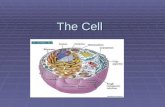
The cell
-
Upload
aurora-yates -
Category
Documents
-
view
20 -
download
0
description
Transcript of The cell
1
The cell
Subject: ScienceAuthor: Allida De CandidoEnglish teacher: Bruna PavanSchool year: 2004/2005
I.P.S.I.A. “L. Zanussi” - Pordenone
CLIL PROJECT
2
Sommario
Lesson plan pqg. 3Procedure 5Secret cell 7Questions 8Cells sizes 9The words meaning 10 Differences between cells 11 How big are cells? 13What are the correct definitions? 14Relative sizes of cells A 15Relative sizes of cells B 16What else about cells? 17
What is there inside the cell? 18Cellcrossword 24Parts of the cell A 25Parts of the cell B 26
Animal and plant cell 27Similarities and differences 28 Comparing plant and animal cell 29
Cell like a busy factory 30
Departements and functions
in the factory 31
Question loop 32
Final test 37
Glossary 38
Answers 41
Bibliography 51
Home
3
Lesson plan
Objectives Students will be able to: describe the cell use appropriate scientific terms for organelles and their
functions remember the names of the organelles explain the resemblances and the differences between animal
and plant cells recognize animal and plant cells know the importance of the cell
Home
Sommario
4
ContentsThe cell structure and function.A comparison between animal and plant cell. Grade levelIt may be adapted for use in a Vocational Training School for students beginning to study Biology. TimeApproximately 3 hours.
ResourcesInternet site; school books.
Home
Sommario
5
ProcedureThe lesson will start with simple information about the cell:
a) all living organisms are made of one or more cells;b) cell size.
Open questions will get some information from the text .With looking up in the dictionary for specific words students will understand better their meaning.In picture1 the students can recognize the shape of different cells and in picture 2 they can see the various sizes of cells and their components.Finally to establish the students’ knowledge there is a chart to fill in with the given definitions. The next step is about what there is inside the cell, the names and the functions of the organelles.The students will be given a paper with all this information and matching halves phrases on the functions to get immediate feedback.With the filling of a crossword the students will be able to remember the names of organelles and their functions. A work in pairs is useful to fix the concepts. Home
Sommario
6
The third step is made to observe the difference between plant and animal cells. Looking at Fig.3 the students will also see what animal and plant cells have in common and will be able to fill in the Venn diagram. Some questions about fig.3 are useful to observe and point out the similarities and the differences.
In the fourth step the student will consolidate and memorise the names of organelles, observing the picture and filling in the empty column.
A game and a final test get students to revise all the lesson.
Home
Sommario
7
Secret cellYour body is made up of about 100 billion living cells.
You can tell when they are alive because there are all sorts of chemical changes going on inside them. Every cell is like a tiny ball of jelly full of chemicals
and it’s far too small to be seen without a microscope. In fact you can squeeze thousands of them into the full stop at the end of this sentence.
Micron is the order size of the cell.
Home
Sommario
8
Questions
1. What other definition of cell do you know?
-------------------------------------------------------
2. What instrument do you use for looking at cells?
---------------------------------------------------------
3. How many cells are there in your body?
--------------------------------------------------------
4. What happens inside the cell?
---------------------------------------------------------
Answer these questions:
Home
Sommario
9
Cells vary greatly in size. Most cannot be seen without a microscope, although a few varieties are visible to the naked eye.
The diameter of an average animal cell is about 10 micrometers (or 0.01 millimetre) and of an average plant cell is about 100 micrometers (0,1 millimetre).
Some cells are quite large. Eggs of animals are single cells before their development begins, and they are usually visible to the eye.
Bacterial cells are very small, with diameters of only 0.35 to 0.40 micrometer, near the limit of resolution of an ordinary light microscope.
Cells sizes
Home
Sommario
10
The words meaning
Look up in the dictionary the meaning of these words:Size……………………………………………………………….Average…………………………………………………………Plant……………………………………………………………..Animal…………………………………………………………..Development…………………………………………………Visible……………………………………………………………Bacterial………………………………………………………………………..
