Long Term and Short Term Changes in Climate; The Albedo Effect.
This Class: Short-term climate change
-
Upload
ladonna-amaya -
Category
Documents
-
view
23 -
download
1
description
Transcript of This Class: Short-term climate change
This Class: Short-term climate change
• Climate – 30 year “average” weather conditions
• Short-term – over the last 1000 to 12,000 years
• Climate records
• Causes of climatic variation
• Past climate change
Records of climate
• Historical (human) records– instrumental– written observations
• maritime records
– paintings• 12,000 paintings• 1400-1967
Records of climate, cont.• Phenological observations
– agricultural records• price of rye in Germany
– bird migrations
Dendrochronology• dating of past events through study of tree
ring growth• thickness of the tree ring indicates growing
season conditions– precipitation
building a chronology
• overlapping rings from different trees• Bristlecone pine chronology is 9000 years
long– long lives - 4,767 years old
Lake and ocean sediments
• Sediments record environmental conditions present when they were deposited
Clues in the sediments
• pollen - vegetation type• skeletons of small
organisms - water chemistry, temperature
• type of organisms - windiness
• chemistry of sediments or organisms – temperature, precipitation
Signals in Elk Lake sediments
• diatoms - heavy, need wind to keep afloat = windy
• quartz - blown into the lake = windy
• sodium – retained in soils, not washed away = dry
• pollen - vegetation type
• 8,500 to 4000 years ago it was drier, prairie vegetation
slide/ calibration curve of 18O and SST in coral
Calibration curveo
xyg
en i
soto
pe tem
peratu
re (oC
)
two prolonged La Niña events
Oxy
gen
iso
top
e in
de
x
-5.3
-4.9
-4.5
-4.1
-3.7
1840 1860 1880 1900 1920 1940 1960 1980 2000
Period of instrumental data
Ice cores
• volcanic eruptions - ashes
• atmospheric gasses - small air bubbles
• temperature - oxygen isotopes
• windiness - dust
Some causes of climatic variation
• Ocean circulation
• Sunspots
• Volcanic eruptions
• Atmospheric conditions– El Nino Southern Oscillation
Sunspots
• Dark spots (cool areas) that move across the surface of the sun*
• Every 11 years there is a period called a “solar maximum” with lots of sunspots and solar flares
• Today’s sunspot number http://www.sunspotcycle.com/
*But these dark areas are surrounded by hotter rings that more than make up for the difference in radiation
Fewer sunspots seem to be associated with:
• lower temperatures
• more severe winters
• glacial advances
Volcanoes
• blast gasses (sulfur dioxide) and ash into the lower stratosphere.
• strong winds in stratosphere blow material around the world.
• sulfur dioxide combines with water to for sulfuric acid aerosols (fine droplets)
How does this affect climate?
Volcanoes, cont.
• scatters incoming radiation back to space• reduces heating of earth’s surface• last up to four years
El Niño – Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
• Oscillation of southern high and low pressure zones– Weakening of Peruvian high pressure zone
– Weakening of Indonesian low pressure zone
– Weakening of southeast trade winds
– Affects local climate
The Medieval Warm Period
• 1000 to 1300 AD• regional warming (not necessarily global)• Longer and warmer growing season
– grapes in England
• Higher treelines• Warmer sea surface temperatures in North
Atlantic• approx. 1o C warmer than present
The Little Ice Age
• Very cold climate between 1560 and 1890• Greater frequency of storms• Glacial advances 1560-1610,1816-1890
• Population declines in Iceland indicated by tax records
• shift from grains to barley (short growing season) to no grains
• fishing failed as fish migrated southward due to water temperatures.
• Height declines– from 5’8” in 900s to 5’6”
in 1700s in Iceland0
100000
1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000
barley no grain
Iceland populationIceland
Greenland
• 1300 highest population (3000)
• Poor harvests, fewer livestock
• Increase in sea ice decreased trade
• Settlements abandoned
• Height decrease from 5’7” to < 5’ by 1400
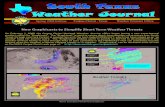
Based on temperature, precipitation, and tree ring records
• http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/paleo/drought/drght_pdsi.html
• http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/paleo/pdsiyear.html
Locations of tree rings•http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/paleo/pdsiyear.html
Many pictures of paintings, wheat prices, etc.• http://www2.sunysuffolk.edu/mandias/lia
/little_ice_age.html