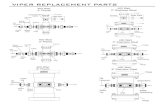
The Viper Main Interface Layout and interpretation.
-
Upload
amice-mcdonald -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of The Viper Main Interface Layout and interpretation.

The Viper Main InterfaceLayout and interpretation

The Viper Main InterfaceLayout and interpretation
Selectingpredictors and
predictands
Global month changes

The Viper Main InterfaceLayout and interpretation
Selectingpredictors and
predictands
Predictorsquality, availability
Global month changes
Historical statistics

The Viper Main InterfaceLayout and interpretation
Selectingpredictors and
predictands
Predictorsquality, availability
Forecast vs observed time series
Station availability, weights
Global month changes
Historical statistics

The Viper Main InterfaceLayout and interpretation
Selectingpredictors and
predictands
Predictorsquality, availability
Forecast vs observed time series
Station availability, weights
Fcst vs obsscatterplot
Helpervariable
Scatterplot/Forecast
progression
Global month changes
Historical statistics

The Viper Main InterfaceLayout and interpretation
Selectingpredictors and
predictands
Predictorsquality, availability
Probabilitybounds
Forecast vs observed time series
Station availability, weights
Fcst vs obsscatterplot
Helpervariable
Scatterplot/Forecast
progression
Settings
Global month changes
Historical statistics

The Viper Main InterfaceLayout and interpretation
Probabilitybounds
Forecast vs observed time series
Station availability, weights
Fcst vs obsscatterplot
Helpervariable
Scatterplot/Forecast
progression
Settings
Historical statistics
There’s more if you scroll right:Relate any variable to another

Selecting the predictand:Specify a type (e.g. Forecast point, snow, precipitation…)

Selecting the predictand:Specify a type (e.g. Forecast point, snow, precipitation…)Specify target station
Sorted by USGS ID, upstream to downstreamIf other than streamflow, ordered alphabetically

Selecting the predictand:Specify a type (e.g. Forecast point, snow, precipitation…)Specify target station
Sorted by USGS ID, upstream to downstreamIf other than streamflow, ordered alphabetically
Specify months“Jan “ : January of this year“Jan-1” : January of last year“Jan F” : 1st half of January (e.g. Jan 1, Jan1-15)“Jan L” : 2nd half of January (e.g. Jan 16, Jan 16-31)

Selecting the predictors:Is the station used or not? (checked = yes)

Selecting the predictors:Is the station used or not? (checked = yes)Station groups as defined on “station” sheet

Selecting the predictors:Is the station used or not? (checked = yes)Station groups as defined on “station” sheet
Clicking on a carat box sends you to the data sheet for that station. Experts may learn how to edit data once there.

Predictor quality, availability

Predictor quality, availability
Station number and status indicator (e.g. low skill, missing)Period of record correlation coefficient with predictand 1=good,0=badPredictor years (overlapping with target/ total)Realtime value as z-score (+1 high,-1 low) and % period of record normalRealtime forecast as if only one predictor was being used

Predictor quality, availability
Station number and status indicator (e.g. low skill, missing)Period of record correlation coefficient with predictand 1=good,0=badPredictor years (overlapping with target/ total)Realtime value as z-score (+1 high,-1 low) and % period of record normalRealtime forecast as if only one predictor was being used

Predictor quality, availability
Station number and status indicator (e.g. low skill, missing)Period of record correlation coefficient with predictand 1=good,0=badPredictor years (overlapping with target/ total)Realtime value as z-score (+1 high,-1 low) and % period of record normalRealtime forecast as if only one predictor was being used

Some data problems
Missing: Realtime data value is unavailableLow skill: The predictor is too poor to be considered (correlation too low)Short por: The predictor does not have enough years in common with the target

Group information
Correlation and predictions are represented by each station group. “All” is using all stations together. The bold yellow cell is the “bottom line” of the forecast (in k-ac-ft).

Historical statistics of target
POR – period of record (all years)71-00 – all available** years from 1971-2000(official 1971-2000 normal available to right)

1 Analysis type: Z-Score or PCA regression
2 Probability bound information: (gray is editable)Probability of exceedence (low probability = wet)Volume in thousands of acre-feetPercent of 1971-2000 normal
1
2

1 Analysis type: Z-Score or PCA regression
2 Probability bound information: (gray is editable)Probability of exceedence (low probability = wet)Volume in thousands of acre-feetPercent of 1971-2000 normal
3 Skill statistics: Correlation^2, Standard Error, Standard Error Skill Score Including all years or jackknifed (leave 1 year out at a time)
4. Official 1971-2000 normal
1
2
34

Forecast (blue) versus observed (red) time series and historical forecasts (green)

Forecast (blue) versus observed (red) time series and historical forecasts (green)

Forecast (blue) versus observed (red) time series and historical forecasts (green)
“Forecast” is the calibration set of forecasting equation you set up“Historical forecast” is historical published outlook, issued back in the day
Leadtime of historical forecast is specified in cell O46 “Publication Date”

Station weighting time series
For each year, what is the relative contribution of skill (R^2) from each station?Taller means more skillful information
Example: 1 station… Contributes 100% of skill in all years
R^2 = .33

Station weighting time series
For each year, what is the relative contribution of skill (R^2) from each station?Taller means more skillful information
Example: 1 station… Contributes 100% of skill in all years3 stations… 1 long, medium and short record
These are the weights used in Z-Score regression. Not used in PCA, but shown anyway.
(Gets more complicated with multiple groups, but idea the same)
R^2 = .44
.33
R^2 = .77

Forecast vs observed scatter plotGray lines show exceedence probabilitiesRed dot shows current forecast“Toggle graph” identifies individual years

Helper predictand (x) vs original target (y)Appears blank if helper not usedIn this example, AWDB vs USGS data shown
“Switch” brings you to a plot of forecast vs leadtime
Helper
Pre
dict
and
Equation output
Published forecasts

1
2
34
1 Do non-linear regression by transforming predictand (e.g. square root)2 Limit the start and end year of the analysis3 Acquire predictand flow data from AWDB or USGS4 Publication date of forecast (changes each month)

1
2
34
5
6
1 Do non-linear regression by transforming predictand (e.g. square root)2 Limit the start and end year of the analysis3 Acquire predictand flow data from AWDB or USGS4 Publication date of forecast (changes each month)5 Buttons to view additional predictors, advanced settings, helper6 Number of principal components retained and % variance explained

“Original” = Value stored in recent data sheet
“Estimated” = What you might expect given the other variable
“O-E” = Original-Estimated
Scroll right onmain interface