Home
Sommario
12
Complete the sentences with the given word:
1. Bacterial cell is the …………………..2. Plant cell is the ………………………3. Animal cell is …………. than the bacterial cell, but
……………..than the animal cell
smaller, smallest, biggest, bigger
The differences
Home
Sommario
14
What is the range in micron to see an animal and a plant cell?
……………………………………
What is the size order of the molecules?
……………………………………
Which instrument do you use to see the plant cell?
……………………………………
What is the range in nm to see the proteins?
……………………………………
Which type of instrument can you use to see the organelles better?
……………………………………
nanometre; electron microscope; between 10 and 100 ;
light microscope; between 0.3 and 10 ;
Complete the chart using the given definitions:
What are the correct definitions?
Home Sommario
15
Relative sizes of cells
Work in pairs. Ask your partner questions to fill the gaps in your worksheet.…………………microscope is an instrument for looking at the shape of cells.Electron microscope is an ……………………for looking inside the cell. There are three types of cells . One example of this is……………………An animal cell is different from a plant cell in size and in ………………….Micron is the unit of measure of……………..……………………. is the unit of measure of ……………… and virus.The ……………….. of an average animal cell is about 10 micrometers. Most bacterial cells are very small, with diameters of only 0.35 to 0.40 micrometer, near the limit of resolution of an ordinary …………… …………………
A
Home
Sommario
16
Relative sizes of cells
Work in pairs. Ask your partner questions to fill the gaps in your worksheet
Light microscope is an …………………… for looking at the shape of the cells.…………………microscope is an instrument for looking inside the cell. There are three types of ……………….. One example of this is bacterium.An animal cell is different from a plant cell in ……………and in shape.……………….. is the unit of measure of cells.Nanometre is the unit of measure of molecules and …………………..The diameter of an average animal cell is about………………Most ………………... cells are very small, with diameters of only 0.35 to 0.40 micrometer, near the ……………….of ………………….. of an ordinary light microscope.
B
Home
Sommario
17
Worksheet _________________ are the building blocks of life. A living thing is called an _______________________
All _____________are made up of cells.
Living organisms are composed of one or more __________________ cells.
Amoeba, Paramecium and Euglena are examples of _________________ cells.
Plants and animals are __________________. Work Bank
What else about cells ?
microscopic multicellular cellsunicellular organism living things
Home Sommario
18
Inside the cell there is a secret world. There are many tiny objects called organelles
which have a specific function.
What is there inside the cell?
Nucleus
It contains all the information needed to produce a new living cell.
Home
Sommario
19
Ribosomes
They produce substances (proteins).
Endoplasmic reticulum
It is the place where ribosomes do their work.
Ribosomes
Home
Sommario
20
Cytoplasm
Part of the cell where the chemical reactions take place.
Mithocondria
They turn glucose and oxygen into energy.
Home
Sommario
21
Golgy body
This system prepares proteins for use and export.
Cell membrane
This structure controls what passes in and out the cell.
Home
Sommario
22
Cell wall
It gives a plant cell strength and support.
Vacuole It contains a solution of salt and sugar. It also gives the support to the cell.
vacuole
Cell wall
Home
Sommario
23
Chloroplasts
It contain a green substance called chlorophyll which absorbs the sun’s energy so that the plant can make its own food during photosynthesis.
Home
Sommario
24
Across
5. It traps energy to make food
6. It produces substances
7. It produces energy
Cellcrossword
Home Sommario
Down
1. It controls what substances pass in and out
of the cell
2. It contains a solution of salt and sugar
3. It controls the activities
4. This is where the cell’s chemical reactions
take place
25
Matching halves phrases A
4. proteins are built in the
4. proteins are built in the 6. a Golgy body prepares proteins for
6. a Golgy body prepares proteins for
1. multicellular organisms are composed of
1. multicellular organisms are composed of
3. mitochondria3. mitochondria
8. plasma membrane is the place where
8. plasma membrane is the place where
9. a microscope9. a microscope
10. the sun’s energy is absorbed by10. the sun’s energy is absorbed by11. the photosynthesis is
11. the photosynthesis is
5. the organelle that controls all cell activity is
5. the organelle that controls all cell activity is
7. cytoplasm7. cytoplasm
Parts of the cell
2. organelles are
2. organelles are
Work in pairs. Match one of the sentences from paper A with a sentences from paper B to form one complete sentence.
