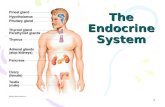
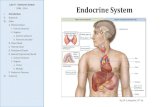
The Endocrine System 1
-
Upload
farah-nabila-luthfiyya -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of The Endocrine System 1

1Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings.
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
PARTH

2
Hormones: Come from endocrine glands Circulate in the blood stream Act on specific cells in the body
Endocrine Functions: Hormones

3
Access to every cell Each hormone acts only on specific
cells (target cells) Only specific cells have receptors for
specific hormones Endocrine control slower than nervous
system Endocrine and nervous systems
interact
Endocrine System Characteristics

4
Steroid Hormone Action on a Target Cell
Figure 13.2

5
Steroid Hormones: Lipid soluble, chemically derived from
cholesterol Enter target cells Activate specific genes to produce
specific proteins Slower acting than nonsteroid hormones,
minutes to hours
Classification of Hormones: Steroid

6
Nonsteroid Hormone Action on a Target Cell
Figure 13.3

7
Nonsteroid hormones: Water soluble Bind to receptors on target cell
membranes Work through intermediate
mechanisms to activate existing enzymes
Faster action than steroid hormones, seconds to minutes
Classification of Hormones: Nonsteroid

8
Example of a Negative Feedback
Loop:
Homeostasis

9
Location of Major Endrocrine OrgansLocation of Major Endrocrine Organs
Slide 9.14Figure 9.3

10
Hormones of the Pituitary Gland
Table 13.1

11
Hypothalamus and the Anterior Pituitary Gland
Figure 13.7

12
Anterior pituitary Connection to hypothalamus: releasing
and inhibiting hormones from hypothalamus travel to pituitary through pituitary portal system
Hormones ACTH: stimulates adrenal cortex TSH: acts on thyroid gland FSH, LH, Prolactin: related to control of
reproductive cycles and lactation Growth Hormone: widespread effects on
body
Hypothalamus and the Anterior Pituitary Gland

13
Posterior pituitary Connection to hypothalamus: hormones
made in hypothalamus, stored in posterior pituitary
Hormones: nonsteroidal Antidiuretic hormone (ADH): conserves water
in kidneys, regulates water balance in body Oxytocin: causes uterine contractions during
labor and milk ejection through neuroendocrine reflex
Hypothalamus and the Posterior Pituitary Gland

14
Gigantism: hypersecretion of growth hormone
Pituitary Dwarfism: hyposecretion of growth hormone
Pituitary Disorders

15
Pituitary Gigantism

16
Pituitary Dwarfism

17
Structures: islets of Langerhans
Hormones: nonsteroidal Glucagon: made by alpha cells, raises
blood sugar Insulin: made by beta cells, lowers blood
sugar
Pancreas: Endocrine Functions

18
Location of Major Endrocrine OrgansLocation of Major Endrocrine Organs
Slide 9.14Figure 9.3

19
Roles of Insulin and Glucagon in Regulating Blood Glucose
Figure 13.9

20
Location of Major Endrocrine OrgansLocation of Major Endrocrine Organs
Slide 9.14Figure 9.3

21
Adrenal cortex Secretion: mediated through
hypothalamus-pituitary secretions Hormones: steroidal
Glucocorticoids: cortisol – blood glucose regulation
Mineralocorticoids: aldosterone – sodium/fluid/urine
Adrenal Glands: Cortex

22
Secretion of Cortisol
Figure 13.10

23
Cushings Disease
Oversecretion of Cortisol

24
Adrenal medulla: neuroendocrine organ
Secretion: sympathetic nervous system Hormones: nonsteroidal
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine: enhance function of sympathetic nervous system (Fight or flight)
Adrenal Glands: Medulla

25
Roles of the Hypothalamus and Adrenal Roles of the Hypothalamus and Adrenal Glands in the Stress ResponseGlands in the Stress Response
Slide 9.31
Figure 9.12

26
Secretion: controlled through hypothalamus-pituitary secretions
Steroidal hormones: Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine
(T3): both regulate production of ATP from glucose, affects metabolic rate
Calcitonin: lowers blood calcium levels
Thyroid Gland

27

28
Grave’s Disease – overactive thyroid

29
Secretion: response to lowered blood calcium levels
Hormone: Parathyroid hormone (PTH), nonsteroidal
Removes calcium and phosphate from bone
Increases absorption of calcium by the digestive tract
Increases renal retention of calcium and excretion of phosphate
Parathyroid Glands

30
Location of Major Endrocrine OrgansLocation of Major Endrocrine Organs
Slide 9.14Figure 9.3

31
Hormone: testosterone (steroidal) Functions:
Regulates development and normal functioning of sperm, male reproductive organs, male sex drive
Development of male secondary sex characteristics
Testes

32
Hormones (steroidal) and functions: Estrogen: initiates development of secondary sex characteristics, regulates menstrual cycle
Progesterone: regulates menstrual cycle
Ovaries

33
Ovarian Cycle
Figure 16.6