The Coniferous Forest
-
Upload
christina-thomas -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
0
description
Transcript of The Coniferous Forest

Click to edit Master subtitle style
4/21/11
The Coniferous Forest
Lauren Maher & Meghan Pint

4/21/11
Climate of Coniferous Forest The Coniferous forest is known as a biome. A
biome is a major regional or global community. It’s climate is temperate. A climate I the weather conditions prevailing in an area in general or over a long period of time. The average temperature in the summer is 57.2 degrees and in the winter it’s 14 degrees Fahrenheit. The summers are short, warm and moist. In the winter it’s different, it is cold, long and dry. The seasons in the Coniferous Forest are well defined. The summers are short and the winters are long, the summers can last from four to six months.

4/21/11
Where is the Coniferous Forest? It is located in the northern latitudes, mostly in
Canada. It’s latitude is 50-60 degrees north. Also, it is found above the hemisphere. It covers most of Canada and some of Alaska. Coniferous forests cover 15% of the land in the world. It’s the largest land habitat on earth. A habitat is the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism. A habitat involves all the biotic factors or all the living organisms.

4/21/11
Effects to the growing season The growing season is a period of time when
harvesting is at its peak. The soil in the Coniferous Forest is thin, lacks nutrients, and is acidic. It’s acidic because peat lands, which is organic material that’s dark brown or black. This matter doesn’t decompose year after year. Since the climate is cold, there is little evaporation. Evaporation is vaporization or the process of becoming vapor. Also, the canopy prevents little to any sunlight through. In result, the growing season is only 130 days. The peat lands are usually located on a hill. The water that is not evaporated runs off into what is known as a bog.

4/21/11
Effects continued… A bog only receive water through precipitation.
It’s water has a higher level of acid and low mineral deposits. When there is a raised bog the water runs off into a fen. In a fen trees may not grow because of the poor mineral soil, sedges cover most of the land. Other factors that could effect the Coniferous Forest are things like volcanoes and fault lines. Luckily, there aren’t either of those in the forest.

4/21/11
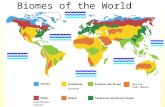
The shaded regions on the map above indicate the areas of Coniferous Forests. They are located in Canada, the U.S., Alaska, and parts of Europe.
CONIFEROUS
FOREST

4/21/11
Countries that have that are in this biome are the northwestern coast of North America such as northern California and southern Alaska, also Chile New Zealand Australia and a few others.
Plants and Animals in this biome also include trees such as Douglas firs. Plants such as the Indian Paint brush. Animals such as various slugs and birds.
Environmentalist and Biologist

4/21/11
Human Threats Clear-cut logging is the biggest threat to
the Coniferous forest! Replanting after logging leads to single-species conifer monocultures - not conducive to species biodiversity. Clear-cutting accelerates soil erosion, degrades wildlife habitat and leads to the loss of biodiversity. Land is being cleared for ski slopes, landfills, housing, new roads.

4/21/11
Food Web

Plant and Animals
Small • Porcupine• Earth Worm• Black Slug• Monarch Butterfly• Waterleaf• Western Wallflower• Snowbrush
Large• Black Bear• Moose• Siberian Tiger• Big horn sheep• Oak tree• Willow• Jeffery Pine

• Grizzly bear• Spotted owl• Woodland caribou • Siberian tiger• Siberian crane• Bald eagle
Endangered Species