A
Home Sommario
26
nucleusnucleus minute structures inside a cell
minute structures inside a cell
ribosomes ribosomes
chlorophyllchlorophyll
produce energy
produce energycontains the organellescontains the organelles
cells make contact with the external environment
cells make contact with the external environment
a number of cells
a number of cells
use and exportuse and export
a chemical reaction
a chemical reaction
enlarges the image of a cell
enlarges the image of a cell
Parts of the cell
Matching halves phrases B Work in pairs. Match one of the sentences from paper B with a sentences from paper A to form one complete sentence.
B
Home Sommario
27
The illustrations (Fig. 3) show some structures found in plant and animal cells.
Animal and plant cell
Nucleus
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion
Nucleus
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi body Golgi body
Chloroplast
Vacuole
Cell wall
Cell membrane
Cell membrane
Home Sommario
animal cell plant cell
28
1. What is the nucleous like?…………………………………………………………………………………..2. Which position does it occupy inside the animal cell?…………………………………………………………………………………3. Does it have a natural colour in the picture?……………………………………………………………………………………4. What does it contain inside?……………………………………………………………………………………5. Which structure is it surrounded by?……………………………………………………………………………………6. Are there mitochondria in both cells? ……………………………………………………………………………………7. Which shape have they got?……………………………………………………………………………………8. What are the things that you can see inside?……………………………………………………………………9. Are there chloroplasts in the plant cell?…………………………………………………………………………………10. Which colour do they have?…………………………………………………………………………………… 11. Is it their true color? Why?……………………………………………………………………………………
12. In which cell is there a big vacuole?…………………………………………………………………………………..13. Do you remember what it contains inside?…………………………………………………………………………………14. In which cell are vacuoles very big?……………………………………………………………………………………15. Have the cells got a cell membrane?……………………………………………………………………………………16. Where is it located in the cell?……………………………………………………………………………………17. Is the animal cell surrounded by a wall? ……………………………………………………………………………………18. Which cell breathes?……………………………………………………………………………………19. Which cell produces oxygen?………………………………………………………………..20. Which cell produces food by itself?…………………………………………………………………………………21. With which colour is Golgy body represented in the picture?……………………………………………………………………………………22. Is this body found in both cells?………………………………………………………………………………
Look at Fig. 3 and answer these questions.
Similarities and differences
Home Sommario
29
Comparing plant and animal cellsAnimal and plant cells are the same in some ways. We say that they have some of the same features. Animal and plant cells are also different.
Look at Fig 3 and try to spot the differences. Fill in the Venn diagram to compare a plant cell to an animal cell. Use the words in the word box.
cell membrane cell wall chloroplast cytoplasm
mitochondria nucleus ribosome vacuole
animal cell plant cell
What's the most complicated cell? ______________________It is because it produces oxygen and food (glucose) for all living things using the sunlight directly. The animal cell depends on the plant cell.
in common
Home Sommario
30
Cell like a busy factory
A cell can be thought as a factory with different departments where many activities take place.
Look at Fig.4. Work in pairs and try to understand what happens in each department. Discuss with each other.
Fig. 4
Home
Sommario
31
In the second column of the chart, write the name of the organelle connected with the factory activities described in the first column.
Ribosomes
Departments and functions in the factory
Departments and functions in the factory Organelle
Executive department: decides what products are made
Power plant: provides energy for all process
Workers: produce materials
Packaging departments: assemble the products
Factory floor: where most products are assembled, finished and shipped
Assembly line (where workers do their work)
Shipping/ Receiving department
Have you filled in the gaps!? If not, try again! This is another clue for you.
