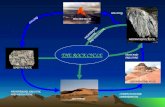
TOPIC 4: WEATHERING, EROSION AND DEPOSITION Weathering.
-
Upload
shavonne-freeman -
Category
Documents
-
view
252 -
download
3
Transcript of TOPIC 4: WEATHERING, EROSION AND DEPOSITION Weathering.

TOPIC 4: WEATHERING, EROSION AND DEPOSITION
Weathering

EROSION

DEPOSITION

Weathering:
PART 1: WEATHERING
The breakdown of rocks, either chemically or physically.

Physical Weathering:The breakdown of rock into smaller pieces
PHYSICAL WEATHERING
Dominant type of Weathering in Cold, Dampclimates

1. Frost Action
EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL WEATHERING
At temperatures below freezing, water trapped in cracks expands, enlarging cracks, eventually breaking rocks.Many cycles of freezing and thawing will cause rock to crumble

2: Plant Action:Roots of plants grow into cracks, widening cracks and eventually breaking rock apart.
EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL WEATHERING

2: Plant Action
EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL WEATHERING
Often begins with lichens

EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL WEATHERING
3: Pressure Unloading:Earthquakes, erosion, and landslides cause overlying material to be removed from rock, allowing the rock to split along lines of weakness.

Pressure Unloading
EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL WEATHERING

Chemical Weathering: The breakdown of rock by changing the minerals the rock is made of. The chemical composition of the rock is changed.
Dominant type of weathering in warm and moist climates.
CHEMICAL WEATHERING

CHEMICAL WEATHERING

Oxidation:Chemical weathering where oxygen from the air combines with elements to form new compounds.Example: Rust = Iron + Oxygen
CHEMICAL WEATHERING

Carbonation:Carbon dioxide combines with WATER to form Carbonic Acid.
This acid easily dissolves limestone and marble.
This is how caves and sinkholes form.
CHEMICAL WEATHERING

CHEMICAL WEATHERING

CHEMICAL WEATHERING

Water is a major agent in both physical and chemical weathering .
WATER