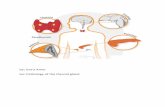
Thyroid Disease M. Alhashash MD 1. Anatomy Over Trachea Two Lobes connected together by an isthmus...
-
Upload
frederick-winland -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
1
Transcript of Thyroid Disease M. Alhashash MD 1. Anatomy Over Trachea Two Lobes connected together by an isthmus...
Arterial supply
• Superior thyroid artery• Inferior thyroid artery• Thyroida ima artery• Anastomosis with esophagus and trachea
5
Venous drainage
• Superior thyroid vein IJV• Middle thyroid vein IJV• Inferior thyroid vein innom. V.
6
Lymphatics
• Direct : Upper and lower deep cervical LN• Indirect : – Pretracheal LN– Paratracheal LN– Inferior and superior thyroid veins LN
7
Normal Physiology
• TSH stimulates secretion of T4 and T3 from thyroid• Most serum T3 produced by deiodination of T4• Think of T3 as active hormone and T4 as prohormone• Only small fraction total T4 and total T3 is unbound –
therefore free and active
10
TFTs
• TSH is the screening test of choice for thyroid function (nml 0.3-5mU/L)
• T4• T3• Antithyroglobulin (TSAb)
11
Evaluation of Thyroid Diseases
1. Clinical history and physical examination2. Serum T3 & T4, TSH determination3. Thyroid scan (RAIU)4. Thyroid ultrasound5. Plain x-ray, CT scan / MRI6. FNAC7. Sleeping pulse & laryngoscope.
12
THYROID GLAND DISORDERS
I. CONGENITALII. SIMPLE
A. Diffuse : 1-physiological 2- colloidB. Nodular 1-multinodular 2- solitary
III. Toxic A. PrimaryB. Secondary
IV. Neoplastic A. BenignB. Malignant.
V. Inflammatory 13
Answer the following questions:(time allowed 5 minutes)
A. Enumerate types of shock: 1. --------------2. ---------------3. ----------------4. ----------------
B. Define:1. Epistaxis: is………………………………………..2. Hemoptesis: is…………………………………...
Good luck.
Congenital anomalies 1• Agenesis------------ L-troxine • Ectopic (along the line of descent)– Lingual ----------at the foramen caecum , may be the only
thyroid tissue, causes yellow swelling, dysphagia and bleeding . Treatment : L-troxine , excision and reimblantation.
– Median ectopic ---------in the upper 2/3 of neck , can be the only thyroid tissue . Treatment excision and reimplantation.
• Aberrant(away from the line of descent)– Median (larynx, trachea, intrathoracic)– Lateral(obsolete term, in LNs= metastasis)
15
Congenital anomalies 2
• Anomalies of thyroglosal tract– Thyroglossal cyst– Thyroglossal fistula(sinus)
17
Simple goiter
• Def : non inflammatory , non toxic, non neoplastic enlargement of thyroid gland.
• Etiology : ch. Decrease of thyroid hormone or rarely pituitary adenoma.– Decrease I2– Decrease synthesis of hormones– Antithyroid drugs– Goitrogenic substances (cabbage, cauliflower)
18
Stress leads to dec. T3 & T4increase TSH physiological goiter.
I. Stress over --> normal gland II. Prolonged stress exhaustion of the gland
diffuse colloid goiter and after time nodular colloid goiter.
III. Stress repeated fibrosis simple multinodular goiter.
19
Treatment of simple goitre.
• Physiological L-troxine + I2 -> good response.• Colloid rarely respond• Nodular goiter never respond to medical
treatment.• Subtotal or total thyroidectomy followed by L-
troxine.
20