The Geometry of Biomolecular Solvation 1. Hydrophobicity Patrice Koehl Computer Science and Genome...
-
Upload
dwight-joseph -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
2
Transcript of The Geometry of Biomolecular Solvation 1. Hydrophobicity Patrice Koehl Computer Science and Genome...

The Geometry of Biomolecular Solvation
1. Hydrophobicity
Patrice Koehl
Computer Science and Genome Center
http://www.cs.ucdavis.edu/~koehl/

The Importance of Shape
KKAVINGEQIRSISDLHQTLKKWELALPEYYGENLDALWDCLTGVEYPLVLEWRQFEQSKQLTENGAESVLQVFREAKAEGCDITI
Sequence
Structure
Function
ligand

Enzyme – Substrate Binding
+Substrate(ligand)
Enzyme(receptor)
Induced Fit

Receptor
Ligand
Co-factors may induce the fit: allostery
Co-factors bind
Co-factorsinduce conformationalChange: allostery
Ligand binds

Biomolecular Solvation
Stability of Protein Structures
Geometric Measures of Protein Structures
ApplicationsAccessibilityBinding sites

Biomolecular Solvation
Stability of Protein Structures
Geometric Measures of Protein Structures
ApplicationsAccessibilityBinding sites

Energy of a Protein
Bonded Interactions (chemistry)
Bonds, Angles, Dihedral angles
Non Bonded Interactions (“local” information)van der Waals interactions, Electrostatics
Solvent (environment)Most difficult

SolventExplicit or Implicit ?

Potential of mean force
( )
( )
∫∫−
−
=dXdYe
eYXP
kT
YXU
kT
YXU
,
,
),(
A protein in solution occupies a conformation X with probability:
X: coordinates of the atoms of the protein
Y: coordinates of the atoms of the solvent
),()()(),( YXUYUXUYXU PSSP ++=
The potential energy U can be decomposed as: UP(X): protein-protein interactions
US(X): solvent-solvent interactions
UPS(X,Y): protein-solvent interactions

Potential of mean force
∫= dYYXPXPP ),()(
We study the protein’s behavior, not the solvent:
PP(X) is expressed as a function of X only through the definition:
∫−
−
=dXe
eXP
kT
XW
kT
XW
P T
T
)(
)(
)(
WT(X) is called the potential of mean force.

Potential of mean force
The potential of mean force can be re-written as:
)()()( XWXUXW solPT +=
Wsol(X) accounts implicitly and exactly for the effect of the solvent on the protein.
Implicit solvent models are designed to provide an accurate and fast
estimate of W(X).

++
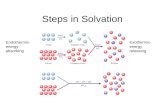
Solvation Free Energy
Wnp
Wsol
VacchW−
SolchW
( ) ( )cavvdWvac
chsol
chnpelecsol WWWWWWW ++−=+=

The SA model
Surface area potential
∑=
=+N
kkkvdWcav SAWW
1
σ
Eisenberg and McLachlan, (1986) Nature, 319, 199-203

Surface area potentialsWhich surface?
MolecularSurface
Accessiblesurface

Hydrophobic potential:Surface Area, or Volume?
(Adapted from Lum, Chandler, Weeks, J. Phys. Chem. B, 1999, 103, 4570.)
“Radius of the molecule”
Volume effect
Surface effect
For proteins and other large bio-molecules, use surface

Biomolecular Solvation
Stability of Protein Structures
Geometric Measures of Protein Structures
ApplicationsAccessibilityBinding sites

Representations of Biomolecules
Space-filling ModelCartoon

Computing the Surface Areaand Volume of a Union of Balls

Computing the Surface Areaand Volume of a Union of Balls
Power Diagram:

Computing the Surface Areaand Volume of a Union of Balls
Decomposition of theSpace-filling diagram

Computing the Surface reaand Volume of a Union of Balls
∑=
=N
iiiA
1
24 σρπ
i
i
∑=
=N
iiiV
1
3
3
4βρ
π
i
VolumeSurface Area

Computing the Surface reaand Volume of a Union of Balls
The weighted Delaunay triangulation is the dual of the power diagram

Computing the Surface reaand Volume of a Union of Balls
The dual complex K is the dual of the decomposition of the space-filling diagram

http://www.cs.ucdavis.edu/koehl/ProShape/
Protein Delaunay Complex
K complex
Computing the Surface Areaand Volume of a Protein

Delaunay Complex
K complex
Computing the Surface Areaand Volume of RNA
P4-P6 domainGroup I intron

Biomolecular Solvation
Stability of Protein Structures
Geometric Measures of Protein Structures
ApplicationsAccessibilityBinding sites

H1’
HO2’
H2’H4’
H3’
H5’
H5’’
Experimental measures of accessibilities
Hydroxyl radical footprinting:

Residue number
Fo
otp
rin
tin
g c
ou
nt
/ R
ibo
se H
acc
essi
bil
ity

BINDING POCKETS IN 16S RIBOSOMAL RNA
PDB structure: 1HZN
Hygromycin B

Probe Size
1.4 Å
8 Å
BINDING POCKETS IN 16S RIBOSOMAL RNA

BINDING POCKETS IN 16S RIBOSOMAL RNA