The scramble for africa. We will look at the following European colonization of africa in the late...
-
Upload
alberta-george -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
1
Transcript of The scramble for africa. We will look at the following European colonization of africa in the late...

The scramble for africa

We will look at the following
European colonization of africa in the late 19th century
Case study: The Ashanti Kingdom
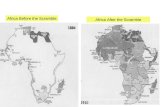
How was Africa before colonization and after the Berlin conference in 1884
How was the Ashanti Kingdom colonised and what were the results of this?

At the end of the 18th century cololinism seemed to be a thing of the past.
100 years later a second wave of colonialization took place. Within 20 years 1880 to 1900, every corner of the earth came to be claimed by a European power.
Africa saw the most dramatic colonization.
This was called the “Scramble of Africa”

The scramble for Africa
Africa has a long precolonial history.There were many powerful kingdoms.Kingdoms of MaliGhanaGreat ZimbabweMapungubwe These Kingdoms were Well organised, complex trading systems. Technologically advanced, own education system, practiced agriculture & religious beliefs.

Some were stateless, while others were state run or kingdoms.
Most were founded on principles of communalism, in that they were self governing autonomous entities.
Land was held commonly and could not be bought or sold.
Some things such as cattle were owned individually.Chiefs ran daily affairs with one or more councils.

Trade
They had well developed trading systems.Across the Sahara dessert, Europe, Arabia,
India and China.Mapungubwe region centre of
trade.Gold, copper, Iron, wood, pottery
& ivory

Education
Timbuktu manuscripts show us very high levels of scolarship.
Many african societies placed a strong emphasis on traditional forms of education.
Education involved transmitting of cultural values and skills.

Technology
Gold, copper and iron artefacts are evidence that these societies had mining technology.
The famous mapungubwe rhinoceros is an example of a decorative artefact.
Cities like Timbuktu in Mali and the ruins of great Zimbabwe are evidence of architectural building skills.

Agricuture
They depended on agriculture and many areas enjoyed fertile soils.
Mapungubwe was agriculturally rich because of large scale flooding that deposited fertile top soil.
They kept domesticated cattle, sheep, goats and dogs.
Chard remains of storage huts were found showing that millet, sorghum and cotton were cultivated.

Culture & religionBased on ancestral worship & beliefs linked
about their religion.Stories of their journeys & cycles & events in
their lives.E.g. rituals for harvesting , coming of the first
rain, going to war or victory after war. Some involved sacrifices.
Healers & diviners communicate with ancestors, heal people & predict the future.
In the Sahara Islam was strong.