Tidal Jeopardy !
description
Transcript of Tidal Jeopardy !

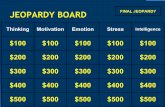
Tidal Jeopardy!

Tidal Jeopardy!Making Waves
Know Your Tides Tables
Wat-er Disaster!
Current Events
Ya Salty Dog
10 10 10 10 10
20 20 20 20 20
30 30 30 30 30
40 40 40 40 40
Final Jeopardy

What is a Wave?

A Wave is a movement of energy through a
body of water.
Back to Menu

What 3 factors influence the size of a wave?

The strength of the wind, the length of time the wind blows, and the distance the
wind blows across.
Back to Menu

Define 4 parts / characteristics of a wave.

1. Crest: highest point2. Trough: lowest point3. Wavelength: distance
between 2 crests / troughs4. Wave Height: distance from
crest to trough5. Frequency: number of waves
during a certain interval of time
Back to Menu

Explain what is happening to the wave at each point.

As the wave nears shore at B, the bottom of the wave slows as it scrapes the
ground. By the time it reaches C, the top crashes over the bottom - topples
Back to Menu
Final Jeopardy

Describe the two types of daily tides.

Back to Menu
High tide is when the water level is at its highest point.
Low tide the lowest point.

What causes tides, and how often does a tidal
cycle occur?

The gravity of the Moon & Sun cause tides. Tides occur every
12 hours and 25 minutes.
Back to Menu

What are Spring & Neap tides? How are the ‘planets’ aligned?

Spring tide is the greatest difference between high & low tide. Neap tide is the
smallest difference.
Back to Menu

Waves do not move water forward. Explain why,
and what happens when waves reach the shore.

Wind energy is transferred through the water. Near the shore, wave
height increases as length decreases, causing wave to break.
Back to Menu
Final Jeopardy

Two natural phenomena we have studied this chapter are...

Tsunamis and El Nino
Back to Menu

What causes a Tsunami and where does it occur?

An earthquake in the ocean floor.
Back to Menu

What is Upwelling and how does El Nino affect it?

Upwelling is when warm water is pushed away by wind and cold
water rises. El Nino brings more warm water, preventing upwelling.
Back to Menu

What is a Tsunami like in the open ocean compared to when it reaches shore? What causes this difference?

In the open ocean, tsunamis have a small wave height, but massive wavelength. On shore, the length rapidly decreases from
friction, causing the height to spike.
Back to Menu
Final Jeopardy

What are the 2 types of currents?

Surface currents and Deep currents.
Back to Menu

What causes a surface current? What is the strongest surface
current in the N. Atlantic Ocean?

Surface currents are driven by wind. The Gulf Stream.
Back to Menu

What kind of currents affect climate and how? What causes
the other kind of current?

Surface currents heat or cool air above them, affecting weather of land nearby. Deep currents are
caused by differences in density.

After spending some time in the ocean, you turn to go dry off… but everything is gone!
What happened?

Waves hitting the beach at an angle causes Longshore Drift.
Your stuff is up current.
Back to Menu
Final Jeopardy

What is Salinity?

The amount of dissolved salt in water.
Back to Menu

What is the average salinity in the ocean?

35 parts per thousand (35ppt).
Back to Menu

What two major effects does salinity have on
the properties of water?

Salinity increases the density of water and decreases the freezing
point (to -1.9⁰C).
Back to Menu

Rank the following locations based on where a ship will float highest in the water to lowest:
Pacific Ocean, at the mouth of a river, Arctic Ocean.

Arctic ocean – frozen water increases amount of salt left behindPacific ocean – has average salinityRiver mouth – supply of fresh water
lowers avg salinity.
Final Jeopardy
Back to Menu

What 4 properties of ocean water change with depth and how do they change as you go deeper?
603010

STOP

As depth increases…1. Temperature decreases2. Salinity increases3. Density increases (salty & cold)4. Pressure increases
Back to Menu