The Digestive System
description
Transcript of The Digestive System

Anatomy & Physiology Mrs. Halkuff
The Digestive System

1. Digestion2. Absorption3. Elimination
Functions

1. Mechanical Begins immediately after ingestion Mastication (chewing) with teeth Purpose is to break down food into smaller
pieces Peristalsis: Squeezing of food down the
esophagus 2. Chemical
Accomplished by digestive enzymes Enzymes break down large molecules (Fats,
Carbohydrates, & Proteins)
2 Types of Digestion

Protease: Breaks down proteinLipase: Breaks down fatAmylase: Breaks down carbohydrates
(starches down to sugars
Enzymes

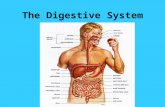
Canal connecting mouth to anus.MouthPharynxEsophagusStomachSmall IntestinesLarge IntestinesColonRectumAnus
Alimentary Canal

Hard Palate: Roof of mouth (front)
Soft Palate: Roof of mouth (back)Uvula: Fleshy flap that keeps
food from moving up into your nasal cavity when swallowed.
Epiglottis: Elastic cartilage attached to root of tongue that directs air into the trachea and food into the esophagus.
Tongue : Moves food around and allows for taste.
Teeth: Used to break down food into smaller pieces.
Mouth

Beginning with the pharynx to the anus, the walls of the alimentary canal are composed of two coats:Mucus Coat
Epithelial Goblet cells line the canal producing mucus.
Muscle CoatInner muscles: CircularOuter muscles: Longitudinal
Both coats facilitate movement of food.
Coats

ThroatAir, Food, Liquid all mix here.
Pharynx

Connects the pharynx to the stomachPushes food down by peristalsis.Bolus: Chewed food
Esophagus

“C-shaped” organ that contains acid to break down food.
Food mixes with stomach acid to produce a thick cream called chyme.
Has 3 Regions:Cardiac: Upper stomach regionBody: Mid stomach regionPylorus: End stomach region
Stomach

Sphincters: Muscular valves that control opening & closing.Cardioesphageal
Sphincter: Valve connecting the esophagus to the stomach.
Pyloric Sphincter: Valve connecting the pylorus to the small intestines.
Stomach

Curvatures:FundusGreater CurvatureLesser Curvature
Rugae: Internal stomach wrinklesFewer rugae when fullMore rugae when empty
Stomach: Curvy & Wrinkly

Main function is absorption of nutrientsHas 3 divisions:
DuodenumJejunumIleum
Small Intestine

First segment of the small intestineConnects to stomachReceives chyme from stomachRegulates gastric emptyingContinues digestionSignals hunger cuesStimulates the liver, gall bladder, & pancreasIn gastric bypass surgery, the duodenum is
usually bypassed.
Duodenum

Second segment of the small intestineFinalizes food digestion
Jejunum

Third & final segment of the small intestineMain function is to absorb nutrientsReturns bile back to liverConnects to the large intestine by the
ileocecal valve
Ileum

Watery waste is passed from the small intestine to large intestine.
Main function is to absorb any water or minerals from the waste.
Compresses waste into compact form for easy removal from the body.
Chyme combines with mucus and bacteria and is converted to feces.
Large Intestine

4 divisions:1. Cecum2. Colon3. Rectum4. Anal Canal
Large Intestine

First segment of large intestine.Connection at the small intestine at ileocecal
valve.
Cecum

4 segments named for their relation to the pelvis:1. Ascending colon2. Transverse colon3. Descending colon4. Sigmoid colon
Colon

Collects feces accumulated in the colon.
Rectum

Short tube (1.5”)2 muscular rings
1. Involuntary (Internal muscle)2. Voluntary (External muscle)These muscles relax to allow for defecation.
Anal Canal