The Cell Membrane. Notes Outline I. History of the Cell and Cell Theory II. The Cell Membrane...
-
Upload
clare-haynes -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of The Cell Membrane. Notes Outline I. History of the Cell and Cell Theory II. The Cell Membrane...

The Cell Membrane

Notes Outline
• I. History of the Cell and Cell Theory• II. The Cell Membrane
a) Selective Permeability• III. Structure
a) Phospholipid Bilayerb) Proteinsc) Cholesterol d) Carbohydrates
• IV. Fluid Mosaic Model

I. History of the Cell and Cell Theory
• Mid 1600’s:-Robert Hooke: used an early compound microscope to observe a thin slice of cork (plant material). The cork had empty chambers which he called “cells”
-Anton van Leeuwenhoek: observed tiny living things in pond water using a simple microscope

I. History of the Cell and Cell Theory
• The Cell Theory:1. All living things are composed
of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of
structure and function in living things
3. New cells are produced from existing cells

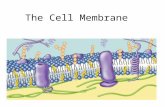
II. The Cell Membrane
• All cells are surrounded by a thin, flexible barrier known as the cell membrane, aka the plasma membrane
• Helps regulate what enters and leaves the cella) Selectively Permeable: only certain substances
are allowed into and out of the cell Ex: Oxygen is allowed into n animal cell but is not
allowed to go out
• Provides structure and protection

III. Structure
a) Phospholipid bilayer (two layers)– Phospholipid has:
• Two fatty acid chains (hydrophobic)• Glycerol backbone• Phosphate head (hydrophilic)

III. Structureb) Proteins:
• Protein markers: helps cells recognize each other – Ex: HIV only attacks white blood cells
because it recognizes only those markers
• Proteins as Enzymes: they help speed up reactions– Ex: sperm cells have enzymes on their
membrane to help break into the egg
• Channel Proteins: serve as tunnels through which large particles can move into or out of the cell

III. Structure
c) Cholesterol: Strengthens the membrane and prevents the fatty acids from sticking together
d) Carbohydrates: Help with identification of cells and help anchor proteins in the membrane

IV. Fluid Mosaic Model
• The membrane is very flexible due to the fatty acid chains
• The membrane also holds all of the structures listed above
• So we call it a:– Fluid (is flowing) Mosaic (lots of different
things) Model• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ULR7
9TiUj80