THE DIENCEPHALON - Univerzita KarlovaTHE THALAMUS - NUCLEI Anterior nuclei Medial nuclei...
Transcript of THE DIENCEPHALON - Univerzita KarlovaTHE THALAMUS - NUCLEI Anterior nuclei Medial nuclei...
-
THE DIENCEPHALONTHE DIENCEPHALONAnatomický ústav 1. LFAnatomický ústav 1. LF
R. DrugaR. Druga
-
DIENCEPHALONDIENCEPHALON
EPITHALAMUSEPITHALAMUS THALAMUSTHALAMUS SUBTHALAMUSSUBTHALAMUS HYPOTHALAMUSHYPOTHALAMUS
-
AMPHIBIANS MAMMALS
AMFIBIA MAMMALIA
-
DIENCEPHALON – medial aspect
-
BRAIN STEM AND DIENCEPHALON
Superior aspect
Pulvinar - cushion
-
THALAMUS AND BASAL GANGLIA – horizontal section
CAPSULA INTERNA
-
THE THALAMUS - NUCLEITHE THALAMUS - NUCLEI
Anterior nucleiAnterior nuclei Medial nuclei (mediodorsalis nc.)Medial nuclei (mediodorsalis nc.) Lateral nuclei – dorsal tier (lateral dorsal nc., lateral posterior Lateral nuclei – dorsal tier (lateral dorsal nc., lateral posterior
nc.,posterior ncc.,(ncc. of pulvinar) nc.,posterior ncc.,(ncc. of pulvinar) ventral tierventral tier ( ventraisl anterior – VA, ventralis lateralis – VL, ( ventraisl anterior – VA, ventralis lateralis – VL,
ventralis posterolateralis- VPL, ventralis posteromedialis – VPM, ventralis posterolateralis- VPL, ventralis posteromedialis – VPM, ventral intermedialis - VIM, ventral intermedialis - VIM,
Medial geniculate nc.,Medial geniculate nc., Lateral geniculate nc.,Lateral geniculate nc., Intralaminar nucleiIntralaminar nuclei Midline nucleiMidline nuclei Reticular nucleus Reticular nucleus
-
SUBTHALAMUS
Zona incerta
Subthalamic nc.
-
PULVINAR – posterior nuclei
METATHALAMUS=
Medial and lateral geniculate bodies
CORPORA GENICULATA
-
Parcellation of thalamic nuclei according Michigan´s school
-
Neuronal connections of thalamic nuclei
Zapojení thalamických jader
-
Podkorová aferentace thalamických jader
-
VA - GP
VA - SNr
VL –cerebellum
VPL + VPM
IL
MD
Post. Ncc..
Termination of subcortical fibers in the thalamus – horizontal section
-
Thalamic nucleiThalamic nuclei
Relay nuclei (Relay nuclei (relé jádrarelé jádra, , přepojovací jádra)přepojovací jádra) – – MGN, LGN, VPL, VPM, VL, VAMGN, LGN, VPL, VPM, VL, VA
Receives input predominantly from a single sourceReceives input predominantly from a single source Processed information is sent to a localized region of Processed information is sent to a localized region of
cortexcortex Are modality specificAre modality specific Specific nuclei (after stimulation sharply localized Specific nuclei (after stimulation sharply localized
cortical response)cortical response)
-
Association nucleiAssociation nuclei
MD, LD, LP, Posterior ncc.,MD, LD, LP, Posterior ncc., Receives input from a number of structures or cortical Receives input from a number of structures or cortical
areasareas Sends fibers to the association cortical areasSends fibers to the association cortical areas Specific nuclei (after stimulation sharply localized Specific nuclei (after stimulation sharply localized
response in the cortex) response in the cortex)
-
Nonspecific nucleiNonspecific nuclei
Intralaminar nuclei (centromedian, Intralaminar nuclei (centromedian, parafascicular)parafascicular)
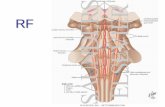
AfferentsAfferents - from RF, spinothalamic fibers, - from RF, spinothalamic fibers, cerebellum, BGcerebellum, BG
EfferentsEfferents – extensive areas of the frontal and – extensive areas of the frontal and parietal lobes, basal ganglia (striatum)parietal lobes, basal ganglia (striatum)
