Thoracic and Abdominal Radiology - MemberClicks - Thoracic Abdomin...2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic...
Transcript of Thoracic and Abdominal Radiology - MemberClicks - Thoracic Abdomin...2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic...
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
1
Thoracic and Abdominal Radiology
Krikor G. Arman, II, MD
General Surgery, Trauma Surgery, Surgical Critical Care
Beaumont Grosse Pointe
Questions/Comments/Feedback: [email protected]
Disclosures
• None
• Images borrowed from Dr. Google
1
2
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
2
Outline and Goals
• Systematic approach to CXR interpretation and Thoracic pathology
• Systematic approach to AXR interpretation and Abdominal pathology
• Brief intro to CT interpretation
• Main Goal: Correlate clinically…
My two cents…
• Don’t order a study unless you know what you’re looking for, and if it will change your management
• Always look at images first before you read the radiologist interpretation
• Go over images with radiologist, surgeon, anyone who is willing to take the time
• Be a practitioner…
3
4
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
3
CXR: Systematic Approach
• Always start by confirming correct patient, study
• Look for prior studies to use for comparison
CXR: Systematic Approach
• Assess image quality with “RIPE”
• R: rotation
• I: inspiration
• P: positioning
• E: exposure
5
6
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
4
CXR: Systematic Approach
• R: rotation
• Clavicular heads equidistant from spinous processes
• Spinous processes centered on vertebrae
CXR: Systematic Approach
• I: Inspiration
• Would like to see at least 8 ribs, lung apices, costophrenic angles, and lateral rib margins
7
8
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
5
CXR: Systematic Approach
• P: projection/positioning
• AP vs PA
• Supine, upright
CXR: Systematic Approach
• E: exposure
• Look to see if the film is over- or under-exposed (ie: too bright or too dark)
• Should see the diaphragm behind the spine and the vertebrae behind the heart
9
10
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
6
CXR: Systematic Approach
• Interpretation: The ABCDE method
• A: airway
• B: breathing
• C: cardiac
• D: diaphragm
• E: everything else
CXR: Systematic Approach
• A: Airway
• Trachea should be midline (more or less)
• It can be pushed or pulled by different pathology
• Look at mainstem bronchi
• Right is shorter, wider and more vertical than left
• Look for carina to measure endotracheal tube (should be 2-6 cm above carina)
11
12
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
7
CXR: Systematic Approach
• B: breathing
• Look for lung markings in all fields
• Atelectasis
• Pulmonary edema
• ARDS
• Pneumonia
• Mucus plug/white out
• Pleural effusion, hemothorax
• Nodules/Tumors
“White out”
• Mucus plug
• Giant pleural effusion
• Large hemothorax
• Large mediastinal tumor
13
14
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
8
CXR: Systematic Approach
• C: cardiac
• Heart should be less than 50% of the total width of the chest on a PA image (will look bigger on AP)
• Heart borders:
• Right is the right atrium, left is the left ventricle
CXR: Systematic Approach
• D: diaphragm
• Right hemidiaphragm is higher than the left (usually)
• Look for sharp vs blunted costophrenic angles
• Look for gastric bubble on the left
• Look for free air
• Chilaiditi syndrome: colon superimposed over the liver, looks like free air
15
16
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
9
Diaphragm rupture
• Most commonly on the left…
CXR: Systematic Approach
• Everything else:
• Lines: Central line, pacemaker leads, PICC line, mediport
• Tubes: ETT, NGT, nasoenteric tube
• Mediastinum: widening, aortic knob, aortopulmonary window, artificial valves
• Hilar structures
• Bones: look for fractured clavicles/ribs, flail chest
17
18
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
10
NGT
Flail Chest
• Two fractures in three consecutive ribs
• Flail segment has paradoxical movement
• Pulmonary contusion
19
20
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
11
A
B B
CD D
E
E
Summary
Outline
• Systematic approach to CXR interpretation and Thoracic pathology
• Systematic approach to AXR interpretation and Abdominal pathology
• Brief intro to CT interpretation
21
22
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
