TEACHER’S INSTRUCTIONS · chromosomes so that they line up at the midline (equatorial plate) of...
Transcript of TEACHER’S INSTRUCTIONS · chromosomes so that they line up at the midline (equatorial plate) of...


TEACHER’S INSTRUCTIONS 1) Choose one of the Shutter Folds from the choices below.
Three Color Choices Black & White Cells without Chromosomes
Choose this option if you want students to draw in the
chromosomes for each stage.
4) To prepare the shutter fold for the notebook, students should cut along the solid lines around the shutter fold and in between each stage of cell division and mitosis.
6) They should apply glue to the back of the two central panels and affix into notebook.
5) They should fold inwards along the dashed lines.
2) Students should label each section of the shutter fold using the terms: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase telophase and after cytokinesis. They should write a description of the events that take place during these stages.
3) Once completed, students can check their answers against the answer key.

Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
CELL DIVISION AND MITOSIS

CELL DIVISION AND MITOSIS Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:

Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
CELL DIVISION AND MITOSIS

Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
CELL DIVISION AND MITOSIS

Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
CELL DIVISION AND MITOSIS

ANSWER KEY Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Description of events:
Interphase
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
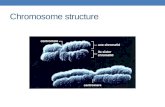
• Centriole pair replicates. • DNA replicates to create duplicated
chromosomes.
• Centriole pair begins to migrate to opposite poles.
• Nuclear membrane begins to dissolve.
• Spindle fibers begin to form between centriole pairs.
• Duplicated chromosomes begin to condense.
• Nucleolus begins to disappear.
• Centriole pairs are fully migrated to opposite poles.
• The spindle apparatus (mitotic spindle) is fully formed.
• Spindle fibers have moved the duplicated chromosomes so that they line up at the midline (equatorial plate) of the cell.
• Nuclear membrane has completely disappeared.
• Duplicated chromosomes are at their most condensed at this stage.
• Spindle fibers pull the sister chromatids apart at the centromere and drag them to opposite poles.
• The cell elongates.
• The cell begins cytokinesis by forming a cleavage furrow to divide the cytoplasm.
• Nuclear membranes begin to reform around the separate (but identical) sets of chromosomes.
• Spindle apparatus has disassembled and the spindle fibers dissolve.
• Chromosomes begin to decondense. • Nucleolus begins to reform.
After Cytokinesis • The two identical daughter cells are
completely separated. • Spindle fibers have completely
disappeared. • The chromosomes are completely
decondensed and lengthened. • The nucleolus is very distinct. • The nuclear membrane has
completely reformed. around the chromosomes.

Created by Anh-Thi Tang – Tangstar Science
Copyright © April 2014 Anh-Thi Tang (a.k.a. Tangstar Science)
All rights reserved by author.
This document is for personal classroom use only.
This entire document, or any parts within, may not be electronically distributed or posted to any website including teacher or classroom blogs or websites.