Golgi body, Cell membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Endoplasmic reticulum, Mitochondrion, Ribosomes
Home Sommario
32
Question loop
There are 25 strips of paper all different, each with a question and an answer. Print the pages and cut the strips.Hand out a strip to each student.Start the loop by getting one pupil to ask their question. Someone should recognize the correct answer and read it. Then they should read out their question and so on. Eventually the loop should return to the first person.
Home
Sommario
33
Question loop
Q 1.What simple units are all living things made of?
A The cell wall
Q What cell has a vacuole and a cell wall? A Cells
Q What does chloroplast contain? A A plant cell
Q What special feature does a sperm cell have?
A It contains the pigment to adsorb light energy for photosynthesis
Q Why are root cells long and thin? A A tail to allow it to move
Q What structures are made from tissues? A To give the maximum surface area to absorb water
34
Q Why does the plant cell have a cell wall? A Organs are made from tissue
Q Why are nerve cells long and thin? A To keep its shape and support the plant
Q What useful product is made in photosynthesis?
A To carry nerve impulses around the body
Q What is the function of the nucleus? A Oxygen
Q Which are the typical three parts of the plant cell?
A It controls the activities of the cell
Q Where in the cell do most of the chemical reactions take place?
A Cell wall, chloroplasts and large permanent vacuole
Q What does the cell membrane do? A In the cytoplasm
Q What occurs in the mitochondria? A It controls what passes in and out of the cell
35
Q Which is the only cell without nucleus? A The energy production
Q Which organelle do the products assemble?
A Red blood cell
Q Which organelle do proteins produce?
A The Golgy body
Q Where in the cell workers make proteins ? A Ribosome
Q Which organelles does the sunlight use? A In the endoplasmic reticulum
Q What is the name of the heredity material in a cell?
A Chloroplasts
36
Q Who was the first person to give the name “cell”?
A DNA
Q What does a plant need for photosynthesis?
A Robert Hook
Q A synonym of organism with many cells
A Water, carbon dioxide, light
Q What functions do lisosomes have? A Multicellular organism
Q Which part of a plant cell is made of cellulose?
A Digest, destroy and recycle materials
Home
Sommario
37
Final test Name_________________Date ______________
1. All living things are made up of_________________________ .
2. The inside of a cell is____________________ which is jelly like. 3. All cells have a _________________ which separates them from the outside world. 4. Some organisms consist of only_____________ cell, like amoeba or bacteria.
5. All cells contain ____________________for storing information. 6. All cells contain _________________ for building proteins. 7. The _________________ prepares proteins for use and export. 8. Plant cells have a group of green structures called________________ . They use the energy from the sun to
make food. 1. A ________________ organism is an animal cell that lives on its own, without other cells. 10. The mitochondria are often called the___________________ of the cell.
Home
Sommario
38
Glossary
Animal Any living organism different from plants by the lack of chlorophyll and the requirement for complex organic nutrients.
Average Arithmetical mean of a series of numbers obtained by dividing their sum by the quantity of numbers.
Bacterium Unicellular microscopic simple organism found almost everywhere.
Cell The microscopic unit of all living organisms
Chemical 1. Related to a science of chemistry. 2. A substance characterized by definite molecular composition.
Chlorophyll Green plant pigments which capture the light photoreceptors of life energy.
Home
Sommario
39
Energy The capacity of doing work.
Euglena Unicellular organism with one or two flagella, chloroplasts and a generally elongated shape.
Glucose A monosaccharide; found free or combined and is the most common sugar.
Limit of resolution
The minimum distance between two point objects which allows them to be seen.
Micron A unit of length equal to one millionth of a metre
Microscope An instrument through which minute objects are enlarged by means of lenses.
Organelle A subcellular structure with a special function.
Home
Sommario
40
Organism An individual which effects all life functions.
Oxygen An essential element in cellular respiration and in combustion processes.
Paramecium An unicellular ciliated protozoan.
Photosynthesis Process in the green part of the plants, that produced oxygen and organic components from carbon dioxide and water.
Plant Any organism distinguished by the presence of chlorophyll, a rigid cell wall and a big vacuole.
Protein An organic substance made up of a variety of amino acids.
