The Animal Welfare Science Centre The effect of milking shed noise on dairy cow behaviour using a Y...
-
Upload
leslie-ethelbert-cunningham -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
1
Transcript of The Animal Welfare Science Centre The effect of milking shed noise on dairy cow behaviour using a Y...
The Animal WelfareScience Centre
The effect of milking shed noise on dairy cow behaviour using a Y mazeAdele Arnold (NZL)
University of MelbourneAnimal Welfare Science CentrePrimary Industries Research Victoria, Australia
Introduction Introduction
The milking parlour is a novel and possibly stressful environment for dairy cattle.
– Human contact
– Conspecifics
– Physical environment:
illumination, noise, confinement, flooring surfaces, etc.
Noise in the milking parlour Noise in the milking parlour
The background sound level in a normal commercial milking facility ranges from 75-85 dB
Acknowledgment of both physiological and psychological effects of environmental noise on human health.
What effect does this noise have on the behaviour and physiology of the dairy cow?
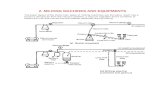
Y maze choice test Y maze choice test
Aimed to evaluate the effect of milking parlour noise on choice behaviour of heifers using a Y maze
Also measured heart rate (HR), time to choose and ease of moving animals
Y maze apparatus Y maze apparatus The Y maze contains two alternative directions of travel
(short maze arms)
Subjects were trained to form associations between each direction and either presence or absence of noise
Procedure Procedure
Day 0: habituation 3 trials
Day 1: training + test 5 trials
Day 2: training + test 5 trials
Day 3: one-off test 1 trial
For each animal, the noise stimulus was presented in the first arm entered on day 1.
16 heifers
Maze side choice Maze side choice
0
20
40
60
80
100
1 2 3 4
Choice No.
% q
uie
t s
ide
ab, p<0.01
a
b b
b
Additional measurements Additional measurements
1. Training trials:
Heart rate in maze arm
Restlessness in maze arm
Number of stops
Handler interventions
2. Choice trials: Maze junction transit time (reflects choice time)
Heart rate in arm
Heart rate in maze arm Heart rate in maze arm
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
1 2Day of training
BP
M
NoiseQuiet
ab, p<0.01
b
a
Restlessness in maze arm Restlessness in maze arm
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
1 2
Day of training
pro
po
rtio
n o
f ti
me
Noise
Quiet
ab, p<0.01
bb
a
a
Number of stops Number of stops
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1 2Day of training
sto
ps
NoiseQuiet
ab, p<0.01
bb
a
a
Maze junction transit time - choices Maze junction transit time - choices
0
5
10
15
20
25
1 2 3 4
Choice No.
Se
cs
Noise
Quiet
Heart rate in maze arm - choices Heart rate in maze arm - choices
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
1 2 3 4
Choice No.
BP
M
NoiseQuiet
Discussion - noise Discussion - noise
These results suggest that dairy heifers prefer to avoid exposure to milking parlour noise if given the opportunity
Noise may affect:
— time to enter the milking facility — ease of moving animals for handlers — restlessness of animals in the parlour
Discussion - method Discussion - method
Heifers showed an increasing tendency to choose the quiet arm
This was slow to develop in some heifers.
— Learning time, or— original bias for choosing the noise arm (first side
chosen)
An original maze arm bias may also explain the increased choice times and reduced HR in those animals that continued to choose the noise arm.
Acknowledgements Acknowledgements
This research was funded by Dairy Australia
PhD Supervisors: Paul Hemsworth, Ellen Jongman and Kim Ng