THE SKULL
description
Transcript of THE SKULL
-
The SkullEhab ZAYYAN, MD, PhD
-
The skull is composed of separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures.
Sutural ligaments: between the bones TMJ: the only mobile joint in the skull Skull bones: external and internal tables of
compact bone separated by spongy bone called diplo
Outer and inner periosteum
-
Anatomical positionFrankfort horizontal plane
The cranium is in the anatomical position when the inferior margin of the orbit and the superior margin of the external acoustic meatus lie in the same horizontal orbitomeatal or Frankfort horizontal plane, a standard craniometric reference
-
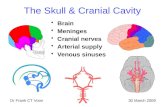
Cranium (Skull)
1. Neurocraniuma) Clavariab) Cranial base
2. Viscerocranium (face bones)
Total : 22 bones
-
NeurocraniumFormed from the mesenchyme of the neural
crest
Clavaria and skull base (basocranium)
Frontal bone 1
Parietal bones 2
Occipital bone 1
Temporal bones 2
Sphenoid bone 1 Ethmoid
bone 1
-
Frontal
-
Clavaria
Frontal Parietal Occipital Temporal
-
Skull base
Occipital Temporal Sphenoid Ethmoid
-
Frontal Parietal Occipital Temporal Sphenoid Ethmoid
-
Frontal Ethmoid Sphenoid Temporal Occipital Parietal
-
Viscerocranium(Facial skeleton)
Develop from the embryonic mesenchymeof the pharyngeal arches
Consists of the bones surrounding the mouth (upper and lower jaws), nose/nasal cavity, and most of the orbits (eye sockets or orbital cavities)
-
Facial bones (viscerocranium)
1Mandible
2Inferior conchae
2Palatine bones
1Vomer
2Lacrimal bones
2Nasal bones
2Maxillae
2Zygomatic bones
-
Maxilla Mandible Zygoma Nasalis Lacrimal
-
Maxilla Mandible Zygoma Nasalis Lacrimal
-
Maxilla Palatine Zygoma Ethmoid
and vomer
-
Mid- sagittal sectionmedial nasal wall
Ethmoid Vomer Maxilla Palatine Nasalis
-
Lateral nasal wall
Nasalis, maxilla, ethmoid, inferior concha, palatine
-
The maxillae contribute the greatest part of the upper facial skeleton, forming the skeleton of the upper jaw, which is fixed to the cranial base.
The mandible forms the skeleton of the lower jaw, which is movable because it articulates with the cranial base at the temporomandibular joints (TMJs).
-
Pneumatized bones of the skull
Several bones of the cranium are pneumatized bones, which contain air spaces (air cells or larger sinuses), presumably to decrease their weight. The total volume of the air spaces in these bones increases with age.
Frontal Ethmoid Sphenoid Maxilla Temporal
-
Paranasal sinuses
-
Paranasal sinuses x-ray
-
Pneumatization of the temporal bone
-
Geometric points of the skull
-
Pterion (G. wing): Junction of the greater wing of the sphenoid, squamous temporal, frontal, and parietal bones; overlies course of anterior division of middle meningeal artery
Lambda (G. the letter L): Point on calvaria at junction of lambdoid and sagittal sutures
Bregma (G. forepart of head): Point on calvaria at junction of coronal and sagittal sutures
Vertex (L. whirl, whorl): Superior point of neurocranium, in the middle with the cranium oriented in anatomical (orbitomeatal or Frankfort) plane
-
Asterion (G. asterios, starry): Star shaped; located at junction of three sutures: parietomastoid, occipitomastoid, and lambdoid
Glabella (L. smooth, hairless): Smooth prominence; most marked in males; on the frontal bones superior to root of nose; most anterior projecting part of forehead
Inion (G. back of head): Most prominent point of external occipital protuberance
Nasion (L. nose): Point on cranium where frontonasal and internasal sutures meet
-
Frontal bone
-
Frontal sinuses
-
Parietal bones
-
Parietal bone internal surface
-
Occipital bone
-
Occipital bone internal surface
-
Temporal bone
1. Squamous
2. Mastoid
3. Petrous
4. Styloid
5. Tympanic
-
Adult skull
-
Neonatal skull
At birth the mastoid process and the bony external canal of the tympanic part are absent.
