The following types of muscle tissue and nervous tissue are covered in this activity: 1.Skeletal...
-
Upload
kelley-cook -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
description
Transcript of The following types of muscle tissue and nervous tissue are covered in this activity: 1.Skeletal...
The following types of muscle tissue and nervous tissue are covered in this activity:
1. Skeletal muscle (muscles attached to the skeleton)
2. Smooth muscle (muscles lining hollow organs)
3. Cardiac muscle (heart)
4. Nervous tissue (nervous system)
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 4.10a Muscle tissues.
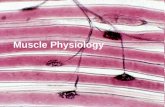
(a) Skeletal muscleDescription: Long, cylindrical,multinucleate cells; obviousstriations.
Function: Voluntary movement;locomotion; manipulation of theenvironment; facial expression;voluntary control.
Location: In skeletal musclesattached to bones oroccasionally to skin.
Photomicrograph: Skeletal muscle (approx. 460x).Notice the obvious banding pattern and thefact that these large cells are multinucleate.
Nuclei
Striations
Part ofmuscle fiber (cell)
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 4.10b Muscle tissues.
(b) Cardiac muscleDescription: Branching, striated, generally uninucleate cells that interdigitate atspecialized junctions (intercalated discs).
Function: As it contracts, it propels blood into the circulation; involuntary control.Location: The walls of the heart.
Photomicrograph: Cardiac muscle (500X);notice the striations, branching of cells, andthe intercalated discs.
Intercalateddiscs
Striations
Nucleus
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
(c) Smooth muscleDescription: Spindle-shapedcells with central nuclei; nostriations; cells arranged closely to form sheets.
Function: Propels substancesor objects (foodstuffs, urine,a baby) along internal passage-ways; involuntary control.
Location: Mostly in the wallsof hollow organs.
Photomicrograph: Sheet of smooth muscle (200x).
Smoothmusclecell
Nuclei
Figure 4.10c Muscle tissues.
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 4.9 Nervous tissue.
Photomicrograph: Neurons (350x)
Function: Transmit electricalsignals from sensory receptorsand to effectors (muscles andglands) which control their activity.
Location: Brain, spinalcord, and nerves.
Description: Neurons arebranching cells; cell processesthat may be quite long extend fromthe nucleus-containing cell body;also contributing to nervous tissueare nonirritable supporting cells(not illustrated).
Dendrites
Neuron processes Cell body
Axon
Nuclei ofsupportingcells
Cell bodyof a neuron
Neuronprocesses
Nervous tissue
Various membranes are also covered:
1. Cutaneous membranes
2. Synovial membranes
3. Mucous/Mucosae membranes
4. Serous membranes (parietal and visceral layers)
a. Peritoneum – abdominal organs
b. Pericardium – heart
c. Pleura – lungs
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 4.11a Classes of membranes.
Cutaneousmembrane(skin)
1. Cutaneous membrane (the skin)covers the body surface for protection.
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
2. Synovial membranesline the joint surfaces/cavity. This membrane is very thin, and produces synovial fluid for bone movement.
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 4.11b Classes of membranes.
Mucosae ofnasal cavity
Mucosae oflung bronchi
Mucosae ofmouth
Esophaguslining
3. Mucous membranes line body cavitiesopen to the exterior (lubricate and protect)
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
ParietalPericardium(outer)
VisceralPericardium(inner)
4. Serous membranes line body cavities closed to the exterior. Serous fluid secreted allows the organs to glide against other structures without causing friction.
ParietalperitoneumVisceralperitoneum
ParietalpleuraVisceralpleura