the urinary system
-
Upload
irene-sabater-valdez -
Category
Documents
-
view
4 -
download
1
description
Transcript of the urinary system
-
Urinary SystemHSC 1531 Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professionals Florida State College of Jacksonville Professor: Michael L. Whitchurch, MHS
-
Urinary System at a glance
KidneysUretersBladderUrethraA purification system for the bloodMaintains fluid, electrolyte and pH balance and removes toxins
-
Urinary System at a GlanceFunctions of Urinary SystemMaintain stable internal environmentRemove waste productsAdjust water and electrolyte levelsMaintain correct pH
-
Urinary System at a GlanceOrgans of Urinary SystemTwo kidneysTwo uretersOne urinary bladderOne urethra
-
Urinary System Combining Formsazot/onitrogenous wastebacteri/obacteriacyst/obladderglomerul/oglomerulusglycos/osugar, glucoseketon/oketones
-
Urinary System Combining Formslith/ostonemeat/omeatusnephr/okidneynoct/inightolig/oscantypyel/orenal pelvis
-
Urinary System Combining Formsren/okidneyur/ourineureter/oureterurethr/ourethraurin/ourinevesic/obladder
-
Urinary System Suffixes-lithstone-lithiasiscondition of stones-ptosisdrooping-tripsysurgical crushing-uriacondition of the urine
-
Anatomy and PhysiologyAlso called genitourinary systemConsists ofTwo kidneysTwo uretersOne urinary bladderOne urethra
-
Click here to view an animation of the urinary system. Urinary System Animation
-
FunctionMain function is to filter and remove waste products from bloodMetabolic processes produce wasteBlood becomes toxic if waste builds upWaste materials are called urineUrine is then removed from body
-
Homeostasis Responsible for homeostasis Maintain proper balance of water and chemicals in bodyRegulate levels of electrolytesSodiumPotassiumChlorideBicarbonateMaintain pH
-
Waste RemovalWaste is removed through system of blood vessels and tubulesCalled the nephronMore than 1 million make up each kidneyProduce urineUrine drains from kidney through ureters to bladder, into urethra, and then out of body
-
http://www.unckidneycenter.org/images/glomerulus.jpghttp://www.unckidneycenter.org/images/glomerulus.jpg
-
KidneysLocated behind peritoneumRetroperitonealConcave area on edge of center called hilumRenal artery entersRenal vein leavesUreter leaveshttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wJ1G4UW4RwI
-
Figure 9.1 Kidney structure. Longitudinal section showing the renal artery entering and the renal vein and ureter exiting at the hilum of the kidney.
-
Internal Structure of KidneysCortexOuter portionMedullaInner portionPyramidsTriangular shaped structures in medullaPapillaTip of each renal pyramid
-
Figure 9.2 Longitudinal section of a kidney illustrating the internal structures.
-
Internal Structures of the KidneysCalyxSmall open area that receives urine from each papillaRenal pelvisLarge open area that receives urine from each calyx Empties into ureter
-
Figure 9.2 Longitudinal section of a kidney illustrating the internal structures.Figure 9.2 Longitudinal section of a kidney illustrating the internal structures.
-
Nephron
-
NephronFunctional unit of kidneyMicroscopicMore than 1 million nephrons in each kidneyConsists ofRenal corpuscleRenal tubules
-
Renal CorpuscleTwo parts:Glomerulus Glomerular or Bowmans capsuleBlood flows through glomerulusSubstances filtered from blood and enter glomerular capsuleNephron Consists ofRenal corpuscleRenal tubules
-
renal blood flowKidney Animation
-
Renal TubulesFour sections:Proximal convoluted tubuleLoop of HenleDistal convoluted tubuleCollecting tubuleFiltrate flows through renal tubules to complete urine production processNephron Consists ofRenal corpuscleRenal tubules
-
The structure of a nephron.