-
Neonatal temporal bone
Squamous part Petrous part Tympanic part
-
Nasal bones
Anterior nasal aperture
-
Zygomatic bone
Cheeks prominence Orbital cavities Zygomatic arch Zygomaticofacial& zygomaticotemporalnerve foraminae
-
Maxilla Upper jaw - anterior
part of hard palate -lateral wall of nasal cavity - floor of orbital cavities
Intermaxillarysuture
Infraorbital foramen Alveolar processes Ant nasal spine Maxillary sinus
-
Palatine bones
-
Vomer
-
Vomer, medial nasal wall
-
Bony nasal septum Maxillary crest Vomer Perpendicular plate of the ethmoid
-
Medial nasal wall
-
Superior and middle nasal conchae: parts of the ethmoid bone
Inferior nasal concha is a separate bone
Inferior concha, lateral nasal wall
-
Lateral nasal wall
-
Paranasal sinuses
-
Paranasal sinuses x-ray
-
The mandible
Condyle Coronoid process Ramus Body Alveolar process Mental
protuberance Angle
-
Body of the mandible
Lateral surface Symphysis menti Mental foramen
mental nerve and vessels
-
Medial surface
Mental spines
genioglossus and geniohyoid
Mylohyoid line Submandibular
fossa Sublingual fossa Digastric fossa
-
Ramus of the mandible
Coronoid process Condyloid process (head) Neck Mandibular notch Masseter muscle attachment
-
Mandibular foramen
inferior alveolar nerve and vessels
mandibular canal
mental foramen Lingula : attachment of sphenomandibular
ligament
-
Anterior view of the skull
Frontal bone Superciliary arches Supraorbital notch Articulation with
maxillae, nasal bones, zygomaticbones
-
Anterior view of the skull
-
Orbital margins Sup: frontal bones Lat: zygomatic bones Inf: maxillae Medial: maxillae and frontal bones
-
Nasal bones and anterior nasal aperture
-
Maxilla
Intermaxillarysuture
Infraorbital foramen Alveolar processes Ant nasal spine Canine fossa
-
Zygomatic bone
Cheeks prominence Orbital cavities Zygomatic arch Zygomaticofacial& zygomaticotemporalnerve foraminae
-
The mandible
-
Lateral view of the skull
Coronal suture: frontal and parietal bones Sagittal suture: two parietal bones Lambdoid suture: parietal and occiptal bones
-
Frontal bone Parietal bone Occipital bone-
squamous part Temporal bone:
squamous-tympanic-mastoid- styloid-zygomaticprocess
Greater wing of sphenoid
-
Pterion The thinnest part of
the lateral wall of the skull
Anterioinferior corner of the parietal bone-greater wing of sphenoid bone
Overlies the anterior division of the middle meningeal artery and vein.
-
Superior and inferior temporal lines Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygomaxillary fissure
-
Infratemporal fossa
-
Pterygopalatine fossa
A small space behind and below the orbital cavity
Pterygomaxillary fissure
infratemporal fossa (laterally)
Sphenoplatine foramen
nasal cavity (medially)
Foramen rotundum
skull (superiorly) Inferior orbital fissure
orbit (anteriorly)
-
Posterior view of the skull
Sagittal suture Lambdoid suture Parietomastoid
suture External occipital
protuberence: attachment to muscles and nuchal ligament
Superior nuchallines
-
Superior view of the skull
Coronal suture Sagittal suture Lambdoid suture
-
Inferior view of the skull
-
Inferior view of the skull- Palate
Hard palate Palatal processes of the maxilla Horisontal plates of palatine bones Incisive fossa and foramen Greater and lesser palatine foramina Choanae (posterior nasal apertures) Vomer
-
Inferior view of the skull- Sphenoid
Medial pterygoid plates Pterygoid hamulus Lateral pterygoid plates Foramen ovale Foramen spinosum
-
Temporal Auditory tube: in the
interval between the greater wing of the sphenoid and the petrous part of the temporal bone
-
Foramen lacerum
Medial end of petrouspart of the temporal -basilar part of the occipital - greater wing of sphenoid.
During life it is closed with fibrous tissue. Few small vessels pass thru it. GSPN may pass too.
-
Zygomaticprocess
Articular tubercle Mandibular fossa Petrotympanic
fissure: separates the mandibular fossa from the tympanic plate. The chordatympani nerveexists from it
-
Carotid canal Jugular foramen Styloid process Stylomastoid foramen External acoustic meatus
-
Suprameatal crest
Suprameatal triangle (Mcewen triangle)
Suprameatal spine (spine of Henle)
-
Occipital Jugular foramen: notch on the petroustemporal and notch on the occipital bones.
Foramen magnum Basilar part of the
occipital bone Pharyngeal tubercle Occiptal condyles:
articulate with atlas The occiptal canal
passes superior to the condyles
Extarnal occipital protuberence and superior nuchal lines.
-
Neonatal skull
Large cranium to face ratio Mandible and maxilla are short Bones are mobile on each others and
connected by fibrous tissue or cartilage Anterior fontanelle
: closes at 18 months of age
Posterior fontanelle
: closes at 1 year of age
Mastoid process not present at birth.