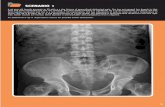
12
AXR: Systematic Approach
• Always start by confirming correct patient, study
• Look for prior studies to use for comparison
• Don’t order a study unless you know what you’re looking for, and if it will change your management
AXR: Systematic Approach
• Assess image quality
• P: positioning (supine, upright, lateral decubitus)
• E: exposure (make sure entire abdomen is included)
• Type of image
• 1 view (supine; “KUB”)
• 2 view (supine, upright)
• Acute abdominal series (CXR plus 2 view)
• 3 view (supine, upright, lateral decubitus)
23
24
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
13
AXR: Systematic Approach
• Decide which study to order based on what you’re looking for
• 1 view (supine): good for tubes, contrast progression, but not for free air or air-fluid levels
• 2 view: air-fluid levels, free air
• 3 view: gives an additional view for free air
AXR: Systematic Approach
• Interpretation: The BBC method
• B: bowels
• B: bones
• C: calcification/contrast/catheters
25
26
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
14
AXR: Systematic approach
• B: bowels
• 3-6-9 rule
• Small bowel 3cm
• Large bowel 6 cm
• Cecum 9cm
• Small intestine: plicae circulares; centrally located
• Large intestine: haustra; peripherally located; stool
AXR: Systematic approach
• Portal venous gas vs pneumobilia
• Portal venous gas: Peripheral
• Common bile duct gas: Central
27
28
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
15
AXR: Systematic approach
• B: bones
• Pelvis
• Ribs
• Vertebrae
AXR: Systematic approach
• C: calcifications, contrast, catheters
• Gallstones, renal stones
• Catheters, stents
• Piercings
• Vascular calcifications
• IV and oral contrast
• Surgical clips
29
30
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
16
Outline
• Systematic approach to CXR interpretation and Thoracic pathology
• Systematic approach to AXR interpretation and Abdominal pathology
• Brief intro to CT interpretation
CT Basics
• The convention of CT
• Slices the patient into multiple 3mm cuts
• Scout film
• Axial/Transverse Plane
• Coronal Plane
• Sagittal Plane
• Contrast
• Window levels
31
32
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
17
CT Basics
• You MUST know the anatomy in order to understand what you’re looking at
• Then you much be able to envision the anatomy in 3-D
• Solid organs are easier than intestine so start with those
CT Basics
• Axial/Transverse Plane
• Patient is laying down
• Head is behind the screen (away from you)
• Feet are in front of the screen (toward you)
• Right/Left anatomic position just like xray
33
34
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
18
CT Basics
• Coronal Plane
• “Corona” is Latin for “crown”
• Coronal suture in neonates
• Patient is standing
• Back is behind the screen
• Front is in front of the screen
• Right/Left anatomic just like xray
• Still 3mm cuts
CT Basics
• Sagittal Plane
• “Sagitta” is Latin for “arrow”
• Patient is standing
• One side is behind the screen
• The other side is in front of the screen
• Front is screen left, Back is screen right
• Still 3mm cuts
35
36
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
19
CT Basics
• Windows
• Default is ”abdomen”/soft tissue
• Choose based on what you’re looking for
• Lung, Bone, Brain, Liver, etc
CT Basics
• Contrast: Oral vs IV vs both vs neither
• For acute pathology, use both if possible, get more info
• Oral: definitely for obstruction, ileus, any process where you need to see the bowel
• Consider NGT if patient can’t tolerate PO
• IV: vasculature, inflammation, tumors
• Risk/benefit if AKI, contrast allergy, etc
• Neither: basic anatomy
• Abdominal wall hernias
37
38
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
20
CT Basics
• You must look at THOUSANDS of CT scans to get comfortable
• Always look at the images yourself before reading the report
• Scroll through quickly, then go back and focus on specific areas
Radiography: Systematic Approach
• Always look at the images before you read the radiologist’s interpretation
• Don’t order a study unless the result will change your management
• Use a systematic approach so that nothing is missed
• Continue to ask questions and keep learning
39
40
2019 PM Conference - Diagnostic Imaging
10/19/2019
21
Questions?
Thank you for your time!
Questions/Comments/Feedback: [email protected]
41