The Effect of Competition Monopoly Oligopoly Bertrand’s model –Quantity can be easily adjusted....
-
Upload
kristian-mclaughlin -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
4
Transcript of The Effect of Competition Monopoly Oligopoly Bertrand’s model –Quantity can be easily adjusted....


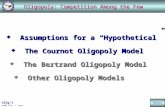
The Effect of Competition
• Monopoly
• Oligopoly
• Bertrand’s model
– Quantity can be easily adjusted.
• Cournot’s model
– Quantities are chosen first, and can’t be easily altered; then prices are set.

Monopolist
P* = 3
Quantity
Marketprice
Demand:p=5-q
c=1
q* = 2
=4

07/14/04 B189 - Simon Rodan 4
LRAC
# of firms
Price
1 2 3 4 5 6
Bertrand model of competition

The Oil Super Majors
Sales ($B)
Net Income ($B) ROE
Royal Dutch Shell 475 26 5%
Exxon 434 45 10%
BP 377 17 5%
Chevron 230 27 12%
Total SA 222 14 6%
Data are for FY2011

Expected Duopoly Profit
P* = 3
Quantity
Marketprice Demand:
p=5-q
c=1
q* = 2
2=2 2=2

Cournot’s Duopoly Prediction
P* = 2.33
Quantity
Marketprice
Demand:p=5-q
c=1
q* = 2.66
=1.77=1.77
1 and 2=3.54
Simulation

Cournot’s Duopoly Prediction
P* = 2
Quantity
Marketprice
Demand:p=5-q
c=1
q* = 3
=1
1,2 and 3=3
=1 =1

07/14/04 B189 - Simon Rodan 9
LRAC
# of firms
Pote
nti
al pri
ce
1 2 3 4 5 6
Cournot model of competition (quantity)

Firm Size Industry Profile
Sale
s
CR4 = 80%
Sale
s
CR4 = 8%

Industry concentration
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
Firm rank (by sales)
Sale
s
• Industries with few firms are ‘concentrated’
• Industries with many firms are ‘fragmented’
• However, most industries have both large and small firms

Some more examples
Sale
s
CR4 = 9%CR4 = 35%CR4 = 62%

Assessing concentration
• Four Firm Concentration Ratio (CR4)– Add up the sales for all firms in the
industry– Add up the sales of the four largest firms
in the industry – Divide the second number by the first
• OR– Add the market shares of the four
largest firms (this is exactly equivalent to the first method)