-
Click here to review kidney internal structures in a labeling activity.Kidney Labeling Exercise
-
3 Stages of Urine ProductionUrine is produced as filtrate moves through renal tubulesThree stages:FiltrationReabsorptionSecretion
-
FiltrationBetween glomerulus and Bowmans capsuleFiltrate is producedWaterGlucoseAmino acidsWastes Filtrate enters renal tubulesThree stages:FiltrationReabsorptionSecretion
-
ReabsorptionAs filtrate moves through renal tubulesWater & desirable molecules are reabsorbed Returned to blood in peritubular capillariesWaste & undesirable molecules remain in renal tubulesThree stages:FiltrationReabsorptionSecretion
-
SecretionAs filtrate moves through renal tubulesAdditional waste products removed from blood in peritubular capillariesAdded to filtrate in renal tubulesThree stages:FiltrationReabsorptionSecretion
-
The three stages of urine production: filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
-
Ureters Urine drains from renal pelvis into uretersExtend from renal pelvis to urinary bladderLined with mucous membranes
-
Figure 9.4 The ureters extend from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
-
Urinary BladderElastic muscular sacSmooth muscle tissueLined with mucous membraneFolded into rugaeLies in base of pelvisBehind pubic symphysis
-
The structure of the urinary bladder.
-
Urinary BladderReceives urine from uretersStores urineHolds 250 mL of urineExcretes through urethraInvoluntary muscle action causes:Bladder to contractInternal sphincter to relaxVoluntary muscles control external sphincter
-
Urinary Bladder
-
Urethra Tubular canal lined with mucous membrane1 inches long in females8 inches long in males Carries urine from bladder to outside of bodyExternal opening is called urinary meatusReleasing urine from body is calledMicturitionVoidingUrination
-
The male urethra extends from the urinary bladder in the floor of the pelvis through the penis to the urinary meatus.
-
The much shorter female urethra extends from the urinary bladder to the floor of the pelvis and exits just in front of the vaginal opening.
-
UrineNormally straw colored to clear95% waterContains:Excess waterExcess electrolytes ToxinsNitrogen wastesNormal 24-hour output 1,000 to 2,000 mLAcidic, specific gravity varies1:001 to 1:030
-
Word Building with cyst/o
algiacystalgiabladder painectomycystectomyexcision of bladdergramcystogramrecord of bladdericcysticpertaining to bladderitiscystitisbladder inflammationlithcystolithbladder stone
-
Word Building with cyst/o
ostomycystostomynew opening in bladderotomycystotomyincision into bladderpexycystopexysurgical fixation of bladderplastycystoplastysurgical repair of bladderrrhagiacystorrhagiarapid bleeding from bladderscopecystoscopeinstrument to examine inside bladder
-
Word Building with lith/o
tripsylithotripsysurgical crushing of stoneotomylithotomyincision to remove stone
-
Word Building with nephr/o
ectomynephrectomyremoval of kidneygramnephrogramrecord of kidneyitisnephritisinflammation of kidneylithnephrolithkidney stonelogistnephrologistkidney specialistmalacianephromalaciakidney softening
-
Word Building with nephr/o
megalynephromegalykidney enlargementomanephromakidney tumorosisnephrosisabnormal condition of the kidneyptosisnephroptosisdrooping kidneyostomynephrostomynew opening into kidney
-
Word Building with nephr/o
otomynephrotomyincision into kidneypathynephropathykidney diseasepexynephropexysurgical fixation of kidneylithiasisnephrolithiasiscondition of kidney stonesclerosisnephrosclerosiskidney hardening
-
Word Building with pyel/o
grampyelogramrecord of renal pelvisitispyelitisinflammation of renal pelvisplastypyeloplastysurgical repair of renal pelvis
-
Word Building with ren/o and ur/o
logisturologisturine specialistemiauremiaurine blood condition
alrenalpertaining to the kidney
-
Word Building with ureter/o
alureteralpertaining to ureterectasisureterectasisureter dilationlithureterolithureter stonestenosisureterostenosisnarrowing of ureter
-
Word Building with urethr/o
alurethralpertaining to urethraalgiaurethralgiaurethra painitisurethritisinflammation of urethrarrhagiaurethrorrhagiarapid bleeding from urethrascopeurethroscopeinstrument to view inside urethrastenosisurethrostenosisnarrowing of urethra
-
Word Building with urin/o
meterurinometerinstrument to measure urinearyurinarypertaining to urine
-
Word Building with uria
ananuriacondition of no urinebacteri/obacteriuriabacteria in the urinedysdysuriadifficult or painful urinationglycos/oglycosuriasugar in the urinehemat/ohematuriablood in the urineketon/oketonuriaketones in the urine
-
Word Building with uria
noct/inocturianighttime urinationolig/ooliguriascanty urinationpolypolyuriafrequent urinationproteinproteinuriaprotein in the urinepy/opyuriapus in the urine
-
Urinary System Vocabulary
anuriacomplete lack of urine production and lack of urine excretionazotemianitrogenous waste in the bloodstreamcalculusstone formed within an organ from mineral saltscatheterflexible tube inserted into the body; commonly through urethra into bladder diuresisincreased formation and secretion of urineenuresisinvoluntary discharge of urine; also called bed-wetting at night
-
Sectioned kidney specimen illustrating extensive renal calculi.(Dr. E. Walker/Science Photo Library/Photo Researchers, Inc.)
