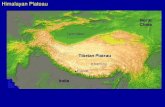
Himalayan Plateau. Himalayan plateau topography Rivers off the Tibetan Plateau.
The Indian Himalayan Range
-
Upload
jatin-chhabra -
Category
Travel
-
view
595 -
download
4
description
Transcript of The Indian Himalayan Range

The Indian Himalayan RangeHimalayans are the youngest fold mountains in the world. The Himalayas abut or cross five countries: Bhutan, India, Nepal, China, and Pakistan, with the first three countries having sovereignty over most of the range. The Indian subcontinent range has 2 parts- Karakoram (ranges like Zaskar, Ladakh and Pirpanjal) and The Himalayas. The Indian Himalayan Region is a range that spans 10 states of India namely, Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram and Tripura as well as the hill regions of two states - Assam and West Bengal. The Himalayan ranges has 3 important ranges- Himadri, Himachal and Siwalik, about 2400 km in lingth & width of 240-320 km.

The Himalayan Range
The Himalayan Ranges can be further studied into 3.1. The Greater Himalayas2. The lesser Himalayas3. The Outer Himalayas

The Greater HimalayasThe greater Himalayas or Himadri or northern ranges, average 6000m in height and has the 3 highest mountain ranges of the world.I. Mount Everest 8848mII. K2 or Mount Godwin 8611mIII. Kanchenjunga 8598mIn such high altitude there are only few passes like Shipki la (in Sutlej valley), Jelep la and Nathu la. The greater Himalayas contains several glaciers which are the source of rivers Ganga and Yamuna. The core part of this range is granite.

The Lesser HimalayasThe lesser Himalayas or Himachal average 1500m to 5000m in height and 50 km width. The range continues east through the Indian states of J&K, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh. The range then enters Nepal, the eastern Indian states of Sikkim & West Bengal, Then cuts through the country of Bhutan and then re-enters into the eastern Indian states Assam and Arunachal Pradesh. Ranges here are - Pir Panjal (longest), Dhaula Dhar, Mahabharat Range. The range consist of many famous valleys like Kashmir valley, Kangra, Kullu.

The Outer HimalayasThe outer Himalayas or the southern Himalayas, average between 900m to 1200m in height lies between lesser Himalayas and Indo Gangetic plains. These ranges are extended till the far eastern part of India. They are composed of unconsolidated sediments brought by rivers from the Himalayan ranges located in further north. These valleys are covered with thick gravel and alluvium.