The basic structure and function of cells
-
Upload
ita-rodriguez -
Category
Science
-
view
457 -
download
3
description
Transcript of The basic structure and function of cells

The Basic Structure and Function of Cells
By Ita P. Rodríguez
3rd Grade

Definition of Cells
• Cells are the basic building blocks of living organisms
–Just like brick can be a building block of a house

Definition of Cells
• Cells are so small you cannot see them with your naked eye
–you need a microscope

Purpose of Cells
• The main purpose of a cell is to organize
–Cells hold different pieces and each cell has a different set of jobs
–Cells are small compartments that hold all of the biological equipment necessary to keep an organism alive and successful on Earth

Purpose of Cells

Types of Cells
• There are many types of cells–They can have different shapes and sizes
Smallest Cells: Longest Cells: Biggest Cells:
6 inches long, 5 inches wide, 3 pounds
Ostrich Egg

Types of Cells
• There are many types of cells–We will discuss animal cells and plants cells

Animal Cells
• Animal cells are eukaryotic (it means they have a nucleus)

Vacuole

Cell Parts
• Nucleus: controls the cell–It helps control eating, movement, and
reproduction just like a brain in animals–The nucleus is not always in the center of the
cell, but you won't find it near the edge of a cell because it's dangerous

Cell Parts
• Mitochondrion: gives the cell energy –converts energy stored in food into usable
energy for work

Cell Parts
• Vacuole: contains the waste or trash

Cell Parts
• Ribosomes: makes the proteins for the cell

Cell Parts
• Golgi Apparatus: packs protein–it receives, processes, packages, and ships
protein

Cell Parts
• Cytoplasm: jelly-like fluid that holds the cell in place
–contains salts, minerals and organic molecules–surrounds the other parts

Cell Parts
• Cell Membrane: the structure that separates the inside of the cell from the outside of the cell

Cell Parts
• Lysosome: purpose is to digest things–breaks down food particles, invading objects,
or worn out cell parts

Plant Cells
• Plant cells are eukaryotic (it means they have a nucleus)

Plant CellsRibosomes

Cell Parts
• Cell Wall: purpose is to help the plant keep its shape
–It's like taking a water balloon and putting it in a cardboard box. The balloon is protected from the outside world.

Cell Parts
• Chloroplast: are the food producers of the cell
–they create sugars that the plant uses

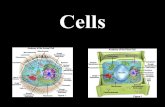
Comparing Animal and Plant Cells
• Look closely at the similarities and differences between an animal cell and a plant cell

THE END