-
Healthcare worker draining urine from a bladder catheter bag.
-
Urinary System Vocabulary
frequencygreater urge to urinate; no increase in total volume of urinehesitancydecrease in force of urine stream, often with difficulty initiating the flowmicturitionanother term for urinationnephrologydiagnosis and treatment of diseases and conditions of the kidneyrenal colicpain caused by a kidney stonestricturenarrowing of a passageway in the urinary system
-
Urinary System Vocabulary
uremiaaccumulation of waste products in the bloodstreamurgencyfeeling the need to urinate immediatelyurinary incontinenceinvoluntary release of urineurinary retentioninability to fully empty the bladderurologydiagnosis and treatment of diseases and conditions of the urinary systemvoidinganother term for urination
-
Kidney Pathology
acute tubular necrosis(ATN)damage to renal tubules due to toxins in the urine; results in oliguriadiabetic nephropathydamage to glomerular capillaries due to high blood sugar of diabetes mellitusglomerulonephritisinflammation of the kidney; more permeable to protein and blood cellshydronephrosisdistention of renal pelvis due to accumulation of urine in the kidney
-
Kidney Pathology
nephrolithiasispresence of calculi in the kidney; solidification of salts in the urinenephrotic syndrome(NS)damage to glomerulus; protein appears in the urinenephroptosisdownward displacement of the kidney; floating kidneypolycystic kidneysformation of multiple cysts within the kidney; destroys normal kidney tissue
-
Kidney Stone VideoClick here to view a video on the topic of kidney stones.
-
Figure 9.10 A polycystic kidney on the left compared to a normal kidney on the right.
-
Kidney Pathology
pyelonephritisinflammation of renal pelvis and kidney; common type of kidney diseaserenal cell carcinomacancerous tumor of renal tubule cellsrenal failureinability of kidneys to filter wastes; results in uremiaWilms tumormalignant kidney tumor; most often found in children
-
Click here to view a video on renal failure.Renal Failure Video
-
Urinary Bladder Pathology
bladder cancercancerous tumor arising from cells lining bladder; symptom is hematuriabladder neck obstruction(BNO)blockage of bladder outlet; often caused by enlarged prostate glandcystoceleprotrusion of the urinary bladder into wall of vagina
-
Urinary Bladder Pathology
interstitial cystitisinflammation and irritation of bladderneurogenic bladderloss of nervous control; leads to retentionurinary tract infection(UTI)infection of any organ of urinary system; usually from bacteria; begins with cystitis and may ascend into ureters and kidneys
-
Clinical Laboratory Tests
blood urea nitrogen(BUN)blood test to evaluate kidney function by measuring level of nitrogenous waste (urea) in the bloodstreamclean catch specimen (CC)urine sample obtained after cleaning off the urinary meatus and collecting sample in midstreamcreatinine clearancetest of kidney function; amount of creatinine in bloodstream is compared to amount in the urine
-
Clinical Laboratory Tests
urinalysis(U/A, UA)physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urineurine culture & sensitivity(C&S)test for bacterial infection; attempt to grow bacteria on a culture medium in order to identify it; then determine which antibiotics it is sensitive to
-
Click here to view a video on urinalysis.Urinalysis Video
-
Diagnostic Imaging
cystographycontrast dye is placed in bladder and then X-ray is taken; outlines bladder excretory urography(EU)dye is injected into bloodstream; X-ray traces the dye as it moves through organs of the urinary systemintravenous pyelogram(IVP)injecting a dye into a vein and then taking an X-ray to outline the renal pelvis
-
Diagnostic Imaging
kidneys, ureters, bladder (KUB)abdominal X-ray showing the kidneys, ureters, and bladder; does not use dyeretrograde pyelogram (RP)dye is inserted through the urethra to outline the bladder, ureters, and renal pelvisvoiding cystourethrography (VCUG)dye is placed in the bladder; X-ray taken to visualize the urethra while patient is voiding
-
Color enhanced retrograde pyelogram X-ray. Radiopaque dye outlines urinary bladder, ureters, and renal pelves. (Clinique Ste. Catherine/CNRI/Science Photo Library/Photo Researchers, Inc.)
