The Digestive System - Abraham Lincoln High School · 2014-08-28 · The Digestive System ....
Transcript of The Digestive System - Abraham Lincoln High School · 2014-08-28 · The Digestive System ....

M E D I C A L T E R M I N O L O G Y
M S . PA S T O R
The Digestive System

Objectives
- Identify and describe the structures of the digestive
using proper medical terminology
- Explore careers relating to this system
Nutrition and Digestion

There are six types of nutrients:
• Water
• Carbohydrates
• Proteins
• Fats
• Minerals
• Vitamins

Carbohydrates
• Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for the body.
• simple and complex carbohydrates supply glucose
• fiber from plant foods helps elimination

• Proteins are necessary for growth and repair of the body’s
cells.
– body makes 12 out of 20 amino acids
– other eight essential amino acids come from food

• Fats provide energy and key building components.
– fats are saturated and unsaturated
– butter, lard and oils
– essential fatty acids come from food

• Minerals are inorganic materials needed in small amounts
– help to build or repair tissues
– replenished by eating variety of foods

• Vitamins are organic molecules that work with enzymes.
– vitamins are fat-soluble and water-soluble
– Fat soluble: A, D, E, K
– Water-soluble: B, C (ascorbic acid) , folic acid
– regulate cell functions, growth, development

• Unbalanced diets can lead to malnutrition or undernutrition
– Malnutrition occurs in when you don’t get the right
nutrients for your body, or you over consume some
nutrients.
– Undernutrition is when you lack the essential nutrients
your body needs in order to function properly.

Key Concept #2 The main stages of food processing are ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination
• Ingestion is the act of eating
• Digestion is the process of breaking food down into
molecules small enough to absorb
• Absorption is uptake of nutrients by body cells
• Elimination is the passage of undigested material out of the
digestive compartment

LE 41-12
Pieces of food
Chemical digestion (enzymatic hydrolysis)
Food
Nutrient molecules enter body cells
Small molecules
Undigested material
ELIMINATION ABSORPTION DIGESTION INGESTION
Mechanical digestion

• More complex animals have a digestive tube with two
openings, a mouth and an anus
– This digestive tube is called a complete digestive
tract or an alimentary canal
– It can have specialized regions that carry out digestion and
absorption in a stepwise fashion


Key Concept #3 Each organ of the mammalian digestive system has specialized food-processing functions
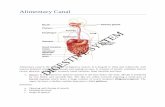
• The human digestive system consists of an alimentary
canal and accessory glands that secrete digestive juices through
ducts
• Accessory glands are the
– salivary glands
– pancreas
– liver
– gallbladder
• Food is pushed along by peristalsis, rhythmic contractions of
muscles in the wall of the canal

LE 41-15a
Esophagus
Pharynx
Oral cavity
Stomach
Pyloric sphincter
Cardiac orifice
Liver
Tongue
Parotid gland
Sublingual gland
Submandibular gland
Salivary glands
Ascending
portion of
large intestine
Gall- bladder
Pancreas
Ileum
of small
intestine
Rectum
Anus
Appendix
Cecum
Large
intestine
Small
intestine
Duodenum of
small intestine

The Oral Cavity, Pharynx, and Esophagus
• In the oral cavity, food is
lubricated and digestion
begins
• Teeth chew food into
smaller particles that are
exposed to salivary
amylase, initiating
breakdown of carbohydrates

• The region we call our throat is the pharynx, a junction that
opens to both the esophagus and the windpipe (trachea)
• The esophagus pushes food from the pharynx down to the
stomach by peristalsis
Epiglottis up
Bolus of food
Esophageal sphincter contracted
Esophagus
To stomach To lungs
Trachea
Tongue
Pharynx
Glottis
Larynx
Esophageal sphincter relaxed
Epiglottis down
Glottis up and closed
Epiglottis up
Esophageal sphincter contracted
Relaxed muscles
Glottis down and open
Relaxed muscles
Contracted muscles
Stomach

The Stomach
• The stomach stores food and secretes gastric juice, which
converts a meal to acid chyme
• Gastric juice is made up of hydrochloric acid and the
enzyme pepsin
• Pepsin is secreted as inactive pepsinogen by chief cells;
pepsin is activated when mixed with hydrochloric acid in the
stomach
– It’s purpose is to break down protein
• Mucus protects the stomach lining from gastric juice

Esophagus
Cardiac orifice
Pyloric sphincter
Small
intestine Folds of
epithelial
tissue
Stomach
Epithelium
Pepsin
(active enzyme)
Pepsinogen
HCl
Pepsinogen and HCl
are secreted into the
lumsden of the stomach.
HCl converts
pepsinogen to pepsin.
Pepsin then activates
more pepsinogen,
starting a chain
reaction. Pepsin
begins the chemical
digestion of proteins.
Parietal cell Chief cell
Chief cells
Mucus cells
Parietal cells
Interior surface of
stomach
Gastric gland
5 µ
m

• Gastric ulcers, lesions in the lining, are caused mainly by
the bacterium Helicobacter pylori
Bacteria
Mucus
layer of
stomach
1 µ
m

The Small Intestine
• The small intestine is the longest section of the alimentary
canal
• It is the major organ of digestion and absorption
• The first portion of the small intestine is the duodenum
– Where acid chyme from the stomach mixes with digestive
juices from the pancreas, liver, gallbladder, and the small
intestine itself

Accessory Glands
Stomach
Pancreas
Liver
Gall-
bladder
Duodenum of
small intestine
Intestinal
juice
Bile
Acid chyme

The Pancreas
• The pancreas has both digestive and endocrine
(hormone) functions.
• Digestive Function
– Releases bicarbonate to neutralize the acid
chyme that enters the small intestine
– Releases proteases to help with further digestion
of proteins
• Endocrine Function
– Releases insulin & glucagon to control blood-
sugar levels

The Liver
• The liver produces bile, which aids in digestion and
absorption of fats

The Small Intestine: Absorption of Nutrients
• The small intestine has a large surface area, due to villi and
microvilli that are exposed to the intestinal lumen
• The enormous microvillar surface greatly increases the rate of
nutrient absorption Key
Nutrient absorption
Microvilli (brush border)
Epithelial cells
Lacteal
Lymph vessel
Villi
Large circular folds
Epithelial cells
Blood capillaries
Vein carrying blood to hepatic portal vessel
Muscle layers
Villi
Intestinal wall

The Large Intestine
• The large intestine, or colon, is connected to the small
intestine
• Its major function is to recover water that has entered the
alimentary canal
• Wastes of the digestive tract, the feces, become more solid as
they move through the colon
• Feces is stored in the rectum until it exits via the anus


Glucose Regulation as an Example of Homeostasis
• Animals store excess calories as glycogen in the liver and fats
in the muscles.
• Hormones like insulin & glucagon regulate glucose
metabolism
• When fewer calories are taken in than are expended, fuel is
taken from storage and broken down to be used by cells.

LE 41-3
STIMULUS: Blood glucose
level rises after eating.
STIMULUS: Blood glucose
level drops below set point.
Homeostasis: 90 mg glucose/ 100 mL blood