Teradata Architecture Basics
-
Upload
nirmalph86 -
Category
Documents
-
view
147 -
download
3
Transcript of Teradata Architecture Basics


Before beginning..
Node
A hardware assembly containing several tightly coupled central processing units (CPUs).

Before beginning contd..
SMP – Symmetric Multi Processing
An SMP Teradata Database has a single node that contains multiple CPUs sharing a memory pool.
MPP – Massively Parallel Processing
Multiple SMP nodes working together comprise a larger, MPP implementation of a Teradata Database. The nodes are connected using the BYNET, which allows multiple virtual processors on multiple nodes to communicate with each other.

Before beginning contd..

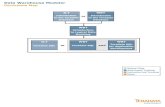
LOGICAL ARCHITECTURE
PARSING ENGINE
BYNET
AMP AMP AMP AMP AMPAMP
DISK DISK DISK DISK DISK DISK
Contd..

COMPONENTS IN DETAIL
PARSING ENGINE
A Parsing Engine (PE) is a virtual processor (vproc). It is made up of the following software components: Session Control, the Parser, the Optimizer, and the Dispatcher.
PE contd..

PARSING ENGINE
Session Control
•Logon and Logoff
Parser
•Interprets SQL statements and check syntax.•Consults data dictionary to ensure that all objects exist.•Also checks the access rights for users.
Optimizer
•Develops least expensive plan which are converted to executable steps.•To maximize throughput and reduce resource contention, optimizer should know system configuration, available units of parallelism & data demographics.•Teradata optimizer is robust and intelligent.•Parallel aware and cost-based using full look-ahead capability.
PE contd..

PARSING ENGINE
Dispatcher
•Controls the sequence in which steps are executed and passes the steps to BYNET.•Composed of two tasks- execution control and response control.•Makes sure that all AMP’s have finished a step before the next step is dispatched.•Depending on nature of SQL requests, a step will be sent to one AMP or all AMPs.
Execution control •Receives the step definitions from Parser. •Transmits them to appropriate AMP’s for processing.•Receives status report from AMP’s as they process the requests.•Passes the results to response control one AMP’s have completed the processing.
Response Control•Returns the result to the user.

BYNET
Dual-redundant, fault tolerant, bidirectional interconnect network that enables:
•Automatic load balancing of message traffic.•Automatic reconfiguration after fault detection.•Scalable bandwidth as nodes are added.
Depending on the nature of dispatch request, the communication between nodes may be a:
Broadcast – message is routed to all nodes in the system.
Point to point – message is routed to specific nodes.
Features of BYNET
•Fault-tolerant•Load balanced•Scalable•High Performance

ACCESS MODULE PROCESSOR
The Access Module Processor is the virtual processor that is responsible for managing a portion of the database. Each AMP holds portion of a table.
A database manager subsystem resides on each AMP. This subsystem will:
•Lock database s and tables.•Create, modify or delete definitions of tables.•Insert, delete or modify rows within table.•Retrieve information from definitions and tables.•Returns the result set to Dispatcher.

DISK ARRAYS
Disk Array is a configuration of disk drives that utilizes specialized controllers to distribute data and parity across disks while providing fast access and data integrity.
The disk array controllers are referred to as dual redundant active array controllers, which means that both controllers are actively used, in addition to serving as backup for each other.
Each AMP vproc must have access to an array controller, which in turn accesses the physical disks. AMP vprocs are associated with one or more ranks (or mirrored pairs) of data. The total disk space associated with an AMP is called a vdisk. A vdisk may have up to three ranks.