-
Clinical
Fontanelles enables us to: Follow up the progress of growth of the
infant Detect dehydration The state of intracranial pressure Take samples of the CSF
-
Internal surface of the skullVault of the skull
Coronal, sagittal and lambdoid sutures
Groove for the superior sagittal sinus
Grooves for the branches of the middle meningeal vessels
Granular pits for archnoid granulations
-
Base of the skull
Anterior cranial fossaSphenoid lesser wing
Middle cranial fossaTemporal bone petrous part
Posterior cranialfossa
-
Anterior cranial fossa
Frontal bone Frontal crest (attachment for falx cerebri) Lesser wing of the sphenoid Anterior clinoid process (attachment to tentorium
cerebelli) Orbital plates
-
Cribriform plate of the ethmoid: olfactory nerve bundles Crista galli Foramen cecum (small vein from nose to SSS) Anterior ethmoid foramen: anterior ethmoid nerve and
vessels Posterior ethmoid foramen: posterior ethmoid nerve and
vessels
-
Middle cranial fossa
Median part: body of sphenoid Lateral part: greater wing of sphenoid and
squamous part of temporal bone
-
Body of the sphenoid bone
Sulcus chiasmaticus (prechiasmatic groove) Optic canal Tuberculum sella Sella turcica (contains the hypophysis) Dorsum sella Posterior clinoid processes
-
Optic canal: optic nerve, opthalmic artery
Superior orbital fissure:- lacrimal, frontal, nasociliary branches of
the opthalmic
nerve (V1)- Oculomotor, trochlear, abducent nerves- Superior ophthalmic vein
-
Foramen rotundum- maxillary nerve
Foramen ovale- mandibular nerve - lesser superficial petrosal nerve - accessory meningeal artery
Foramen spinosum- middle meningeal artery - meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve
-
Foramen lacerum: usually closed by cartilage and fibrous tissue. Occasionally the GSPN
Carotid canal: internal carotid artery. The artery runs in the side of the sphenoid body to reach the cavernous sinus
Impression of the trigeminal ganglion: lateral to the foramen lacerum, on the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone
-
Greater petrosal nerve hiatus
groove for GSPN
passes to foramen lacerum
joins the deep petrosal nerve
nerve of the pterygoid canal (Vidian nerve)
Lesser petrosal nerve hiatus
groove for the lesser petrosal nerve
foramen ovale
otic ganglion in the infratemporal fossa
-
Posterior cranial fossa
Foramen magnum- Medulla oblangata- Meninges- Vertebral arteries- Spinal roots of the accessory nerves
-
Jugular foramen- Inferior petrosal sinus-
CN 9, 10, 11- Sigmoid sinus
internal jugular vein
Internal acoustic meatus: facial nerve and vestibulucochlear nerves
Hypoglossal canal: hypoglossal nerve
-
Groove for the occipital sinus Internal occipital crest Internal occipital protuberance Groove for the transverse sinus Groove for the sigmoid sinus Groove for the superior petrosal sinus Clivus
-
The Skull Anatomical positionFrankfort horizontal plane Neurocranium Clavaria Skull base Viscerocranium(Facial skeleton)Facial bones (viscerocranium) Slide166Mid- sagittal section medial nasal wallLateral nasal wall Pneumatized bones of the skullParanasal sinuses Slide228Slide229Paranasal sinuses x-ray Pneumatization of the temporal boneGeometric points of the skull Frontal bone Slide175Slide176Frontal sinusesParietal bones Parietal bone internal surfaceOccipital bone Occipital bone internal surfaceTemporal bone Adult skull Neonatal skullNeonatal temporal bone Slide211Slide210Slide234Slide235Slide209Slide212Slide213Nasal bonesZygomatic boneSlide214Maxilla Palatine bonesVomer Vomer, medial nasal wall Medial nasal wall Slide215 Lateral nasal wallParanasal sinuses Paranasal sinuses x-ray The mandibleBody of the mandibleSlide193 Ramus of the mandible Slide81Anterior view of the skullAnterior view of the skull Maxilla Zygomatic boneThe mandibleLateral view of the skull Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossaSlide241Slide242Posterior view of the skullSuperior view of the skullInferior view of the skullInferior view of the skull- Palate Inferior view of the skull- Sphenoid Slide245Temporal Slide23 Slide24 Occipital Slide261Slide260Slide262Neonatal skull Slide265Slide263Slide264Clinical Internal surface of the skullBase of the skullSlide266Anterior cranial fossa Middle cranial fossaBody of the sphenoid bone Slide269 Slide270 Slide271Slide268Posterior cranial fossa Slide274 Slide70