-
Endoscopic Procedures
cystoscopy(cysto)visual examination of the urinary bladder using a cystoscope
-
Medical Treatments
catheterization (cath)insertion of a tube through urethra and into the urinary bladderextracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy (ESWL)use of ultrasound waves to break up renal calculihemodialysis (HD)use of artificial kidney machine to filter the bloodperitoneal dialysisremoves wastes using chemically balanced solutions placed into peritoneal cavity
-
Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy, a non-invasive procedure using high frequency sound waves to shatter kidney stones.
-
Patient undergoing hemodialysis. Patients blood passes through hemodialysis machine for cleansing.
-
Figure 9.14 Peritoneal dialysis. Chemically balanced solution is placed into the abdominal cavity to draw impurities out of the bloodstream. It is removed after several hours.
-
Click here to view a video on peritoneal dialysis.Peritoneal Dialysis Video
-
Surgical Treatments
lithotripsycrushing a stone in the bladder or urethrameatotomyincision into the meatusnephrolithotomyincision to directly remove stones from the kidneyrenal transplantsurgical placement of a donor kidney
-
Figure illustrates location utilized for implantation of donor kidney.
-
Urinary System Pharmacology
antibiotictreats bacterial infectionsCipro, Macrobidantispasmodicprevent or reduce bladder muscle spasmsDitropan, Prostigminediureticsincreases volume of urineLasix, Aldactone
-
Urinary System Abbreviations
AGNacute glomerulonephritisARFacute renal failureATNacute tubular necrosisBNObladder neck obstructionBUNblood urea nitrogencathcatheterization
-
Urinary System Abbreviations
ClchlorideCRFchronic renal failureC&Sculture and sensitivityCAPDcontinuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysisCCclean catch urine specimencystocystoscopyESRDend-stage renal disease
-
Urinary System Abbreviations
ESWLextracorporeal shockwave lithotripsyEUexcretory urographyGUgenitourinaryHCO3bicarbonateHDhemodialysisH2OwaterI&Oinput and output
-
Urinary System Abbreviations
IPDintermittent peritoneal dialysisIVPintravenous pyelogramK+potassiumKUBkidney, ureter, bladdermLmilliliterNa+sodiumNSnephrotic syndrome
-
Urinary System Abbreviations
pHacidity or alkalinity RPretrograde pyelogramSG, sp.gr.specific gravityU/A, UAurinalysisUCurine cultureUTIurinary tract infectionVCUGvoiding cystourethrography
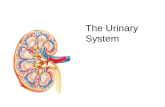
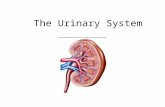
**The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra.. Take care in not confusing the two terms ureter and urethra.
This system can be thought of as a kind of purification system for the blood in the bodies circulatory system.. The urinary system also functions to maintain fluid, electrolytes and pH balance and remove toxins from the blood in the body.
Next slide..**************************************************************************************