin’s agents(1940 Mexico) by Stalin’s agents

The Soviet Union Under The Soviet Union Under StalinStalin
Lenin’s Politburo was purgedLenin’s Politburo was purged Lenin’s NEP was scrappedLenin’s NEP was scrapped 1928 The First 5-Year Plan1928 The First 5-Year Plan Objectives: Objectives:
Increase industrial output by 250%Increase industrial output by 250% Increase steel production by 300%Increase steel production by 300% Increase agricultural output by 150%Increase agricultural output by 150%

The First 5-Year Plan’s The First 5-Year Plan’s ResultsResults
Steel Production up 400%Steel Production up 400% USSR the 2USSR the 2ndnd largest steel producer in largest steel producer in
EuropeEurope Oil production up 300%Oil production up 300% Massive urbanizationMassive urbanization 25 million moved to the cities25 million moved to the cities BUT standard of living did not improveBUT standard of living did not improve AND quality of goods was substandardAND quality of goods was substandard

StalinStalin
Said, “We are 50 or 100 years behind Said, “We are 50 or 100 years behind the advanced countries. We must make the advanced countries. We must make good this distance in 10 years. Either good this distance in 10 years. Either we do it or we shall go under.”we do it or we shall go under.”
Under 1Under 1stst 5-Year Plan 20% of peasants 5-Year Plan 20% of peasants were scheduled to give up their private were scheduled to give up their private plots and join collective farms.plots and join collective farms.

CollectivizationCollectivization
Purpose:Purpose: To bring the peasants under direct To bring the peasants under direct
control of the statecontrol of the state Machinery was used in agriculture Machinery was used in agriculture
to provide more workers for industryto provide more workers for industry Government control over productionGovernment control over production Extend socialism to the countrysideExtend socialism to the countryside

Collectivization Collectivization continuedcontinued
Individual peasant farms were Individual peasant farms were consolidated into large, state-consolidated into large, state-controlled farmscontrolled farms
Farmers were paid according to the Farmers were paid according to the amount of work they didamount of work they did
A portion of the harvest was taken by A portion of the harvest was taken by the government to feed urban workers the government to feed urban workers
Farmers had to meet grain quotas Farmers had to meet grain quotas before they could feed themselvesbefore they could feed themselves

Results of Results of CollectivizationCollectivization
Much opposition by the farmersMuch opposition by the farmers The Kulaks (wealthiest peasants) put up the The Kulaks (wealthiest peasants) put up the
greatest oppositiongreatest opposition Stalin ordered them liquidated…they wereStalin ordered them liquidated…they were 10 million died as a result of collectivization10 million died as a result of collectivization 7 million in forced starvation in the Ukraine7 million in forced starvation in the Ukraine Agricultural output: no improvement over Agricultural output: no improvement over
19131913 1933: 60% on collectives, 1938 was 93%1933: 60% on collectives, 1938 was 93%

Government Structure Government Structure under Stalinunder Stalin
General SecretaryGeneral Secretary was the highest was the highest position in government. This was position in government. This was Stalin’s titleStalin’s title
PolitburoPolitburo about 12 members. about 12 members. Discussed policy and personnelDiscussed policy and personnel
Central CommitteeCentral Committee: about 70 people : about 70 people in the 30’sin the 30’s

Stalin’s propaganda Stalin’s propaganda campaigncampaign
Purpose: To glorify work and Purpose: To glorify work and encourage productivityencourage productivity
Used technology for propaganda:Used technology for propaganda: Newspapers (Newspapers (The Pravda)The Pravda) Radio broadcastsRadio broadcasts Films (Sergi Eisenstein)Films (Sergi Eisenstein) All emphasized Soviet achievements All emphasized Soviet achievements
and capitalist plotsand capitalist plots

Stalin’s propaganda Stalin’s propaganda campaigncampaign
Writers and artists were expected to Writers and artists were expected to glorify Stalin and the stateglorify Stalin and the state
Their work was closely monitoredTheir work was closely monitored
Religions were persecutedReligions were persecuted Stalin hoped to turn churches into Stalin hoped to turn churches into
“museums of atheism”“museums of atheism”

Benefits for WorkersBenefits for Workers
Old age pensionsOld age pensions Free medical servicesFree medical services Free educationFree education Free day care for childrenFree day care for children Education was the key to the way upEducation was the key to the way up Mainly specialized skills and technological Mainly specialized skills and technological
educationeducation Disillusioned Westerners were attracted Disillusioned Westerners were attracted
to USSRto USSR

WomenWomen
Women were given complete equality with Women were given complete equality with the revolutionthe revolution
In 1920’s divorce and abortion readily In 1920’s divorce and abortion readily availableavailable
The state encouraged women to work The state encouraged women to work outside of the home and to “liberate” outside of the home and to “liberate” themselvesthemselves
Rapid change led to broken familiesRapid change led to broken families Men still got the best jobsMen still got the best jobs Women still stuck with household dutiesWomen still stuck with household duties

The Great Terror 1934-The Great Terror 1934-19381938
Terror was used on peasants, leading Terror was used on peasants, leading communists, & ordinary people often for communists, & ordinary people often for no apparent reasonno apparent reason
The “Great Terror” resulted in 8 million The “Great Terror” resulted in 8 million arrestsarrests
““Show Trials” usually of ex-party Show Trials” usually of ex-party members to eradicate “enemies of the members to eradicate “enemies of the people”people”
Late 1930’s the Old Bolsheviks (followers Late 1930’s the Old Bolsheviks (followers of Lenin) were tried and executedof Lenin) were tried and executed

PurgesPurges
40,000 army officers were expelled 40,000 army officers were expelled or liquidatedor liquidated
This hurt Russia badly in WWIIThis hurt Russia badly in WWII
Millions were killed or disappeared Millions were killed or disappeared or sent to forced labor camps called or sent to forced labor camps called GulagsGulags