Solution A mixture in which the components are uniformly distributed.
Home
Sommario
41
AnswersSecret cell
1. Cell is the smallest living part of an animal or a plant body
2. I use a light microscope for looking at the shape of cells; I use electron microscope for looking inside the cell.
3. There are about 100 billion cells in my body.
4. Chemical changes happen inside the cell.
Sizes of cells
Size: measure
Average: medium amount
Plant: a living thing that grows in earth and has a stem, leaves and roots
Animal:a living creature that is not a plant
Development: a process of regulated growth and differentiation
Bacterium: Extremely small, relatively simple prokaryotic microrganism
The differences
1. Smallest 2. Biggest 3. Bigger 4. Smaller
Home
Sommario
42
What is the range in micron to see an animal and a plant cell?
between 10 and 100
What is the size order of the molecules?
nanometre
Which instrument do you use to see the plant cell?
light microscope
What is the range in nm to see the proteins?
between 0,3 and 10
Which type of instrument can you use to see the organelles better?
electron microscope
What are the correct definitions?
Relative sizes of cellsA = underlined B= in bold
Light microscope is an instrument for looking at the shape of cells.
Electron microscope is an instrument for looking inside the cell.
There are three types of cells . One example of this is bacterium.
An animal cell is different from a plant cell in size and in shape.
Micron is the unit of measure of cells.
Home
Sommario
43
Nanometre is the unit of measure of molecules and virus.
The diameter of an average animal cell is about 10 micrometers. Most bacterial cells are very small, with diameters of only 0.35 to 0.40 micrometer, near the limit of resolution of an ordinary light microscope.
What else about cells? Cells are the building blocks of life. A living thing is called an organism.All living things are made up of cells.Living organisms are composed of one or more microscopic cells.Amoeba, Paramecium and Euglena are examples of unicellular cells. Plants and animals are multicellular.
To remind the organelles
Across: 5. Chloroplast; 6. Ribosome; 7. Mitochondrion.
Down: 1. Cellmembrane; 2. Vacuole; 3. Nucleus; 4. Cytoplasm
Parts of the cell
A italic B bold
1. Multicellular organisms are composed of
a number of cells
2. Organelles are
minute structures inside a cell
3. Mitochondria
produce energy
Home
Sommario
44
4. Proteins are built in the ribosomes5. The organelle that controls all cell activity nucleus 6. Golgy body prepares proteins for use and export7. Cytoplasm contains the organelles8. Plasma membrane is the place where cells make contact with the external environment9. A microscope enlarges the image of a cell10. The sun’s energy is absorbed by chlorophyll11. Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction
Home
Sommario
45
1. The nucleous shape is round.
2. It occupies a central position inside the animal cell.
3. No, because it is transparent. To see it you need colouring.
4. It contains DNA, the genetic material.
5. It is surrounded by endoplasmic reticulum.
6. Yes, there are mithochondria in both cells.
7. They have got an extended shape.
8. You can see some membrane foldings.
9. Yes, in the plant cell there are chloroplasts.
10. They are green.
11. This is a true color for the presence of chlorophyll.
Similarities and differences
12. There is a big vacuole in the plant cell.
13. It contains inside a solution of water, salts and sugar.
14. They are very big in the plant cell.
15. Both cells have a cell membrane.
16. It’s located at the periphery of the cell and envelops it and contain the cytoplasm.
17. No it isn’t. The plant cell is surrounded by a wall .
18. Both cells breathe.
19. Plant cell produces oxygen.
20. The plant cell produces food by itself. Because of this its name is autotrophic.
21. Golgy body is pink in the picture. 22. Yes, it is in both cells.
Home
Sommario
46
Comparing the plant and animal cell
animal cell plant cell
What's the most complicated cell? Plant cell
Cell MembraneMitochondriaNucleusCytoplasmRibosoma Cell wall
ChloroplastVacuole
in common
Departments and functions in the factory Organelle
Executive department: decides what products are made Nucleus
Power plant: provides energy for all process Mitochondrion
Workers: produce materials Ribosomes
Packaging department: assembles the products Golgy body
Factory floor: where most products are assembled, finished and shipped
Cytoplasma
Assembly line (where workers do their work) Endoplasmic reticulum
Shipping/ Receiving department Plasma membrane
47
Question loop
Q1 What simple units are all living things made of ?A1 Cells
A25 The cell wall
Q2 What cell has a big vacuole and a cell wall?A2 A plant cell
A1 Cells
Q3 What does chloroplast contain?A3 It contains the pigment to adsorb light energy for photosynthesis
A2 A plant cell
Q4 What special feature does a sperm cell have?A4 A tail to allow it to move
A3 It contains the pigment to adsorb light energy for photosynthesis
Q5 Why are root cells long and thin?A5 To give the maximum surface area to absorb water
A4 A tail to allow it to move
Q6 What structures are made from tissues?A6 Organs are made from tissue
A5 To give the maximum surface area to absorb water
Q7 Why do the plant cells have a cell wall?A7 To keep its shape and support the plant
A6 Organs are made from tissue
Q8 Why are nerve cells long and thin?A8 To carry nerve impulses around the body
A7 To keep its shape and support the plant
48
Q9 What useful product is made in photosynthesis?A9 Oxygen
A8 To carry nerve impulses around the body
Q10 What is the function of the nucleus?A10 It controls the activities of the cell.
A9 Oxygen
Q11 Which are the three parts of the cell that are only found in the plants?A11 Cell wall, chloroplasts and large permanent vacuole.
A10 It controls the activities of the cell.
Q12 Where in the cell do most of the chemical reactions take place?A12 In the cytoplasm.
A11 Cell wall, chloroplasts and large permanent vacuole.
Q13 What does the cell membrane do?A13 It controls what passes in and out of the cell
A12 In the cytoplasm
Q14 What occurs in the mitochondria?A14 The energy production
A13 It controls what passes in and out of the cell
Q15 Which is the only cell without a nucleus?A15 The red blood cell
A14 The energy production
Q16 Which organelles do the products assemble?A16 The Golgy body
A15 The red blood cell
Q17 Which organelle do proteins produce?A17 the ribosome
A16 The Golgy body
49
Q18 Where in the cell workers make proteins ?A18 In the endoplasmic reticulum
A17 The ribosome
Q19 Which organelles does the sunlight use?A19 Chloroplasts
A18 In the endoplasmic reticulum
Q20 What is the name of the heredity material in a cell?A20 DNA
A19 Chloroplasts
Q21 Who is the first person to give the name “cell”?A 21 Robert Hook
A20 DNA
Q22 What three things does a plant need for photosynthesis?A22 Water, carbon dioxide, light
A 21 Robert Hook
Q23 A synonym of organism with many cellsA23 Multicellular organism
A22 Water, carbon dioxide, light
Q24 What is the job of lisosomesA24 Digest, destroy and recycle materials
A23 Multicellular organism
Q25 Which part of a plant cell is made of cellulose?A25 Cell wall
A24 Digest, destroy and recycle materials
Home
Sommario
50
1. All living things are made up of cells.
2. The inside of a cell is cytoplasm which is jelly like.
3. All cells have a cell membrane, which separates them from the outside world.
4. Some organisms consist of only one cell, like amoeba or bacteria.
5. All cells contain nucleus for storing information.
6. All cells contain ribosomes for building proteins.
7. The Golgy body prepares proteins for use and export.
8. Plant cells have a group of green structures called chloroplasts. They use the energy from the Sun to make food.
9. A unicellular organism is an animal cell that lives on its own, without other cells.
10. The mitochondria are often called the power plant of the cell.
Final test
Home
Sommario
51
Bibliography
Internet sites:www.emc.maricopa.edu/.../ BIOBK/BioBookCELL2.html www.coe.uga.edu/.../ glynn/models/cell/cell.html www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/ comparingcells.html www.teach-nology.com/.../ science/rain/venn4/
Home
Sommario
H. Kingston ( 2002) – GCSE Biology – Letts
J. Martin (2003) - Biology – Cambridge