FunctionFunction – influence levels of – influence levels of consciousness and degrees of alertnessconsciousness and degrees of alertness
-
Projekce thalamických jader do neokortexu (thalamokortikální projekce)
VL
-
Somatotopic organization of the VPL and VPM ncc. = termination of the lemniscal systém and trigeminothalamic pathway
Somatotopická organizace VPL a VPM
-
Thalamokortikální projekce
-
Lemniskální systém
-
Dentato-thalamická projekce
-
EPITHALAMUS
-
EPITHALAMUSEPITHALAMUS Habenular nucleiHabenular nuclei Afferent fibersAfferent fibers – stria medullaris thalami (septum verum, olfactory – stria medullaris thalami (septum verum, olfactory
cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia (globus pallidus)cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia (globus pallidus) Efferent fibersEfferent fibers – tractus habenulointerpeduncularis (RF, – tractus habenulointerpeduncularis (RF,
hypothalamus, ANS)hypothalamus, ANS)
Pineal gland- Pineal gland- in amphibian and fishes contains light-in amphibian and fishes contains light-sensitive cells. In mammals transformed to the endocrine gland. sensitive cells. In mammals transformed to the endocrine gland. Pinealocytes produce serotonin.Pinealocytes produce serotonin.
Afferent fibersAfferent fibers – superior cervical ganglion, hypothalamus, – superior cervical ganglion, hypothalamus, colliculus superior, LGBcolliculus superior, LGB
Pinealocytes produce serotonin – melatonin (night ), Pinealocytes produce serotonin – melatonin (night ), Supresses development of gonads (pinealectomy stumulates Supresses development of gonads (pinealectomy stumulates
growth of of the reproductive organsgrowth of of the reproductive organs
-
SUBTHALAMUS – příští týdenSUBTHALAMUS – příští týden
-
HYPOTHALAMUS
-
PROJEKCE HYPOTHALAMICKÝCH JADER NA MEDIÁLNÍ PLOCHU HYPOTHALAMU
-
Aferentace hypothalamu
-
Eferentace hypothalamu
-
Posterior lobe Anterior lobe
Hypothalamo-hypofyseální vztahy
-
Hypothalamo-hypofyseální vztahy ACTH, FSH, LH PRL, MSH
Releasing – inhibiting faktory
-
THE HYPOTHALAMUSTHE HYPOTHALAMUS
No discrete nucleiNo discrete nuclei Regulation of food and water Regulation of food and water
intakeintake
Tuberal regionTuberal region VM – satiety center (lesion VM – satiety center (lesion
produces hyperphagia + produces hyperphagia + obesity)obesity)
Arcuate nc. - delivers peptides Arcuate nc. - delivers peptides to the portal vesselsto the portal vessels
Mamillary regionMamillary region Posterior nc.- elevating of Posterior nc.- elevating of
blood pressure, pupillary blood pressure, pupillary dilatation, body heat dilatation, body heat conservationconservation
Mammillary ncc. – Mammillary ncc. – memory memory formation !!!formation !!!
•Medial zone•Well defined nuclei
•Chiasmatic region • (SO,PV – hormone release)
•Cardiovascular function (Ant.)
•Circadian rhytms (SCH)
•Body temperature (Preoptic nc.)
• Lateral zone
-
Termination of subcortical projections in the thalamus
Zakončení podkorových vstupů v thalamu
-
Snímek 1Snímek 2Snímek 3Snímek 4Snímek 5Snímek 6Snímek 7Snímek 8Snímek 9Snímek 10Snímek 11Snímek 12Snímek 13Snímek 14Snímek 15Snímek 16Snímek 17Snímek 18Snímek 19Snímek 20Snímek 21Snímek 22Snímek 23Snímek 24Snímek 25Snímek 26Snímek 27Snímek 28Snímek 29Snímek 30Snímek 31Snímek 32Snímek 33Snímek 34Snímek 35Snímek 36Snímek 37Snímek 38Snímek 39Snímek 40Snímek 41Snímek 42Snímek 43Snímek 44Snímek 45Snímek 46Snímek 47Snímek 48Snímek 49Snímek 50Snímek 51Snímek 52